Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Error Control in Computer Network
Uploaded by
ALOKOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Error Control in Computer Network
Uploaded by
ALOKCopyright:
Available Formats
Error Control in Data Link Layer
Data-link layer uses the techniques of error control simply to ensure and confirm
that all the data frames or packets, i.e. bit streams of data, are transmitted or
transferred from sender to receiver with certain accuracy. Using or providing error
control at this data link layer is an optimization, it was never a requirement. Error
control is basically process in data link layer of detecting or identifying and re-
transmitting data frames that might be lost or corrupted during transmission. In
both of these cases, receiver or destination does not receive correct data frame and
sender or source does not even know anything about any such loss regarding data
frames.
Therefore, in such type of cases, both sender and receiver are provided with some
essential protocols that are required to detect or identify such types of errors as loss
of data frames. The Data-link layer follows a technique known as re-transmission
of frames to detect or identify transit errors and also to take necessary actions that
are required to reduce or remove such errors. Each and every time an error is
detected during transmission, particular data frames are retransmitted and this
process is known as ARQ (Automatic Repeat Request).
Ways of doing Error Control : There are basically two ways of doing Error
control as given below :
Ways of Error Control
1. Error Detection : Error detection, as the name suggests, simply means
detection or identification of errors. These errors may occur due to noise or any
other impairments during transmission from transmitter to the receiver, in
communication system. It is a class of techniques for detecting garbled i.e.
unclear and distorted data or messages.
2. Error Correction : Error correction, as the name suggests, simply means
correction or solving or fixing of errors. It simply means reconstruction and
rehabilitation of original data that is error-free. But error correction method is
very costly and very hard.
Various Techniques for Flow Control : There are various techniques of error
control as given below :
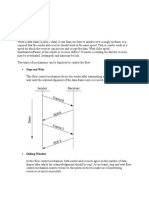
1. Stop-and-Wait ARQ : Stop-and-Wait ARQ is also known as alternating bit
protocol. It is one of the simplest flow and error control techniques or mechanisms.
This mechanism is generally required in telecommunications to transmit data or
information between two connected devices.
Receiver simply indicates its readiness to receive data for each frame. In these,
sender sends information or data packets to receiver. Sender then stops and waits
for ACK (Acknowledgment) from receiver. Further, if ACK does not arrive within
given time period i.e., time-out, sender then again resends frame and waits for
ACK. But, if sender receives ACK, then it will transmit the next data packet to
receiver and then again wait for ACK from receiver. This process to stop and wait
continues until sender has no data frame or packet to send.
2. Sliding Window ARQ : This technique is generally used for continuous
transmission error control. It is further categorized into two categories as given
below :
Go-Back-N ARQ: Go-Back-N ARQ is form of ARQ protocol in which
transmission process continues to send or transmit total number of frames
that are specified by window size even without receiving an ACK
(Acknowledgement) packet from the receiver. It uses sliding window flow
control protocol. If no errors occur, then operation is identical to sliding
window.
Selective Repeat ARQ : Selective Repeat ARQ is also form of ARQ
protocol in which only suspected or damaged or lost data frames are only
retransmitted. This technique is similar to Go-Back-N ARQ though much
more efficient than the Go-Back-N ARQ technique due to reason that it
reduces number of retransmission. In this, the sender only retransmits
frames for which NAK is received. But this technique is used less because
of more complexity between sender and receiver and each frame must be
needed to be acknowledged individually.
The main difference between Go Back ARQ and Selective Repeat ARQ is that in
Go Back ARQ, the sender has to retransmit the whole window of frame again if
any of the frame is lost but in Selective Repeat ARQ only the data frame that is lost
is retransmitted.
You might also like
- Handout 5 - ProtocolsDocument9 pagesHandout 5 - ProtocolsHirut GetachewNo ratings yet
- 10 Data Link LayerFlow ControlDocument56 pages10 Data Link LayerFlow Controlcodingstuff18No ratings yet
- 09 Data Link Layer-Flow ControlDocument56 pages09 Data Link Layer-Flow ControlSatyajeet GaurNo ratings yet
- Data Link Control and ProtocolsDocument14 pagesData Link Control and ProtocolsJohnMark LubricaNo ratings yet
- 10 Data Link LayerFlow ControlDocument56 pages10 Data Link LayerFlow Controlanushka aroraNo ratings yet
- Network Unit 5 and 6Document28 pagesNetwork Unit 5 and 6Blank FlashNo ratings yet
- Data Link LayerDocument18 pagesData Link Layerpc03198007No ratings yet
- Flow and Error ControlDocument11 pagesFlow and Error Controlkainat khalidNo ratings yet
- Unit-IV Computer NetworkDocument14 pagesUnit-IV Computer Networkharpreetchawla7No ratings yet
- Data Link LayerDocument43 pagesData Link LayerVenkatakrishnan SubramaniyanNo ratings yet
- Data Communication & NetworkingDocument14 pagesData Communication & NetworkingHafiz Muhammad Zulqarnain JamilNo ratings yet
- Datalink LayerDocument10 pagesDatalink LayerTong Thanh VinhNo ratings yet
- Micro-Link It College: Data Communication Assignment Name IdDocument13 pagesMicro-Link It College: Data Communication Assignment Name IdNuge SoloNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Arq Method: Submitted By: Santosh Kumar Sahu 0124EC071095 Vii SemesterDocument17 pagesPresentation On: Arq Method: Submitted By: Santosh Kumar Sahu 0124EC071095 Vii SemesterrajeevNo ratings yet
- Data Link LayerDocument27 pagesData Link LayerRohan Kishor neogNo ratings yet
- Data Link LayerDocument8 pagesData Link LayersaloniNo ratings yet
- Mod3 Flow Control PDFDocument91 pagesMod3 Flow Control PDFAyush kumarNo ratings yet
- Topic No 3Document46 pagesTopic No 3Aditya TidkeNo ratings yet
- Petrinet ReportDocument27 pagesPetrinet ReportEsha KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit-3-The Data Link Layer (Edited)Document24 pagesUnit-3-The Data Link Layer (Edited)Neeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- CN Practical-9Document6 pagesCN Practical-9JencyShah 2045No ratings yet
- Harq ArqDocument12 pagesHarq ArqHemanth Kumar SontiNo ratings yet
- Q1: What Are The Different Types of ARQ? Elaborate On The Working of The Same With Neat DiagramsDocument2 pagesQ1: What Are The Different Types of ARQ? Elaborate On The Working of The Same With Neat DiagramsMukul NarwaniNo ratings yet
- DLC PROTOCOL (Flow Control)Document19 pagesDLC PROTOCOL (Flow Control)Jonald BualNo ratings yet
- DLL 1Document9 pagesDLL 1Sumit PatilNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Data Link LayerDocument28 pagesUnit 3 Data Link LayerSagar wagleNo ratings yet
- CN Unit-IiiDocument27 pagesCN Unit-IiiSelva PalaniNo ratings yet
- Link LayerDocument18 pagesLink Layerkishanbharati2002No ratings yet
- Datalink LayerDocument41 pagesDatalink LayerAnnie AkhanNo ratings yet
- Data Link Control: Business Data Communications, 4eDocument14 pagesData Link Control: Business Data Communications, 4eAnonymous evHjsXnNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks and SecurityDocument24 pagesComputer Networks and SecurityKamal ThelagaNo ratings yet
- DCN UNIT3 CompleteDocument19 pagesDCN UNIT3 CompleteNamrathaNo ratings yet
- Flow ControlDocument15 pagesFlow ControlAbhay ThakurNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Notes - Computer CommunicationDocument24 pagesUnit 4 Notes - Computer CommunicationKARAN PAWAR (RA2011032020019)No ratings yet
- Unit 4&5 CNDocument49 pagesUnit 4&5 CNmsk.official321No ratings yet
- MMMMMDocument54 pagesMMMMMjeeturathiaNo ratings yet
- 1.selective Repeat ARQ Protocol: (Author)Document9 pages1.selective Repeat ARQ Protocol: (Author)Natorious Gaming YTNo ratings yet
- Flow Control and Error ControlDocument5 pagesFlow Control and Error ControlThaddeus MooreNo ratings yet
- Data Link Control: Business Data Communications, 4eDocument14 pagesData Link Control: Business Data Communications, 4eGunz Teritory OmzNo ratings yet
- Edu Eng Unit 5Document29 pagesEdu Eng Unit 5SahulNo ratings yet
- NET 201 Module 5Document13 pagesNET 201 Module 5RickCy Perucho PccbsitNo ratings yet
- Data Link Control: Lecture Notes of Computer Communications and Networks Prepared by DR - Eng. Ziyad Tariq Al-Ta'iDocument14 pagesData Link Control: Lecture Notes of Computer Communications and Networks Prepared by DR - Eng. Ziyad Tariq Al-Ta'iMustafa AlobeidiNo ratings yet
- EC307 Fundamentals of Data Communication: Module-2 Data Link ControlDocument56 pagesEC307 Fundamentals of Data Communication: Module-2 Data Link ControlrajNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 Datalink LayerDocument8 pagesUnit-5 Datalink LayerNawal K SahNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks 3Document10 pagesComputer Networks 3eshanpadhiar3No ratings yet
- Data Link Layer - Unit3 1Document72 pagesData Link Layer - Unit3 1Bikash KhanalNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 - Linklayer - BCADocument79 pagesChap 3 - Linklayer - BCAajitsah110920No ratings yet
- Computer Network Unit 2 NotesDocument11 pagesComputer Network Unit 2 Notesankitupadhyay2241No ratings yet
- Flow and Error ControlDocument31 pagesFlow and Error ControlRafia ShoukatNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv: Framing, Flow Control, Error Detection & Correction, CSMA, CSMA/CD, HDLC and PPPDocument137 pagesUnit Iv: Framing, Flow Control, Error Detection & Correction, CSMA, CSMA/CD, HDLC and PPPKOLLI VASAVI (RA2011028010013)No ratings yet
- Module 3 2Document23 pagesModule 3 2SINGH NAVINKUMARNo ratings yet
- CN Unit 2Document25 pagesCN Unit 2SaumyaNo ratings yet
- Error ControlDocument22 pagesError ControlSuhail QadirNo ratings yet
- Flow Control-Error ControlDocument10 pagesFlow Control-Error ControluksusarlaNo ratings yet
- Unit IIIDocument13 pagesUnit IIIabdul jawadNo ratings yet
- Automatic Repeat RequestDocument2 pagesAutomatic Repeat RequesttjypthazNo ratings yet
- ACN Chapter 2Document48 pagesACN Chapter 2kasahun bedasoNo ratings yet
- Data Link Layer-IIDocument12 pagesData Link Layer-IIimtiyaz beighNo ratings yet
- 7.flow and Error Control - Express Learning - Data Communications and Computer NetworksDocument23 pages7.flow and Error Control - Express Learning - Data Communications and Computer NetworksMuhammad FayazNo ratings yet
- What Is SDLCDocument20 pagesWhat Is SDLCALOKNo ratings yet
- Switching TechniquesDocument8 pagesSwitching Techniquesnak patNo ratings yet
- Role and Responsibilities of A Software Project ManagerDocument5 pagesRole and Responsibilities of A Software Project ManagerALOKNo ratings yet
- Symmetric and Asymmetric CryptographyDocument13 pagesSymmetric and Asymmetric CryptographyALOKNo ratings yet
- HashingDocument3 pagesHashingALOKNo ratings yet
- Cryptography: NetworkDocument3 pagesCryptography: NetworkALOKNo ratings yet
- Virus Vs WormDocument4 pagesVirus Vs WormALOKNo ratings yet
- 92 Corrected and Approved by B.T.E. On Dated 19.04.2017Document2 pages92 Corrected and Approved by B.T.E. On Dated 19.04.2017ALOKNo ratings yet
- 92 Corrected and Approved by B.T.E. On Dated 19.04.2017Document2 pages92 Corrected and Approved by B.T.E. On Dated 19.04.2017ALOKNo ratings yet
- E Comm FirewallDocument28 pagesE Comm FirewallALOKNo ratings yet
- Denial of Service AttackDocument8 pagesDenial of Service AttackALOKNo ratings yet
- Denial of Service AttackDocument8 pagesDenial of Service AttackALOKNo ratings yet
- HypermediaDocument1 pageHypermediaALOKNo ratings yet
- Simple Interest in Java PDFDocument1 pageSimple Interest in Java PDFALOKNo ratings yet
- CyberDocument1 pageCyberALOKNo ratings yet
- Law of EconomicsDocument1 pageLaw of EconomicsALOKNo ratings yet
- Nas SyllabusDocument3 pagesNas SyllabusALOKNo ratings yet
- Simple Interest in Java PDFDocument1 pageSimple Interest in Java PDFALOKNo ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hours Total Marks: 100: Printed Pages:01 Sub Code: HMCT 803 Paper Id: 174222 Roll NoDocument1 pageTime: 3 Hours Total Marks: 100: Printed Pages:01 Sub Code: HMCT 803 Paper Id: 174222 Roll NoALOKNo ratings yet
- Powervault-Tl2000 Reference Guide2 En-UsDocument16 pagesPowervault-Tl2000 Reference Guide2 En-UsNguyen Cong ThangNo ratings yet
- Moxa Managed Ethernet Switch Manual v9.6Document112 pagesMoxa Managed Ethernet Switch Manual v9.6marcosNo ratings yet
- Hathway BillDocument1 pageHathway BillHemant Patel50% (4)
- VBSDocument7 pagesVBSAnonymous S8Iw89tCbNo ratings yet
- Module 7-Lesson 2Document3 pagesModule 7-Lesson 2Kel LumawanNo ratings yet
- Cambium Networks Data Sheet WiFi-6 XV2-21X APDocument8 pagesCambium Networks Data Sheet WiFi-6 XV2-21X APrf.waveguideNo ratings yet
- ITSV-2: Quick Installation & Configuration Guide IP Touch Station With VideoDocument11 pagesITSV-2: Quick Installation & Configuration Guide IP Touch Station With VideoShanavasNo ratings yet
- Additive Particle - 도 - Learn Korean - LP's Korean Language LearningDocument12 pagesAdditive Particle - 도 - Learn Korean - LP's Korean Language LearningreonNo ratings yet
- Lan Cabling: BY: Sharee Lei U. UmosoDocument33 pagesLan Cabling: BY: Sharee Lei U. UmosoShar LeiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Computer NetworksDocument29 pagesAssignment 2 Computer Networksapi-537058125No ratings yet
- Hierarchy in PDMS - World, Site, ZoneDocument5 pagesHierarchy in PDMS - World, Site, ZoneMuthu KumarNo ratings yet
- Security Risk AssessmentDocument5 pagesSecurity Risk AssessmentCROSTNo ratings yet
- Prevention and Control of Cyber Crimes in India: Problems, Issues and StrategiesDocument2 pagesPrevention and Control of Cyber Crimes in India: Problems, Issues and StrategiesRajesh JainNo ratings yet
- 28 Year-Old Becomes Richest ManDocument12 pages28 Year-Old Becomes Richest ManNaheed MirNo ratings yet
- FontFont AnnualReport 2011Document0 pagesFontFont AnnualReport 2011Joe MoreNo ratings yet
- Bloquear Corel InternetDocument3 pagesBloquear Corel Internetvgmaluzan73.0307No ratings yet
- Intranet Mailing SystemDocument5 pagesIntranet Mailing Systemengr_zoonNo ratings yet
- 8 Antonyms - Turkish Language LessonsDocument3 pages8 Antonyms - Turkish Language LessonsAlongMXNo ratings yet
- Hozier (Musician)Document3 pagesHozier (Musician)BlueClawNo ratings yet
- Oracle Itm Partner Specs PDFDocument61 pagesOracle Itm Partner Specs PDFSaurabhNo ratings yet
- 11g Advanced Compression 3Document20 pages11g Advanced Compression 3agangapurNo ratings yet
- Cyber CrimeDocument37 pagesCyber Crimerajanityagi23No ratings yet
- UsbFix ReportDocument3 pagesUsbFix Reportkinglove194No ratings yet
- Netflix Headquarters DefinitivoDocument3 pagesNetflix Headquarters DefinitivojeffreylopezNo ratings yet
- Iec 61850-90-12Document222 pagesIec 61850-90-12Alexander RodriguesNo ratings yet
- 17.5 System Requirements 17.5 System Requirements: Automated Network DocumentationDocument3 pages17.5 System Requirements 17.5 System Requirements: Automated Network DocumentationSuman RathNo ratings yet
- Fisheries ENTREPLecture From Mam HelenDocument176 pagesFisheries ENTREPLecture From Mam Helengriffith jamesNo ratings yet
- OSINTDocument2 pagesOSINTjohnNo ratings yet
- (Tutorial) Android-Host LocalMultiplayer Using PortableWifiHotspotDocument9 pages(Tutorial) Android-Host LocalMultiplayer Using PortableWifiHotspotKUPALIN SUAWNo ratings yet
- Information and Communication TechnologyDocument24 pagesInformation and Communication TechnologyAbellar Shania CristineNo ratings yet