Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cultural Differences Examples
Uploaded by
April Jeannelyn FenizaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cultural Differences Examples
Uploaded by
April Jeannelyn FenizaCopyright:
Available Formats
Cultural Differences Examples
Kinship – Kinship principles generally form the basis of societal organization. Families
consisting of at least one parent and one child are customary in all societies, but there
are many differences beyond this.
Marriage – Marriage and families seem to be human universals, but there is significant
variability in customs related to these aspects of social life.
Sexuality – Interestingly enough, societies vary significantly in the degree to which they
encourage or discourage intimacy and its different forms at different stages of life.
Art – Virtually all societies have some forms of art. Visual art, music, song, dance,
literature, etc. of different cultures vary significantly.
Religion – Religious beliefs and practices are features of all known societies, but they
vary significantly between cultures.
Gender – Categorizing children into the binary categories of female and male is fairly
common, but there is significant cultural variability in the toleration of switching
categories and the number of genders.
Sports – Games and sports seem to be human universals, but the types of games and
sports played by different cultures vary.
Dwellings – Different societies, often due to environmental as well as cultural reasons,
have very different types of houses or dwellings.
Celebrations – Cultural celebrations in different cultures include New Years Eve,
Chinese New Year, birthdays, and Diwali.
Cultural taboos – While there are some universal taboos, you’ll also notice that some
cultures consider certain things you consider ‘normal’ to be very much taboo! For
example, some cultures encourage eye contact while other cultures find it offensive.
Rites of passage – Rites of passage can include the walkabout in Indigenous
Australian culture, baptisms in Christianity, school graduation ceremonies, and so forth.
Worldviews – In broad strokes, Western nations like the modern United States have
had a strong history of individualism, while Indigenous cultures often embrace
communalism and stewardship of nature.
Dress codes – When you travel the world, you quickly learn that some cultures
encourage conservative dress, such as covering your shoulders and knees in public.
Food and eating habits (foodways) – This includes not only what you eat, but when.
Go to Spain, for example, and learn all about very late dinners!
Educational methods – In 21st Century Western nations, we are accustomed to formal
education in classrooms and standardized testing. But go to Indigenous Australian
communities, and we can see that they have their own learning styles heavily reliant on
story sharing, symbolism, and non-verbal cues.
You might also like
- Philippine Pop CultureDocument5 pagesPhilippine Pop CultureMaritoni Medalla89% (9)
- Philippine Pop CultureDocument12 pagesPhilippine Pop CultureMaritoni Medalla86% (7)
- Charles Jencks What Is Postmodernism 01Document24 pagesCharles Jencks What Is Postmodernism 01Den Tovic33% (3)
- Western Classical Arts Traditions (Painting) PPT Grade 9 - 104142Document18 pagesWestern Classical Arts Traditions (Painting) PPT Grade 9 - 104142Rolfamreh Noellag100% (2)
- Guiding Philosophy in Art EducationDocument31 pagesGuiding Philosophy in Art EducationLucina Sunga SalongaNo ratings yet
- Moves Towards The Incomprehensible WildDocument14 pagesMoves Towards The Incomprehensible WildemmacockerNo ratings yet
- The Different Modes of Existence PDFDocument241 pagesThe Different Modes of Existence PDFAlexandre VerasNo ratings yet
- Culture Consists of The Beliefs, Behaviors, Objects, and Other Characteristics CommonDocument5 pagesCulture Consists of The Beliefs, Behaviors, Objects, and Other Characteristics CommonhsjhsNo ratings yet
- 18 Major Elements of Culture Explained For Students 2023Document17 pages18 Major Elements of Culture Explained For Students 2023norfaqihah zulaiqha binti zulkifleNo ratings yet
- Culture:: Low Culture, and Popular CultureDocument7 pagesCulture:: Low Culture, and Popular CultureUmair SaeedNo ratings yet
- Readings in Culture 2021Document25 pagesReadings in Culture 2021Amiri IbtissamNo ratings yet
- Socio Antropology CompilationDocument8 pagesSocio Antropology CompilationAlbert Francisco OstayaNo ratings yet
- Prelim Philpop Culture Chapters 1 5 PDFDocument28 pagesPrelim Philpop Culture Chapters 1 5 PDFMary Grace LadiosNo ratings yet
- Language and CultureDocument48 pagesLanguage and CultureAli Raza BokhariNo ratings yet
- SocietyDocument3 pagesSocietybieberzone8No ratings yet
- The Nature and Meaning of CultureDocument31 pagesThe Nature and Meaning of CultureregieNo ratings yet
- Us - Uk History and CultureDocument59 pagesUs - Uk History and CultureCODE -ONENo ratings yet
- IBTDocument10 pagesIBTNecy AlbuenNo ratings yet
- What Is Culture?Document2 pagesWhat Is Culture?Rahul ThakranNo ratings yet
- Us - Uk History and CultureDocument59 pagesUs - Uk History and CultureMohamed BouladamNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Hum102Document6 pagesLesson 1 Hum102Sambo Brayan JayNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Philippine Popular CultureDocument5 pagesModule 1 - Philippine Popular CultureAdonimar Pugales100% (1)
- Grade 7A & 7B Class Assembly Presentation (Finalised) With The 2 SongDocument18 pagesGrade 7A & 7B Class Assembly Presentation (Finalised) With The 2 SongudaanthusaraNo ratings yet
- Chapters 4, 5 & 6 Outline (Review This For The Test!)Document11 pagesChapters 4, 5 & 6 Outline (Review This For The Test!)bibbbii parkNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of CultureDocument20 pagesCharacteristics of CulturelutfiNo ratings yet
- VENUS Mod 3Document21 pagesVENUS Mod 3Jhimar Peredo JuradoNo ratings yet
- Understanding Others CultureDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Others CultureDream CatcherNo ratings yet
- PPC 3A Local Popular CultureDocument26 pagesPPC 3A Local Popular CultureMaria Luisa VillalunaNo ratings yet
- Elec 121Document14 pagesElec 121MARITONI MEDALLANo ratings yet
- CULTUREDocument40 pagesCULTUREEscalante, JuliaNo ratings yet
- GNS201 Assignment Week 10Document2 pagesGNS201 Assignment Week 10josephadenekan2019No ratings yet
- Nature of CultureDocument24 pagesNature of CultureIvan Dwight Lagura BautistaNo ratings yet
- Culture: Week 7 - 5 & 7 March, 2019Document20 pagesCulture: Week 7 - 5 & 7 March, 2019moeed ahmedNo ratings yet
- Ethnocentrism and Cultural RelativismDocument19 pagesEthnocentrism and Cultural RelativismJeff LacasandileNo ratings yet
- Cultural RelativismDocument56 pagesCultural RelativismAlijaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affects The Problem of CultureDocument5 pagesFactors Affects The Problem of CultureCerilla Mae AsejoNo ratings yet
- Diana MODULE-3-UCSPDocument30 pagesDiana MODULE-3-UCSPJhimar Peredo JuradoNo ratings yet
- Scandinavian and Nordic CultureDocument8 pagesScandinavian and Nordic Culturebtsxblck1No ratings yet
- APHG CHPT 4 PDFDocument16 pagesAPHG CHPT 4 PDFRajendra PilludaNo ratings yet
- PPC ReviewerDocument8 pagesPPC ReviewerJanjan ToscanoNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document23 pagesWeek 3orhanuyakNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Philippine Popular CultureDocument26 pagesLesson 1 - Philippine Popular Cultureit.rjcastronuevoNo ratings yet
- DAVILLO - Midterms ExamDocument3 pagesDAVILLO - Midterms ExamKhrisha Anne DavilloNo ratings yet
- Philippine Popular CultureDocument17 pagesPhilippine Popular CultureAbigail VillagomezNo ratings yet
- Culture SentisitiveDocument4 pagesCulture SentisitivekeerthanaNo ratings yet
- Cultural EnvironmentDocument11 pagesCultural EnvironmentparibetaNo ratings yet
- How Does Geography Affect CultureDocument4 pagesHow Does Geography Affect CultureDaniel S. SantosNo ratings yet
- How Do You Define Your CultureDocument19 pagesHow Do You Define Your CultureMahad HassanNo ratings yet
- The Anthropological View: The Self Embedded in CultureDocument35 pagesThe Anthropological View: The Self Embedded in CultureJohanna Marie GantalaoNo ratings yet
- Anthro - Report OutlineDocument7 pagesAnthro - Report OutlineAshlyne Palmero OlivarezNo ratings yet
- Optimal Human Key Points - 'Document6 pagesOptimal Human Key Points - 'Nazmoon NaharNo ratings yet
- Module in Multi Cultural EducationDocument105 pagesModule in Multi Cultural EducationRichelle Jane CalanaoNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Melc 3Document4 pagesUcsp Melc 3Joseph Magallanes GrulloNo ratings yet
- Concept of CultureDocument16 pagesConcept of CultureRapeanu TudorNo ratings yet
- Exploring Cultures: A Traveler's Guide to Figuring Out the NativesFrom EverandExploring Cultures: A Traveler's Guide to Figuring Out the NativesNo ratings yet
- Cultural PluralismDocument14 pagesCultural PluralismVanessa Pangan Keller100% (1)
- Lesson 3 - CultureDocument2 pagesLesson 3 - CultureLawrence MatunogNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives: West Bay Learning Center, IncDocument3 pagesLearning Objectives: West Bay Learning Center, IncAcilla Mae BongoNo ratings yet
- Grupos ÉtnicosDocument19 pagesGrupos ÉtnicosTiago FreitasNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Aboriginal SpiritualitiesDocument11 pagesContemporary Aboriginal SpiritualitiesEugene YambaoNo ratings yet
- Alejandro Solis Hinojosa 1911397 MSTR: Elda Guadalupe Espinoza SaucedoDocument5 pagesAlejandro Solis Hinojosa 1911397 MSTR: Elda Guadalupe Espinoza Saucedoviviana ocañasNo ratings yet
- Module On CultureDocument14 pagesModule On CultureKriezl Labay CalditoNo ratings yet
- Concept of CultureDocument39 pagesConcept of CultureSarmad Aftab Lashari100% (1)
- Culture and EducationDocument68 pagesCulture and EducationEdelaine EncarguezNo ratings yet
- Presentations On Cultures and SocietiesDocument2 pagesPresentations On Cultures and SocietiescocoNo ratings yet
- Peace Between and Among StatesDocument1 pagePeace Between and Among StatesApril Jeannelyn FenizaNo ratings yet
- Disciplines and Ideas in The Applied Social Sciences Quarter 2 - Module 6Document6 pagesDisciplines and Ideas in The Applied Social Sciences Quarter 2 - Module 6April Jeannelyn FenizaNo ratings yet
- Concept Notes in UcspDocument4 pagesConcept Notes in UcspApril Jeannelyn FenizaNo ratings yet
- Music 9 InstrumentsDocument4 pagesMusic 9 InstrumentsApril Jeannelyn FenizaNo ratings yet
- QUIZDocument1 pageQUIZApril Jeannelyn FenizaNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN in Global Peace and SecurityDocument2 pagesLESSON PLAN in Global Peace and SecurityApril Jeannelyn FenizaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Peace&valueDocument2 pagesLesson Plan - Peace&valueApril Jeannelyn FenizaNo ratings yet
- DLL in ENTREP Week 1Document1 pageDLL in ENTREP Week 1April Jeannelyn FenizaNo ratings yet
- Cot1 DLP Ucsp MaterialDocument5 pagesCot1 DLP Ucsp MaterialApril Jeannelyn FenizaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan-Peace and Values 2Document2 pagesLesson Plan-Peace and Values 2April Jeannelyn FenizaNo ratings yet
- Medical Parent-ConsentDocument2 pagesMedical Parent-ConsentApril Jeannelyn FenizaNo ratings yet
- Objective 2 Annotations.Document1 pageObjective 2 Annotations.April Jeannelyn FenizaNo ratings yet
- TRENDSDocument6 pagesTRENDSApril Jeannelyn FenizaNo ratings yet
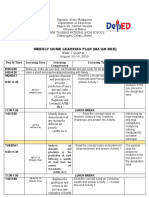
- Weekly Home Learning Plan (Ma'Am Rex)Document3 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan (Ma'Am Rex)April Jeannelyn FenizaNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan Grade 9: Week 1 Quarter 1 August 10-14, 2020Document3 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan Grade 9: Week 1 Quarter 1 August 10-14, 2020April Jeannelyn FenizaNo ratings yet
- Per Dev-TestDocument2 pagesPer Dev-TestApril Jeannelyn FenizaNo ratings yet
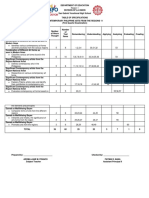
- Summary of Findings, Corrections, and ReviewDocument3 pagesSummary of Findings, Corrections, and ReviewApril Jeannelyn FenizaNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan Grade 7 ENGLISH: Week 1 Quarter 1 October 5 - 9, 2020Document3 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan Grade 7 ENGLISH: Week 1 Quarter 1 October 5 - 9, 2020April Jeannelyn Feniza100% (2)
- Orca Share Media1601452814528 6716979945787847166Document3 pagesOrca Share Media1601452814528 6716979945787847166April Jeannelyn Feniza100% (4)
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VII, Central Visayas Division of Bohol Creative WritingDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VII, Central Visayas Division of Bohol Creative WritingApril Jeannelyn Feniza100% (4)
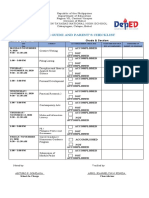
- Module Guide and Parent'S Checklist: Fermin Tayabas National High SchoolDocument2 pagesModule Guide and Parent'S Checklist: Fermin Tayabas National High SchoolApril Jeannelyn FenizaNo ratings yet
- List of Students SY 2020 - 2021 Grade 7 - PeaceDocument9 pagesList of Students SY 2020 - 2021 Grade 7 - PeaceApril Jeannelyn FenizaNo ratings yet
- SHS - HUMSS - Intro To Philo - Week1Day1-3Document4 pagesSHS - HUMSS - Intro To Philo - Week1Day1-3April Jeannelyn FenizaNo ratings yet
- Happy Bitrhday To You!Document1 pageHappy Bitrhday To You!April Jeannelyn FenizaNo ratings yet
- Marie Perkins - Print & Pattern - Geometric-Laurence King Publishing (2015)Document305 pagesMarie Perkins - Print & Pattern - Geometric-Laurence King Publishing (2015)Camilo Montañez100% (18)
- Music: Quarter 1, Wk.4 - Module 4Document21 pagesMusic: Quarter 1, Wk.4 - Module 4Mary Jean MagdayNo ratings yet
- Design ModernDocument2 pagesDesign ModernDamonNo ratings yet
- E-Portfoliotask 2 Nograles Benavente Polaris 1-ADocument6 pagesE-Portfoliotask 2 Nograles Benavente Polaris 1-Aapi-655853692No ratings yet
- 1999 Frederick at The Center of It All PDFDocument13 pages1999 Frederick at The Center of It All PDFMelchiorNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan (English 1)Document37 pagesUnit Plan (English 1)JOPHNEL NOA GAGARINNo ratings yet
- Library Book SpreadsheetDocument142 pagesLibrary Book Spreadsheetwasabi999No ratings yet
- Art Through Social StudiesDocument29 pagesArt Through Social Studiesapi-665826314No ratings yet
- The Mediums of The Visual: - EncausticDocument27 pagesThe Mediums of The Visual: - EncausticRuby MalunesNo ratings yet
- Emoji LPDocument2 pagesEmoji LPapi-273585331No ratings yet
- Film - A Montage of TheoriesDocument388 pagesFilm - A Montage of TheoriesDebanjan BandyopadhyayNo ratings yet
- BS8-SOL-24TC-1Document32 pagesBS8-SOL-24TC-1Adjei NketiahNo ratings yet
- 2nd Qua ExamDocument2 pages2nd Qua Exammaricar jodelah uyegNo ratings yet
- Ecp711 - At2 Visual Arts Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesEcp711 - At2 Visual Arts Lesson Planapi-358413062No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Practical ResearchDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 5 Practical ResearchWilhar TagudNo ratings yet
- (Lesson Plan) : Education in Spanish RegimeDocument10 pages(Lesson Plan) : Education in Spanish RegimeRussell CasipleNo ratings yet
- Discover KG2 t2 EDocument168 pagesDiscover KG2 t2 EChristina GamilNo ratings yet
- Art Curriculum - Grade 2Document5 pagesArt Curriculum - Grade 2api-461817250No ratings yet
- 12 Business Studies CH 01 Nature and Significance of ManagementDocument7 pages12 Business Studies CH 01 Nature and Significance of ManagementAman SinghNo ratings yet
- MLubojanski VHakala Thesis A D 10sem PDFDocument144 pagesMLubojanski VHakala Thesis A D 10sem PDFSOUMIL SENAPATINo ratings yet
- Indian Sculpture and Painting E.B. HavellDocument512 pagesIndian Sculpture and Painting E.B. HavellAnkit Agrawal100% (7)
- Vts Lesson PlanDocument1 pageVts Lesson Planapi-581785496No ratings yet
- Tos Contemporary ArtsDocument2 pagesTos Contemporary ArtsAroma EyreNo ratings yet
- ART Criticism: Four Principal ApproachesDocument14 pagesART Criticism: Four Principal ApproachesQuenard Medillo GalesNo ratings yet
- Benjamin 01Document3 pagesBenjamin 01Mahbubur RahmanNo ratings yet