Professional Documents
Culture Documents
delayed-hypersensitivity-reaction-to-hyaluronic-acid-dermal-
Uploaded by
Josefa VenegasCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
delayed-hypersensitivity-reaction-to-hyaluronic-acid-dermal-
Uploaded by
Josefa VenegasCopyright:
Available Formats
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology Dovepress
open access to scientific and medical research
Open Access Full Text Article
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Delayed hypersensitivity reaction to hyaluronic
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology downloaded from https://www.dovepress.com/ by 181.203.65.52 on 18-Nov-2020
acid dermal filler following influenza-like illness
This article was published in the following Dove Press journal:
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology
Mohammed G Turkmani 1 Background: Delayed reactions after facial hyaluronic acid injection are relatively rare
Koenraad De Boulle 2 complications. Their cause may be infectious or immune-mediated in origin, and their
Wolfgang G Philipp- outbreak can be triggered, for example, by an influenza-like illness.
Dormston 3 Objective: To describe potential adverse event of influenza like illness following dermal
1
filler injection.
Derma Clinic, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia;
2
Aalst Dermatology Clinic, Aalst,
Methods: We report fourteen unusual cases of delayed hypersensitivity reaction to several
brands of hyaluronic acid dermal filler following influenza like illness.
For personal use only.
Belgium; 3Cologne Dermatology,
Cologne, Germany Results: Increasing evidence implicates influenza infection in the pathogenesis of late onset
filler reaction.
Conclusion: Although there is a low risk of late onset adverse reaction with hyaluronic acid
fillers, injecting physicians must be aware of the possible filler reaction following the
influenza infection.
Keywords: fillers, hyaluronic acid, reaction, hypersensitivity, complications, influenza,
infection
Introduction
Fillers have become an important treatment for patients who seek noninvasive
rejuvenation. The American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) reported that
approximately 2.7 million dermal filler procedures were performed by plastic
surgeons and other board-certified physicians in 2017. Moreover, the
American Society for Dermatologic Surgery ASDS reported that dermatologic
surgeons performed 1.64 million dermal filler injections in the same year
(over 10% more than 2016 and doubled since 2012).1,2 As the field of soft
tissue augmentation has become increasingly popular, reports of adverse
events have also risen.
Post filler injection complications vary and can be categorized based on their
timing in relation to the filler injection as early events (occurring up to several
days post treatment) or delayed events (occurring weeks to years post
treatment).3
Delayed hypersensitivity reactions are characterized by induration, erythema,
and edema and are mediated by T lymphocytes rather than antibodies.4 They
typically occur 48–72 hrs after injection but may be seen as late as several weeks
Correspondence: Mohammed post injection and can persist for months.5
G Turkmani
Derma Clinic, P.O Box 20632, Riyadh Herein we describe fourteen cases of delayed hypersensitivity reaction to
11465, Saudi Arabia hyaluronic acid (HA) dermal filler following influenza-like illness from two der-
Tel +96 650 416 1171
Email mgtderma@yahoo.com matology centers in Saudi Arabia and Belgium.
submit your manuscript | www.dovepress.com Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology 2019:12 277–283 277
DovePress © 2019 Turkmani et al. This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/
terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution – Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/). By accessing
http://doi.org/10.2147/CCID.S198081
the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed.
For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms (https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php).
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
Turkmani et al Dovepress
Methods experienced influenza-like illness (fever, headache, sore
A total of fourteen females, 22–65 years old, were throat, cough, and fatigue).
presented to our clinics between September 2016 and All patients described their history of multiple injec-
September 2018 complaining of localized redness and tions (between 2–6) over the last four years prior to onset
firm, painful swelling on their faces at the sites of of their symptoms in different sites of their face. Duration
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology downloaded from https://www.dovepress.com/ by 181.203.65.52 on 18-Nov-2020
previously injected fillers (Figure 1). In all cases, the of the last filler injection varied from 2–10 months before
reactions had started 3–5 days after patients had experiencing the reaction (Table 1).
For personal use only.
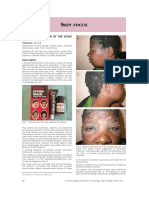
Patient 1. Cheeks and tear trough Patient 2. Cheeks and tear trough Patient 3. Tear trough
Patient 5. Left side of the face (tear trough
Patient 4. Lips Patient 6. Tear trough
cheeks and upper lip)
Patient 7. Cheeks Patient 8. Tear trough
Figure 1 Sites of reaction.
submit your manuscript | www.dovepress.com Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology 2019:12
278
DovePress
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
Dovepress Turkmani et al
Table 1 The injected fillers, number of injections, and time to onset
Patient Patient Injected product(s) Number of treat- Time to onset of Treatment(s)
number age ments in the 4 years symptoms received
prior to onset of (months after
symptoms final treatment)
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology downloaded from https://www.dovepress.com/ by 181.203.65.52 on 18-Nov-2020
1 32 Teosyal Deep Lines 4 4 Prednisolone
Belotero Intense Hyaluronidase
Belotero Volume
2 31 Teosyal Deep Lines 3 2 Prednisolone
Juvederm Volbella
Belotero Balance
3 29 Teosyal Puresense 2 10 Prednisolone
Juvederm Volift
4 22 Juvederm Volbella 2 4 Prednisolone
Teosyal Kiss
5 40 Juvederm Volbella 6 6 Prednisolone
Juvederm Voluma Hyaluronidase
Juvederm Volift
For personal use only.
6 65 Teosyal 2 4 Methyl Prednisolone
7 57 Hylaform 8 7 Methyl Prednisolone
Surgiderm
8 63 Juvederm Volbella 5 9 Prednisolone
Belotero Balance Hyaluronidase
9 41 Juvederm Volbella 3 3 Prednisolone
Juvederm Voluma Hyaluronidase
Juvederm Volift
10 25 Restylane Volyme Restylane Defyne 4 5 Prednisolone
Belotero Intense
11 34 Juvederm Voluma 6 3 Methyl Prednisolone
12 45 Belotero Balance 4 5 Methyl Prednisolone
13 23 Belotero Balance 2 6 Methyl Prednisolone
14 61 Restylane Refyne 6 4 Methyl Prednisolone
Restylane Defyne
The injections were performed by dermatologists or plastic Inamed (Nasdaq:IMDC) (Table 2). The most common sites of
surgeons using needles or cannula in different clinics. Patients’ the reactions were the cheeks (n=9), tear trough (n=8), and
files depicted no history of allergies or autoimmune disease and lips (n=3).
none of patients were injected with permanent fillers. All of the Patients were treated with oral prednisolone 20–30 mg
patients were unaware of the amounts of the injected fillers but or Methyl prednisolone 16–24 mg daily for 5 days, fol-
fully aware of the number of injections on their face, and the lowed by tempering of the dose for another 5 days. After
filler brands which were Juvederm (Allergan Inc. Pringy, a 2 week follow up, there was a complete resolution of the
France), Teosyal (Teoxane S.A., Geneva, Switzerland), symptoms in 10 patients following the oral steroid therapy.
Belotero (Anteis S.A, Geneva, Switzerland), Surgiderm The remaining 4 patients still presented minimal swelling
(Allergan Inc.) Restylane (Q-med AB Uppsala, Sweden) and that was treated with hyaluronidase one month after the
submit your manuscript | www.dovepress.com
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology 2019:12 279
DovePress
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
Turkmani et al Dovepress
Table 2 Number of injections in each anatomical site of each mediated by CD4+ cells. The memory of macrophages and
kind of filler a trigger, such as an infection or a drug-drug interaction,
Site of Brand of filler Number of could explain the unpredictability of foreign body granu-
injection injections in loma, which may occur even many years after the biode-
each site gradation of the implant.11 Macrophages are known to be
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology downloaded from https://www.dovepress.com/ by 181.203.65.52 on 18-Nov-2020
Tear trough Juvederm Volbella 6 memory cells even when they move away from their site
Belotero Balance 4 of action once degradation of their target is complete.12
Teosyal Puresense 2 Still, the exact etiology of delayed hypersensitivity in
Lip Teosyal Kiss 1 relation to HA fillers and the influenza virus infection
Belotero intense 2 remains not completely understood.6,13
Juvederm Volbella 2 HA molecules in all fillers are the same polysaccharide
Cheeks Juvederm Voluma 6 molecules that compose a major part of our skin.
Restylane Refyne 3 Therefore, HA molecule itself is not usually considered
Restylane Defyne 1 an immunogen. As suggested by Bitterman-Deutsch et al,
Belotero Volume 1 however, in some conditions, glycosaminoglycans, such as
Nasolabial folds Restylane Refyne 2 HA, could directly trigger a specific immune response
Belotero Balance 2 without the primary phase of inflammation, like a -
Chin Juvederm Voluma 3 “superantigen”.14 Other components that are added to sta-
For personal use only.
Teosyal Deep Lines 3 bilize HA molecules in soft tissue fillers (eg, crosslinkers,
conserving) may also be immunogenic.
Nose Juvedrem Volift 2
Restylane Refyne 1
Beleznay et al have suggested a mechanism involving
the release of pro-inflammatory low molecular weight HA
fragments during an accelerated breakdown of HA gels
onset of symptoms (Figure 2). Patients were followed up triggered by a systemic inflammatory response to an
two months following the complete resolution of their unknown antigen.7 The definition of low molecular weight
symptoms and experienced another influenza-like infection HA, however, is not well defined in clinical research.
or a recurrence of symptoms at the sites of filler injections. Furthermore, whether low molecular weight HA fragments
Each individual patient from all the clinics provided cause a pro-inflammatory response is open to debate in
written informed consent for the case details and accom- scientific literature. Therefore, due to lack of a clear under-
panying images to be published. standing of the exact etiology of delayed hypersensitivity
Institutional approval from all clinics was not required reactions in some filler patients, it is difficult to conclude
to publish the case details. that specific filler technologies are more prone to induce
these reactions in comparison with others.15
Discussion The majority of patients here developed reactions at all
Delayed hypersensitivity may manifest from weeks to the previously injected sites at the same time (except
months after an uneventful HA filler injection. Hence, it is patient 7 who developed the reaction only in one side of
impossible to predict the probability of occurrence. Several the face) regardless of filler type, number of injections, or
published reports, however, have attempted to understand the injected volumes. Interestingly, two patients (patient
the etiology in relation to HA soft tissue fillers.6–9 It has #1 and #3) did not react at the previously injected sites
been suggested that biological/patient factors (eg, previous (nasolabial fold and nose, respectively). This is likely due
skin or systemic conditions such as infections and to the fact that the injections were done more than two
trauma),10 injection technique (eg, filler volume, repeat years from the time of the hypersensitivity reaction, and so
treatments, intramuscular implantation), and the different most of the injected fillers can be expected to have been
properties of HA fillers may explain the etiology. degraded and removed by then.
Type IV hypersensitivity following HA implantation An immunologic interaction between a concomitant amino
and influenza infection seems to be the most probable penicillin treatment and an Ebstein–Barr viral infection (ie,
explanation for our observed late-onset events. This rare sore throat) is known to induce maculopapular exanthems.16
systemic response may be initiated by T-lymphocytes and The exact mechanism behind the interaction is unclear and it is
submit your manuscript | www.dovepress.com Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology 2019:12
280
DovePress
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
Dovepress Turkmani et al
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology downloaded from https://www.dovepress.com/ by 181.203.65.52 on 18-Nov-2020
Patient 9. Cheeks and tear trough
For personal use only.
Patient 10. Cheeks, lips, and chin
Figure 2 Patient 1 and patient 2: sites of reaction before (left) and two weeks after (right) treatment.
not yet well explained whether a true allergic drug reaction, asymptomatic granulomas that may even subside on
infectious-dependent eruption or transient loss of drug toler- their own, especially in the case of hyaluronic acid.19
ance due to the infection, is responsible for the symptoms.17 Delayed complications of the soft tissue fillers are
The use of other medications such as antibiotics, antipyretic particularly difficult to diagnose and treat due to the
and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are commonly seen time lapse from the procedure.20 Type IV hypersensitiv-
in daily practice for treatment of acute respiratory tract infec- ity reactions are unresponsive to antihistamines.21
tions. HA, like viral infection, is known to activate in vitro Steroids are required to alleviate the inflammatory
T-lymphocytes via CD44.18 Therefore, HA could be consid- signs. Hyaluronidase may be injected to remove the
ered as a risk factor in the development of hypersensitivity allergen in some cases.22,23
reactions when any medication is introduced. Delayed hypersensitivity reaction to hyaluronic acid
The differential diagnosis of late onset nodules following infection is relatively rare. Homsy et al24
include infection (including biofilm), foreign body gran- reported multiple inflammatory collections on the face
ulomatous reaction, and immune-mediated delayed following sore throat in two patients. One case of cold
hypersensitivity reactions. Exact diagnosis may be diffi- sore and flu-like illness has been reported by Dr. Bhojani-
cult since delayed filler reactions can present in many Lynch,25 and one more case described a patient who
ways. Biofilms can present as erythematous, tender developed a granulomatous lip 8 months after silicone
nodules and papules.19 They can also present as inert, injections and 1 week after a flu-like syndrome.24 Here,
submit your manuscript | www.dovepress.com
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology 2019:12 281
DovePress
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
Turkmani et al Dovepress
we present 10 rare cases of late onset hypersensitivity to
hyaluronic acid injection following influenza-like illness. References
The main limitation of this article is the absence of 1. The American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Plastic Surgery
StatisticsReport. Available from: https://www.plasticsurgery.org/
a histological analysis. Biopsies were not performed due to
news/press-releases/new-statistics-reveal-theshape-of-plastic-surgery.
the patients’ desire to have minimally invasive resolutions Accessed March 1, 2017.
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology downloaded from https://www.dovepress.com/ by 181.203.65.52 on 18-Nov-2020
for their symptoms as quickly as possible. 2. The American Society for Dermatologic Surgery. ASDS Survey.
Available from: https://www.asds.net/_Media.aspx?id=9449, https://
An immunologic interaction between dermal fillers www.asds.net/. Accessed May 17, 2018.
and influenza infection may be the cause of the delayed 3. Lowe NJ, Maxwell CA, Patnaik R. Adverse reactions to dermal
fillers: review. Dermatol Surg. 2005;31(11 Pt 2):1616–1625.
hypersensitivity. The exact mechanism is unclear and
4. De Boulle K. Management of complications after implantations of
not yet well understood; it is unknown whether the fillers. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2004;3(1):2–15. doi:10.1111/j.1473-
hypersensitivity is due to a true allergic filler reaction 2130.2004.00058.x
5. Arron ST, Neuhaus IM. Persistent delayed-type hypersensitivity reac-
or to an influenza infection. To verify this hypothesis, an tion to injectable non-animal-stabilized hyaluronic acid. J Cosmet
allergic work-up can be performed with the same HA Dermatol. 2007;6:167–171. doi:10.1111/j.1473-2165.2007.00331.x
6. Rongioletti F. Complications granulomateuses des techniques de
that was used in each patient. It is, however, difficult to
comblement. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2008;135:59–65. doi:10.1016/
make definite conclusions from this test, as even if the S0151-9638(08)70213-8
results are negative, a hypersensitivity reaction cannot 7. Beleznay K, Carruthers JD, Carruthers A, Mummert ME,
Humphrey S. Delayed-onset nodules secondary to a smooth cohesive
be excluded due to the limited sensitivity of these 20 mg/mL hyaluronic acid filler: cause and management. Dermatol
tests.26–28 Commercially available HA – based fillers Surg. 2015;41:929–939. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000000418
For personal use only.
8. André P. Evaluation of the safety of a non-animal stabilized hyaluro-
have a wide variety of properties including the degree
nic acid (NASHA – Q-Medical, Sweden) in European countries:
of cross-linking and gel concentration that have an a retrospective study from 1997 to 2001. J Eur Acad Dermatol
extensive effect on their expected clinical outcome. Venereol. 2004;18:422–425.
9. Lee JM, Kim YJ. Foreign body granulomas after the use of dermal fillers:
Understanding these characteristics may be important pathophysiology, clinical appearance, histologic features, and treatment.
in deciphering the etiology of delayed hypersensitivity Arch Plast Surg. 2015;42:232–239. doi:10.5999/aps.2015.42.5.596
10. De Boulle K, Heydenrych I. Patient factors influencing dermal filler
reactions. It should be note that the actual causes are
complications: prevention, assessment, and treatment. Clin Cosmet
dependent not only on the characteristics of the HA Investig Dermatol. 2015;15(8):205–214. doi:10.2147/CCID.S80446
fillers, but also on the response of the biological host. 11. Moscona RR, Bergman R, Friedman-Birnbaum R. An unusual late
reaction to Zyderm I injections: A challenge for treatment. Plast
Other possible causes of delayed hypersensitivity in our Reconstr Surg. 1993;92:331. doi:10.1097/00006534-199308000-00021
patients may be injections of large volumes of dermal 12. Williams CT, Williams WJ. Granulomatous inflammation: a review.
J Clin Pathol. 1983;36:723.
filler in many facial sites and repeated treatments. Many
13. Alijotas-Reig J, Fernández-Figueras MT, Puig L. Late-onset inflamma-
questions still remain; for example: Why all the patients tory adverse reactions related to soft tissue filler injections. Clin Rev
injected with HA fillers do not display a hypersensitivity Allergy Immunol. 2013;45:97–108. doi:10.1007/s12016-012-8348-5
14. Bitterman-Deutsch O, Kogan L, Nasser F Delayed immune mediated
response when having influenza or influenza- like ill- adverse effects to hyaluronic acid fillers: report of five cases and review
ness? Why patient number 7 was presented with the of the literature. Dermatol Report. 2015;7:5851. doi:10.4081/
dr.2015.5851
symptoms only on the left side of the face although
15. Cyphert JM, Trempus CS, Garantziotis S. Size matters: molecular
she was injected with the same filler equally in both weight specificity of Hyaluronan effects in cell biology. Int J Cell
sides? What will happen if these patients get another flu Biol. 2015;2015:563818. doi:10.1155/2015/563818
16. Gonzalez-Delgado P, Blanes M, Soriano V, Montoro D, Loeda C,
attack? Are these patients proper candidates for receiv- Niveiro E. Erythema multiforme to amoxicillin with concurrent infec-
ing HA-based fillers again? We believe that more stu- tion by Epstein-Barr virus. Allergol Immunopathol. 2006;34:76–78.
doi:10.1157/13086752
dies should be conducted to explain the mechanism of
17. Onodi-Nagy K, Kinyo A, Meszes A, et al. Amoxicillin rash in patients
this reaction. with infectious mononucleosis: evidence of true drug sensitization. Allergy
Asthma Clin Immunol. 2015;11:1. doi:10.1186/s13223-015-0099-4
18. Jordan AR, Racine RR, Hennig MJ, Lokeshwar VB. The role of
Disclosure CD44 in disease pathophysiology and targeted treatment. Front
Wolfgang G Philipp-Dormston reports being a clinical Immunol. 2015;6:182. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2015.00182
19. Wagner RD, Fakhro A, Cox JA, Izaddoost SA. Etiology, prevention,
trial investigator, scientific advisor, and/or speaker for and management of infectious complications of dermal fillers. Semin
Allergan, Galderma, and Merz, and no other conflicts of Plast Surg. 2016;30:83–86. doi:10.1055/s-0036-1580734
20. Tseng CHW, Chen AM, Chang JYF. Hyaluronic acid injectionin-
interest or payments for this publication. The other duced delayed-onset foreign body granuloma. J Dental Sci.
authors report no conflicts of interest in this work. 2015;10:341–343. doi:10.1016/j.jds.2015.03.008
submit your manuscript | www.dovepress.com Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology 2019:12
282
DovePress
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
Dovepress Turkmani et al
21. Funt D, Pavicic T. Dermal fillers in aesthetics: an overview of 25. Bhojani-Lynch T. Late-onset inflammatory response to hyal-
adverse events and treatment approaches. Plast Surg Nurs. uronic acid fillers. Dermal Plast Reconstruc Surg. 2017;5(12):
2015;35:13–32. doi:10.1097/PSN.0000000000000087 e1532.
22. Signorini M, Liew S, Sundaram H, et al.; Global Aesthetics Consensus 26. Wolkenstein P, Chosidow O, Flechet ML, et al. Patch testing in severe
Group. Global aesthetics consensus: avoidance and management of cutaneous adverse drug reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome
complications from hyaluronic acid fillers-evidence and opinion-based and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Contact Derm. 1996;35:234–236.
review and consensus recommendations. Plast Reconstr Surg. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1996.tb02364.x
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology downloaded from https://www.dovepress.com/ by 181.203.65.52 on 18-Nov-2020
2016;137:961e–971e. doi:10.1097/PRS.0000000000002184 27. Britschgi M, Steiner UC, Schmid S, et al. T-cell involvement in
23. Alijotas-Reig J, Fernández-Figueras MT, Puig L. Pseudocystic encap- drug-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. J Clin
sulation: a late noninflammatory complication of hyaluronic acid filler Invest. 2001;107:1433–1441. doi:10.1172/JCI10501
injections. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:1726–1728. doi:10.1111/dsu.12316 28. Padial MA, Alvarez-Ferreira J, Tapia B, et al. Acute generalized
24. Homsy A, Rüegg EM, Jandus P, Pittet-Cuénod B, Modarressi exanthematous pustulosis associated with pseudoephedrine. Br
A. Immunoligical reaction after facial hyaluronic acid injection. Case J Dermatol. 2004;150:139. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.05717.x
Reports Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2017;4(1):68–72.
For personal use only.
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology Dovepress
Publish your work in this journal
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology is an interna- The manuscript management system is completely online and
tional, peer-reviewed, open access, online journal that focuses on includes a very quick and fair peer-review system, which is all easy
the latest clinical and experimental research in all aspects of skin to use. Visit http://www.dovepress.com/testimonials.php to read real
disease and cosmetic interventions. This journal is indexed on CAS. quotes from published authors.
Submit your manuscript here: https://www.dovepress.com/clinical-cosmetic-and-investigational-dermatology-journal
submit your manuscript | www.dovepress.com
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology 2019:12 283
DovePress
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
You might also like
- 26 Apr 2019 Ccid 198081 Delayed Hypersensitivity Reaction To Hyaluronic Acid DermalDocument7 pages26 Apr 2019 Ccid 198081 Delayed Hypersensitivity Reaction To Hyaluronic Acid DermaldominiqueNo ratings yet
- Vitiligo - New Treatment ApproachDocument7 pagesVitiligo - New Treatment Approachsawaira khanNo ratings yet
- A 10-Point Plan For Avoiding Hyaluronic Acid Dermal Filler-Related Complications During Facial Aesthetic Procedures and Algorithms For ManagementDocument9 pagesA 10-Point Plan For Avoiding Hyaluronic Acid Dermal Filler-Related Complications During Facial Aesthetic Procedures and Algorithms For Managementleenatalia93100% (1)
- CCID 37327 Use of Tazarotene Foam For The Treatment of Acne Vulgaris 052714Document6 pagesCCID 37327 Use of Tazarotene Foam For The Treatment of Acne Vulgaris 052714Camila torresNo ratings yet
- InJPharPract 13 4 355Document4 pagesInJPharPract 13 4 355Yeol LoeyNo ratings yet
- CCID 84903 The Role of Vitamin C in Pushing Back The Boundaries of Skin - 090215Document8 pagesCCID 84903 The Role of Vitamin C in Pushing Back The Boundaries of Skin - 090215sebastianNo ratings yet
- The 10-Point Plan 2021 Updated Concepts For ImprovDocument36 pagesThe 10-Point Plan 2021 Updated Concepts For ImprovdnaielNo ratings yet
- Wollenberg Et Al 2000 AllergyDocument9 pagesWollenberg Et Al 2000 AllergyArturo VeraNo ratings yet
- Baru 1Document6 pagesBaru 1Nazihan Safitri AlkatiriNo ratings yet
- Ccid 11 175Document11 pagesCcid 11 175Remo Alnovryanda PutraNo ratings yet
- Ccid 12 911Document7 pagesCcid 12 911Imanuel CristiantoNo ratings yet
- Treatment-Resistant Prurigo Nodularis: Challenges and SolutionsDocument10 pagesTreatment-Resistant Prurigo Nodularis: Challenges and SolutionsIBHNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 9Document8 pagesJurnal 9rizkaNo ratings yet
- Dupilumab Side Effect in A Patient With Atopic Dermatitis: A Case Report StudyDocument4 pagesDupilumab Side Effect in A Patient With Atopic Dermatitis: A Case Report StudyKihyun YooNo ratings yet
- Ccid 179430 A Series of in Vitro and Human Studies of A Novel Lip Cream 032119Document16 pagesCcid 179430 A Series of in Vitro and Human Studies of A Novel Lip Cream 032119Lina WinartiNo ratings yet
- Microbiome in Atopic Dermatitis: Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology DoveDocument6 pagesMicrobiome in Atopic Dermatitis: Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology DoveTrustia RizqandaruNo ratings yet
- The Efficacy of Colloidal Oatmeal Cream 1 Percent As Addon Therapy in The Management of Chronic Irritant Hand Eczema - A Double-Blind StudyDocument11 pagesThe Efficacy of Colloidal Oatmeal Cream 1 Percent As Addon Therapy in The Management of Chronic Irritant Hand Eczema - A Double-Blind StudyQualityMattersNo ratings yet
- Chemical Peels in The Treatment of Acne PDFDocument8 pagesChemical Peels in The Treatment of Acne PDFSpica AdharaNo ratings yet
- Soothing Fluid Effective for Perioral DermatitisDocument7 pagesSoothing Fluid Effective for Perioral DermatitisAmelyalesmanaNo ratings yet
- Surgical Mask Contact Dermatitis and Epidemiology of Contact Dermatitis in Healthcare WorkersDocument6 pagesSurgical Mask Contact Dermatitis and Epidemiology of Contact Dermatitis in Healthcare WorkersJuan Stuart Xaverius JohanesNo ratings yet
- Ccid 8 257 PDFDocument9 pagesCcid 8 257 PDFFahmil AgungNo ratings yet
- Efficacy and Safety of Cream Containing Climbazole/Piroctone Olamine For Facial Seborrheic Dermatitis: A Single-Center, Open-Label Split-Face Clinical StudyDocument7 pagesEfficacy and Safety of Cream Containing Climbazole/Piroctone Olamine For Facial Seborrheic Dermatitis: A Single-Center, Open-Label Split-Face Clinical StudynurulNo ratings yet
- A Series of in Vitro and Human Studies of A Novel Lip Cream FormulationDocument16 pagesA Series of in Vitro and Human Studies of A Novel Lip Cream FormulationDummy CipawNo ratings yet
- 2023 Article 1070Document12 pages2023 Article 1070Noema AmorochoNo ratings yet
- Treatmen-Resistant Bacterial Keratitis, Challenges and SolutuionsDocument11 pagesTreatmen-Resistant Bacterial Keratitis, Challenges and SolutuionsGraitaaNo ratings yet
- Allergic Contact Dermatitis - TranslateDocument9 pagesAllergic Contact Dermatitis - Translatewahyuni taslimNo ratings yet
- Surgical Mask Contact Dermatitis and Epidemiology of Contact Dermatitis in Healthcare WorkersDocument7 pagesSurgical Mask Contact Dermatitis and Epidemiology of Contact Dermatitis in Healthcare Workersnur dinNo ratings yet
- A Hands On Approach To Patch TestingDocument11 pagesA Hands On Approach To Patch TestingSundar RamanathanNo ratings yet
- Treatment-Resistant Prurigo Nodularis: Challenges and SolutionsDocument10 pagesTreatment-Resistant Prurigo Nodularis: Challenges and Solutionsranz ibonkNo ratings yet
- Contact Dermatitis: Allergic and IrritantDocument9 pagesContact Dermatitis: Allergic and IrritantatikaNo ratings yet
- "前路"化学磨削治疗痤疮疤痕Document9 pages"前路"化学磨削治疗痤疮疤痕kkNo ratings yet
- 2020 Cutaneous Protothecosis As An Unusual Complication Following Dermal Filler Injection A Case Report.Document4 pages2020 Cutaneous Protothecosis As An Unusual Complication Following Dermal Filler Injection A Case Report.Dimitris RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 2010 - Octenidine Dihydrochloride, A Modern Antiseptic For Skin, Mucous Membranes and WoundsDocument15 pages2010 - Octenidine Dihydrochloride, A Modern Antiseptic For Skin, Mucous Membranes and Woundsnovia100% (2)
- Gau Glitz 2013Document12 pagesGau Glitz 2013Stella SunurNo ratings yet
- High Frequency Equipment Promotes Antibacterial Effects Dependent On Intensity and Exposure TimeDocument5 pagesHigh Frequency Equipment Promotes Antibacterial Effects Dependent On Intensity and Exposure TimeJéssica CarvalhalNo ratings yet
- Acute scalp and hairline dermatitis from hair dye allergyDocument3 pagesAcute scalp and hairline dermatitis from hair dye allergyretrianisutrisnoNo ratings yet
- Letters To The Editor: Hand Eczema Due To Hygiene and Antisepsis Products: Not Only An Irritative EtiologyDocument2 pagesLetters To The Editor: Hand Eczema Due To Hygiene and Antisepsis Products: Not Only An Irritative Etiologysaka wibawaNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Module 3Document7 pagesDermatology Module 3joseph joshua ngushualNo ratings yet
- CCID 75908 Management of Pemphigus Vulgaris Challenges and Solutions 102115Document7 pagesCCID 75908 Management of Pemphigus Vulgaris Challenges and Solutions 102115M Marliando Satria PangestuNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument10 pagesJurnalagungNo ratings yet
- CCID 111019 Hidradenitis Suppurativa From Pathogenesis To Diagnosis and 041917Document11 pagesCCID 111019 Hidradenitis Suppurativa From Pathogenesis To Diagnosis and 041917Popi ZeniusaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Allergic and Irritant Contact Dermatitis: January 2012Document9 pagesPathophysiology of Allergic and Irritant Contact Dermatitis: January 2012cemm_11No ratings yet
- Niculet2020 Glucocorticoid Induced Skin AtrophyDocument10 pagesNiculet2020 Glucocorticoid Induced Skin AtrophyYuri YogyaNo ratings yet
- Challenges of COVID-19 Pandemic For Dermatology: Uwe WollinaDocument5 pagesChallenges of COVID-19 Pandemic For Dermatology: Uwe Wollinamiss betawiNo ratings yet
- Benefits of antioxidant furfuryl palmitate in eczema treatmentsDocument9 pagesBenefits of antioxidant furfuryl palmitate in eczema treatmentsLevaszkaNo ratings yet
- Ccid 9 241Document9 pagesCcid 9 241indah ayuNo ratings yet
- Epidemiological Characterization of Dermatomycosis in EthiopiaDocument7 pagesEpidemiological Characterization of Dermatomycosis in EthiopiaLuthfiyah SalsabillaNo ratings yet
- ccid-281901-the-one21-technique-an-individualized-treatment-for-glabellDocument9 pagesccid-281901-the-one21-technique-an-individualized-treatment-for-glabellAtena KhrdmndNo ratings yet
- Urticarial Lesions If Not Urticaria WhatDocument29 pagesUrticarial Lesions If Not Urticaria WhatGabriella -No ratings yet
- Pigmented Contact Dermatitis 2376 0427 1000214Document4 pagesPigmented Contact Dermatitis 2376 0427 1000214iqbal dsNo ratings yet
- Gloves Handling Chemotherapeutic: AgentsDocument4 pagesGloves Handling Chemotherapeutic: AgentsDarren TanNo ratings yet
- WEEK 8 - Skincare Products Part 2Document31 pagesWEEK 8 - Skincare Products Part 2johnbiel.barsana26No ratings yet
- ACLOVATE - ACLOMETASONE by SOVON SAMANTADocument7 pagesACLOVATE - ACLOMETASONE by SOVON SAMANTASovon SamantaNo ratings yet
- The Immunogenicity of Hyaluronic Fillers and Its ConsequencesDocument14 pagesThe Immunogenicity of Hyaluronic Fillers and Its ConsequencesDaniel CoelhoNo ratings yet
- Reading AsthmaDocument7 pagesReading AsthmaLovely Grace PoreNo ratings yet
- 2021 Article 1000Document14 pages2021 Article 1000Novia KurniantiNo ratings yet
- System Disorder: Dermatitis and Acne: Atopic Dermatitis 57Document1 pageSystem Disorder: Dermatitis and Acne: Atopic Dermatitis 57Kassandra MerrillNo ratings yet
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: BackgroundDocument5 pagesDyshidrotic Eczema: BackgroundHiedajatNo ratings yet
- Approach to Allergic Contact Dermatitis from Topical MedicationsDocument29 pagesApproach to Allergic Contact Dermatitis from Topical MedicationsAng GaNo ratings yet
- Perfil Linfocitario Th17Document5 pagesPerfil Linfocitario Th17Josefa VenegasNo ratings yet
- Mercury Amalgam RiskDocument6 pagesMercury Amalgam RiskJosefa VenegasNo ratings yet
- Aas. - Flora Normal en La Cavidad OralDocument13 pagesAas. - Flora Normal en La Cavidad OralJosefa VenegasNo ratings yet
- Nursing History: An Irrelevance For Nursing Practice?: Monica Baly LectureDocument15 pagesNursing History: An Irrelevance For Nursing Practice?: Monica Baly LectureJosefa VenegasNo ratings yet
- DV - Laringoskopi IndirekDocument4 pagesDV - Laringoskopi Indirekdies_vadisNo ratings yet
- "One Day Health Post Visit": A Report OnDocument16 pages"One Day Health Post Visit": A Report OnBikram KushaalNo ratings yet
- The PH Miracle For Diabetes - The Revolutionary Diet Plan For Type 1 and Type 2 DiabetesDocument358 pagesThe PH Miracle For Diabetes - The Revolutionary Diet Plan For Type 1 and Type 2 DiabetesBalasubramanian Ponnuswami100% (3)
- Anti Leg CrampDocument1 pageAnti Leg CrampIsrael ExporterNo ratings yet
- Kuesioner BasDocument11 pagesKuesioner BasTia Gita WulandariNo ratings yet
- TranscriptDocument13 pagesTranscriptKetheesaran Lingam100% (3)
- Hypersensitivity 2Document3 pagesHypersensitivity 2kuldip.biotechNo ratings yet
- Marc Stranz Understanding PH and Osmolarity INS 2008Document37 pagesMarc Stranz Understanding PH and Osmolarity INS 2008escanaba292No ratings yet
- Perio-Prog Class 2012Document80 pagesPerio-Prog Class 2012moorenNo ratings yet
- Intuitive Surgical Investor Presentation 05/12/15Document39 pagesIntuitive Surgical Investor Presentation 05/12/15medtechyNo ratings yet
- PH Should Be Performed Before Placing Into The Saline Commercial PH Test Paper With A Narrow PH Range Is RecommendedDocument13 pagesPH Should Be Performed Before Placing Into The Saline Commercial PH Test Paper With A Narrow PH Range Is RecommendedJanielle FajardoNo ratings yet
- NCM 105:psychiatric NursingDocument20 pagesNCM 105:psychiatric NursingKaye CorNo ratings yet
- Be Educated Crystal MethDocument23 pagesBe Educated Crystal Methapi-374574782% (28)
- Case Study 1Document9 pagesCase Study 1Mark SanchezNo ratings yet
- 1001 Ways To Reward Employees PDFDocument1 page1001 Ways To Reward Employees PDFAnn Palamarchuk0% (1)
- Pid Casestudy 2014 PDFDocument4 pagesPid Casestudy 2014 PDFNur Syamsiah MNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Dental ServicesDocument6 pagesGuidelines For Dental Servicesdruzair007No ratings yet
- Respiratory System DisordersDocument353 pagesRespiratory System Disordersይደግ አብነውNo ratings yet
- NCP Cataract SurgeryDocument5 pagesNCP Cataract SurgeryKristaJaneCelmarBagcatNo ratings yet
- Corona-Fehlalarm - Anhang-Immunitaet - ENGLISHDocument20 pagesCorona-Fehlalarm - Anhang-Immunitaet - ENGLISHMarcus100% (1)
- Latest JCR List 2022Document1,287 pagesLatest JCR List 2022bupssyNo ratings yet
- Immunonutrition and Critical Illness An UpdateDocument8 pagesImmunonutrition and Critical Illness An Updateklinik kf 275No ratings yet
- PNLE Nursing Licensure Exam OutlineDocument11 pagesPNLE Nursing Licensure Exam OutlineJehanie LukmanNo ratings yet
- Health and Fitness Is The Real Wealth A Person Should Acquire To Lead A Peaceful and Harmonious LifeDocument3 pagesHealth and Fitness Is The Real Wealth A Person Should Acquire To Lead A Peaceful and Harmonious LifeAnthony Kerkich RosalesNo ratings yet
- Efficacy of Attachment-Based Family Therapy Compared To Treatment As Usual For Suicidal Ideation in Adolescents With MDDDocument11 pagesEfficacy of Attachment-Based Family Therapy Compared To Treatment As Usual For Suicidal Ideation in Adolescents With MDDGabriela MoralesNo ratings yet
- FMSC List of Rejected CandidatesDocument3 pagesFMSC List of Rejected CandidatesMota ChashmaNo ratings yet
- Healthcare System in MalaysiaDocument11 pagesHealthcare System in MalaysiaHui Pin100% (1)
- Size Matters A Review of The Effect of Pellet Size On Animal Behaviour and DigestionDocument6 pagesSize Matters A Review of The Effect of Pellet Size On Animal Behaviour and DigestionHerald Scholarly Open AccessNo ratings yet
- Dental Claim Form SubmissionDocument2 pagesDental Claim Form Submissionnicholas beehnerNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure Diagnosis and Evaluation GuideDocument29 pagesHeart Failure Diagnosis and Evaluation Guide黃昱睿No ratings yet