Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cryptography For Dummys
Cryptography For Dummys
Uploaded by
Filipa Miranda0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageOriginal Title
cryptography for dummys
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageCryptography For Dummys
Cryptography For Dummys
Uploaded by
Filipa MirandaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
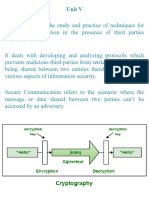
What is Cryptography?
Cryptography is the practice of hiding or coding information by using
algorithms (ciphers), transforming the information into something unreadable
by unauthorised parties.
It is categorised in two main categories:symmetric (single key/cypher for
both encryption and decryption) and asymmetric (pair of keys a public and a
private one for encryption and decryption).
Encryption is the process of converting plain text into ciphers and
decryption is the reverse.
Cryptography ensures privacy and confidentiality by protecting data
being accessed by unauthorised people. It is used on Virtual Private Networks
(ensuring safe browsing) and messaging apps (preventing messages being
hacked or intercepted).
Cryptography is used to ensure the integrity of data: ensuring data
wasn’t changed when transmitted or in storage. And, it verifies the origin of the
data ensuring it wasn’t tampered with. This is achieved with digital signatures
and hashes.
There is in place as well, the law of non repudiation: the senders and
the recipients can't deny their actions and intentions.
You might also like
- Data EncryptionDocument5 pagesData EncryptionEZULDEEN SAEIDNo ratings yet
- Cns QuestionDocument23 pagesCns QuestionRuveda ShakeelNo ratings yet
- CryptographyDocument20 pagesCryptographySrilekha RajakumaranNo ratings yet
- SohaiDocument16 pagesSohaiJHON ANDREI SEMANo ratings yet
- CryptographyDocument5 pagesCryptographyShivam SonkarNo ratings yet
- Basics To CryptographyDocument18 pagesBasics To CryptographyEvehn KadusaleNo ratings yet
- IS AssignmentDocument24 pagesIS Assignmentyuvanpgr-wm20No ratings yet
- Cryptography and Its Types and Stenography and Digital SignDocument8 pagesCryptography and Its Types and Stenography and Digital SignSaloni ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Q. What Do You Mean by Cryptology, Where We Use Cryptology in Real-Time? ADocument1 pageQ. What Do You Mean by Cryptology, Where We Use Cryptology in Real-Time? AJoy PatelNo ratings yet
- 3630-Article Text-6635-1-10-20180104Document5 pages3630-Article Text-6635-1-10-20180104Anonymous uGow9p7y8No ratings yet
- Cryptography & Network SecurityDocument5 pagesCryptography & Network SecurityAlok ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Topic: Cryptology: History of CryptographyDocument24 pagesTopic: Cryptology: History of CryptographyAziz Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1.1 Introduction Cryptography-UpdatedDocument7 pagesLecture 1.1 Introduction Cryptography-UpdatedNurdin YussufNo ratings yet
- 2021KUCP1001Document5 pages2021KUCP1001Shivam SonkarNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Its TypesDocument2 pagesCryptography and Its TypesSaloni ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Ali AhmadDocument2 pagesAli AhmadNadeem MahmoodNo ratings yet
- CryptographyDocument8 pagesCryptographySadia Islam ShefaNo ratings yet
- What Is Cryptography - Definition FromDocument2 pagesWhat Is Cryptography - Definition FromGirgio Moratti CullenNo ratings yet
- A Seminar ReportDocument39 pagesA Seminar ReportDivyaswaroop Srivastav100% (1)
- Cryptography: Latika Arora, IT/06/321Document5 pagesCryptography: Latika Arora, IT/06/321Yatish TagraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document6 pagesUnit 1Gulshan ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - Part 2 - CryptographyDocument11 pagesAssignment 2 - Part 2 - CryptographyPJ1988No ratings yet
- A Technique Cryptography PDFDocument4 pagesA Technique Cryptography PDFThet Hmue Hay ThiNo ratings yet
- Context of Cryptography: ConfidentialityDocument13 pagesContext of Cryptography: ConfidentialityAnay ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Its TypesDocument1 pageCryptography and Its TypesSweta BarnwalNo ratings yet
- CRYPTOGRAPHYDocument7 pagesCRYPTOGRAPHYsaeed BarzaghlyNo ratings yet
- CryptographyDocument19 pagesCryptographySrilekha RajakumaranNo ratings yet
- Security in EcommerceDocument18 pagesSecurity in EcommerceMukund HindujaNo ratings yet
- Cryptography1 113832Document17 pagesCryptography1 113832Priyanka NaikNo ratings yet
- Cryptography (Module 1) NotesDocument21 pagesCryptography (Module 1) NotesColossus GamingNo ratings yet
- Ghaffa Ndaru Sandyeta Bin Marsudi - (32DDT20F2034) Muhammad Azeem Amirul Bin Mohd Zulkeflee - (32DDT20F2031)Document18 pagesGhaffa Ndaru Sandyeta Bin Marsudi - (32DDT20F2034) Muhammad Azeem Amirul Bin Mohd Zulkeflee - (32DDT20F2031)Triple DDDNo ratings yet
- Lovely Professional University: Cryptography in Digital SignatureDocument4 pagesLovely Professional University: Cryptography in Digital Signaturegoyal_No ratings yet
- Cse CryptographyDocument18 pagesCse CryptographysavisuNo ratings yet
- LESSON 6 - CryptographyDocument12 pagesLESSON 6 - CryptographyKIBENo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Authentication and Encryption TechnologyDocument34 pagesChapter 5 Authentication and Encryption TechnologyHasniza HarunNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology NotesDocument44 pagesBlockchain Technology NotesShraddhey SatputeNo ratings yet
- CSS KNC301 Unit 4 and Unit 5Document18 pagesCSS KNC301 Unit 4 and Unit 5anchal kardamNo ratings yet
- Cryptography: P.Nikhila N.Vishnu PriyaDocument13 pagesCryptography: P.Nikhila N.Vishnu PriyaNIkhila ReddyNo ratings yet
- CryptographyDocument5 pagesCryptographyHritika RawatNo ratings yet
- FSS CH-2Document24 pagesFSS CH-2metasebiamerkin7275No ratings yet
- Information and Network SecurityDocument10 pagesInformation and Network SecurityashaNo ratings yet
- Networks Internet E-Commerce Mobile Telephones Wireless Microphones Wireless Intercom Bluetooth Automatic Teller MachinesDocument6 pagesNetworks Internet E-Commerce Mobile Telephones Wireless Microphones Wireless Intercom Bluetooth Automatic Teller MachinessufiyanamujawarNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: A.Irfana Cse-First Year Deepthi Cse-First YearDocument14 pagesSubmitted By: A.Irfana Cse-First Year Deepthi Cse-First YearNiranjan ChandarrajNo ratings yet
- Cryptography Full ReportDocument9 pagesCryptography Full ReportSushant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cryptography: Joemari Saysay Sabao, MitDocument17 pagesCryptography: Joemari Saysay Sabao, Mitpia espanilloNo ratings yet
- Types of Crptography + Security MechanismDocument6 pagesTypes of Crptography + Security Mechanismlaiqatalia46No ratings yet
- A Seminar ReportDocument39 pagesA Seminar ReportNutan BhorNo ratings yet
- Cryptography: Name: T Sampathkumar Name: Sudeep Year: III/IV CSE, Year: III/IV CSE, E-MailDocument9 pagesCryptography: Name: T Sampathkumar Name: Sudeep Year: III/IV CSE, Year: III/IV CSE, E-MailAnimesh PrasadNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument99 pagesUnit VYogita TiwariNo ratings yet
- Ethics Lect4 CryptographyDocument15 pagesEthics Lect4 Cryptographyomarnader16No ratings yet
- CryptographyDocument14 pagesCryptographyPankaj AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Paper of CryptographyDocument3 pagesPaper of CryptographySuinNo ratings yet
- Cse CryptographyDocument18 pagesCse Cryptographyholyshit453No ratings yet
- Nis MPDocument12 pagesNis MPjaibvp123No ratings yet
- A Definition of Data EncryptionDocument8 pagesA Definition of Data EncryptionSameen KhanNo ratings yet
- CryptographyDocument7 pagesCryptographyZonia NillNo ratings yet
- Network SecurityDocument15 pagesNetwork SecuritySurajit SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document37 pagesUnit 1SutikshanNo ratings yet
- Cse CryptographyDocument15 pagesCse CryptographyPrasannaNo ratings yet