0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views22 pagesChemistry of Carbon Compounds Guide
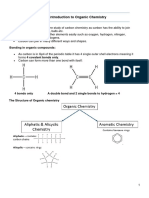
The document discusses organic chemistry, specifically discussing different types of carbon compounds including hydrocarbons, saturated and unsaturated compounds, carbon bonds, representations of organic molecules, organic families and isomers. It also discusses IUPAC naming and provides examples of naming conventions for alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, haloalkanes, alcohols, carboxylic acids, esters, aldehydes and ketones.
Uploaded by
rileydebeer21Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views22 pagesChemistry of Carbon Compounds Guide
The document discusses organic chemistry, specifically discussing different types of carbon compounds including hydrocarbons, saturated and unsaturated compounds, carbon bonds, representations of organic molecules, organic families and isomers. It also discusses IUPAC naming and provides examples of naming conventions for alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, haloalkanes, alcohols, carboxylic acids, esters, aldehydes and ketones.
Uploaded by
rileydebeer21Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd