Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Xenobiotics Report Notes
Uploaded by
hoythereCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Xenobiotics Report Notes
Uploaded by
hoythereCopyright:
Available Formats
Conjugates - considered to be polar molecules that can be readily excreted by the body and are often
inactive
Most of the reactions do this except for glycine and glutamine since the substrate is initially activated.
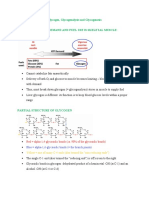
Glucuronidation reaction
Most common reaction in adults: Glucuronidation
Most common reaction in children: Sulfation
Formation of the β-glucuronides involves two steps: synthesis of the activated coenzyme which is
uridine-5’diphospho-α-D-glucuronic acid (UDPGA) and the subsequent transfer of the glucuronyl group
from UDPGA to the substrate. Synthesis of UDPGA utilizes α-D-glucose-1-phosphate as its initial
precursor (Wilson et al., 2011).
Unconjugated bilirubin may go to the blood brain barrier and may cause kernicterus encephalopathy
Phenolic and alcoholic hydroxyls are the most common functional groups undergoing glucuronidation in
drug metabolism
Sulfate conjugation
Missing enzyme: APs phosphokinase
However, O-sulfate conjugates of some N-hydroxy compounds give rise to chemically reactive
intermediates that are toxic. Phenacetin, an analgesic, is metabolized into N-hydroxyphenacetin and
subsequently conjugated with sulfate. The O-sulfate conjugate of N-hydroxyphenacetin can bind
covalently to microsomal proteins which can lead to reactive intermediates responsible for
hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity of the discontinued drug
Amino Acid Conjugation
Phenylacetic acid derivatives: Diclofenac, Ketorolac
GSH or Mercapturic Acid Conjugation
GSH can protect cells against chemically reactive species due to its nucleophilic SH group
Azathioprine- immunosuppressant; prodrug of 6-mercaptopurine; can be used for rheumatoid arthritis
and immunosuppresion
Methylation
Common endogenous compounds: epinephrine and melatonin
Inactivation of biologic amines: NE, Dopamine, Serotonin, and Histamine
Methionine: presence of thioether
You might also like
- GalactosemiaDocument3 pagesGalactosemiaChiatsuNo ratings yet
- 9 GlycogenDocument37 pages9 GlycogenShendi SuryanaNo ratings yet
- 8glycogen Metabolism2013 PDFDocument90 pages8glycogen Metabolism2013 PDFNazeer Baig MogalmearjaNo ratings yet
- GlycogenesisDocument7 pagesGlycogenesishammad646No ratings yet
- Biochem TopicsDocument28 pagesBiochem TopicsLoraine ReuyanNo ratings yet
- 2020 Glycogen MetabolismDocument29 pages2020 Glycogen MetabolismChayanika KumarNo ratings yet
- Glycosaminoglycans: 1. Write Brief Notes On Uronic Acid PathwayDocument6 pagesGlycosaminoglycans: 1. Write Brief Notes On Uronic Acid PathwayTamene TekileNo ratings yet
- 2021 CHO Metabolism 2Document32 pages2021 CHO Metabolism 2xb2k9gzkc9No ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis Group6Document9 pagesGluconeogenesis Group6JasneetaNo ratings yet
- BCH421 2019-20 Harmattan 1Document7 pagesBCH421 2019-20 Harmattan 1idriscognitoleadsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Glycogen-HZDocument20 pagesLesson 3 Glycogen-HZliaorNo ratings yet
- Zoology AssignmentDocument9 pagesZoology AssignmentBiba JaanNo ratings yet
- 2.6 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Glycogen MetabolismDocument10 pages2.6 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Glycogen Metabolismlovelots1234No ratings yet
- GlycolysisDocument10 pagesGlycolysiselowanegNo ratings yet
- 1 - Biochemistry Notes by Dr. M A Bari Siddiqui: DrmentorsDocument3 pages1 - Biochemistry Notes by Dr. M A Bari Siddiqui: DrmentorsShiva KumarNo ratings yet
- Glycogen, Glycogenolysis and GlycogenesisDocument8 pagesGlycogen, Glycogenolysis and GlycogenesisSierra OrtizNo ratings yet
- Glycogen MetabolismDocument27 pagesGlycogen Metabolismdrbishalchowdhury13No ratings yet
- Biochemical Importance of Carbohydrate (2015)Document38 pagesBiochemical Importance of Carbohydrate (2015)Agnes Treyssia SandewaNo ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis: Margareta Chintia Amba Dewi 2170121185Document12 pagesGluconeogenesis: Margareta Chintia Amba Dewi 2170121185Devina ArieshantyNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism (Unit 2) : Gluconeogenesis Continued .Document22 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism (Unit 2) : Gluconeogenesis Continued .qwerty123No ratings yet
- GLIKOGENESISDocument45 pagesGLIKOGENESISChrista24796No ratings yet
- Metabolism of CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesMetabolism of Carbohydrateskathleenmaisiedevilla.021105No ratings yet
- Glycogen MetabolismDocument16 pagesGlycogen MetabolismMuhammad HashirNo ratings yet
- Department of Industrial Chemistry: Biochemistry (Ichem.3052) Chapter 8: Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument67 pagesDepartment of Industrial Chemistry: Biochemistry (Ichem.3052) Chapter 8: Carbohydrate MetabolismBizuayehu Ze GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis: Glycolysis (From Glycose, An Older TermDocument22 pagesGlycolysis: Glycolysis (From Glycose, An Older TermChai Hong XuanNo ratings yet
- GluconeogenesisDocument3 pagesGluconeogenesisyam pdNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis For NursesDocument17 pagesGlycolysis For NursesAaron WallaceNo ratings yet
- Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument2 pagesPentose Phosphate PathwayRohanNo ratings yet
- Important The 2 Mid Term Exam Is On November17 (Monday), 2014 in Remsen 017 at 5.00 PMDocument34 pagesImportant The 2 Mid Term Exam Is On November17 (Monday), 2014 in Remsen 017 at 5.00 PMjessjayleeNo ratings yet
- Glycogen Metabolism-FBADocument104 pagesGlycogen Metabolism-FBAozerbilge24No ratings yet
- Unit Ii: Bioenergetics and Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument51 pagesUnit Ii: Bioenergetics and Carbohydrate MetabolismErjel J. MalabananNo ratings yet
- Glycogen MetabolismDocument40 pagesGlycogen MetabolismAastha SinhaNo ratings yet
- 4.metabolism of Glycogen: Biomedical ImportanceDocument9 pages4.metabolism of Glycogen: Biomedical ImportanceMd. Ismail HosenNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism and BiosynthesisDocument44 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism and BiosynthesisEmman RegondolaNo ratings yet
- Glycogenesis & GlycogenolysisDocument10 pagesGlycogenesis & Glycogenolysiskarmakarrupsha48100% (1)
- GlycogenDocument25 pagesGlycogencandysunNo ratings yet
- M SC Zoology 4 Sem PG by DR Lata Bhattacharya-1Document10 pagesM SC Zoology 4 Sem PG by DR Lata Bhattacharya-1Arbab MazharNo ratings yet
- 8 Gluconeogenesis Different PresentationDocument33 pages8 Gluconeogenesis Different PresentationSecret AgentNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme GlikogenDocument17 pagesMetabolisme GlikogenMUHAMMAD RIDONo ratings yet
- Uronic Acid PathwayDocument4 pagesUronic Acid PathwayAlen Arthur100% (2)
- C454 Lect3 ViewDocument66 pagesC454 Lect3 ViewAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis Group 3Document10 pagesGluconeogenesis Group 3PatPat GalaxyNo ratings yet
- Dietary Sources of Carbohydrates: Carbohydrate Oxidation Is The Central Energy Yielding Pathway in Most CellsDocument23 pagesDietary Sources of Carbohydrates: Carbohydrate Oxidation Is The Central Energy Yielding Pathway in Most CellsMiki MausNo ratings yet
- 6 Glycogen 2017 MD PDFDocument36 pages6 Glycogen 2017 MD PDFIbrahim BarhamNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Carbohydrate Metabolism Part 2Document13 pages2.2 Carbohydrate Metabolism Part 2John Louis PulidoNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis 2Document9 pagesGlycolysis 2ahmedmansy991No ratings yet
- Biochemistry Class 1 - GlycolysisDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Class 1 - GlycolysischanudiGajadeeraNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Yusron SugiartoDocument27 pagesBiochemistry: Yusron SugiartoRoyNo ratings yet
- 3 Glikolisis 9Document17 pages3 Glikolisis 9Rafi Ahmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Chem 3560 Lecture 14: Glycogen Metabolism: Glycogen Phosphorylase Is Responsible For Glycogen BreakdownDocument4 pagesChem 3560 Lecture 14: Glycogen Metabolism: Glycogen Phosphorylase Is Responsible For Glycogen BreakdownزينبالجنابيNo ratings yet
- Isolation of GlycogenDocument6 pagesIsolation of GlycogenAlleia Mae Urbano Mazo0% (2)
- Glycogen MetabolismDocument11 pagesGlycogen MetabolismSimra ZahidNo ratings yet
- Glucuronic Acid: Metabolic Reaction and ImportanceDocument3 pagesGlucuronic Acid: Metabolic Reaction and Importanceaneeda shabirNo ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis and GlycogenolysisDocument14 pagesGluconeogenesis and Glycogenolysissima mhammedNo ratings yet
- Glucose-6-Phosphate Is Also Known As A Central Metabolite Because It Can Enter A Lot of PathwaysDocument10 pagesGlucose-6-Phosphate Is Also Known As A Central Metabolite Because It Can Enter A Lot of PathwaysNica Lopez FernandezNo ratings yet
- 2.glycolysis & Oxidation of PyruvateDocument12 pages2.glycolysis & Oxidation of Pyruvateقتيبه خالد دحام خلفNo ratings yet
- Glycogen MetablismDocument17 pagesGlycogen MetablismlkokodkodNo ratings yet
- Glycogen Metabolism: Lourdes L. Balcueva, M.DDocument27 pagesGlycogen Metabolism: Lourdes L. Balcueva, M.Dlovelots1234No ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Insulin Resistance as a Risk Factor in Visceral and Neurological DisordersFrom EverandInsulin Resistance as a Risk Factor in Visceral and Neurological DisordersNo ratings yet
- Er QuizDocument3 pagesEr QuizhoythereNo ratings yet
- December 5, 2000: Fidel V. RamosDocument88 pagesDecember 5, 2000: Fidel V. RamoshoythereNo ratings yet
- Discuss What Is Meant by Pharmaceutical Distribution Channels, Its Functions and LevelsDocument3 pagesDiscuss What Is Meant by Pharmaceutical Distribution Channels, Its Functions and LevelshoythereNo ratings yet
- Toxicity Testing: (Micronucleus Assay and Chorioallantoic Membrane Assay)Document20 pagesToxicity Testing: (Micronucleus Assay and Chorioallantoic Membrane Assay)hoythereNo ratings yet
- Draize Irritation Test PDFDocument27 pagesDraize Irritation Test PDFhoythereNo ratings yet