Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gec 12 Popular Culture Written Act
Uploaded by
abegail.orolfo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views6 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views6 pagesGec 12 Popular Culture Written Act
Uploaded by
abegail.orolfoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
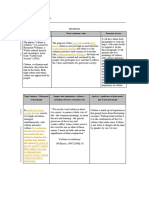
GEC 12 POPULAR CULTURE
Directions: Discuss the THEORIES in Popular culture
comprehensively using the indicators below. Acknowledge
the sources you used in answering this activity. This
is to be SUBMITTED individually within the day through
g-drive. The more information and sources the better!
Theory Definit Key View about Example/ Reference
ion and Features Culture s s
Theoris and its
t Implicatio
n
Cultura Cultura •Focuses Culturalis •The •Stuart
lism lism, on the m views study of Hall's
also ways in culture as how works on
known which dynamic, popular cultural
as culture constantly culture studies.
cultura influence evolving, reflects (Hall,
l s and deeply and Stuart.
theory, individua intertwine reinforc Cultural
is a ls and d with es Studies:
perspec societies power societal Two
tive . relations. norms Paradigms
that •Emphasiz It sees and . 1980.
emphasi es the culture as values. Media,
zes the role of a site of •Analysi Culture &
signifi symbols, contestati s of how Society,
cance rituals, on, where cultural 2(1), 57–
of language, different practice 72.)
culture and norms groups s and •
in in negotiate symbols Clifford
shaping shaping meanings are used Geertz's
human cultural and to anthropol
behavio identitie identities construc ogical
r, s. . The t and approach
beliefs •Recogniz implicatio perpetua to
, and es the n of te culture.
societa diversity culturalis identiti (Geertz,
l of m is the es, such Clifford.
structu cultures recognitio as The
res. and the n of the gender, Interpret
Its need to importance race, or ation of
roots understan of national Cultures.
can be d them cultural ity. 1973.
traced within diversity Basic
back to their and the Books.)
cultura specific need for
l contexts. intercultu
anthrop •Acknowle ral
ology, dges the dialogue
sociolo power and
gy, and dynamics understand
cultura inherent ing.
l in However,
studies cultural it also
. interacti highlights
ons. the
potential
for
cultural
imperialis
m and
domination
.
Marxism Marxism •Focuses Marxism •Analysi •Karl
is a on the sees s of how Marx's
socio- economic culture as mainstre "Capital"
economi base of a tool am media and "The
c society, used by promotes Communist
theory particula the ruling consumer Manifesto
develop rly the class to ism and ":
ed by ownership maintain perpetua
Karl of the their tes Marx, K.
Marx means of power and false (1867).
and productio control consciou Capital:
Friedri n. over the sness Critique
ch •Emphasiz means of among of
Engels. es the production the Political
It exploitat . It working Economy.
analyze ion of argues class. Marx, K.,
s the that •Examina & Engels,
society working cultural tion of F.
through class institutio how (1848).
the (proletar ns, such cultural The
lens of iat) by as media, industri Communist
class the education, es Manifesto
struggl capitalis and operate .
e and t class religion, within •Antonio
the (bourgeoi propagate capitali Gramsci's
dynamic sie). ideologies st theory of
s of •Views that serve systems, cultural
capital culture the exploiti hegemony:
ism. as a interests ng labor
reflectio of the and Gramsci,
n of the bourgeoisi commodif A.
dominant e. The ying (1971).
economic implicatio culture Selection
system n of s from
and Marxism is the
serves to the need Prison
maintain for Notebooks
the cultural .
status critique Lawrence
quo. and the and
•Advocate promotion Wishart.
s for of
social cultural
change forms that
through challenge
the capitalist
overthrow hegemony.
of
capitalis
m and the
establish
ment of a
classless
society.
Feminis Feminis •Focuses Feminism •Analysi •Simone
m m is a on gender views s of de
diverse as a culture as gender Beauvoir.
movemen social deeply roles in (1949).
t that construct entrenched film and “The
seeks and the in televisi Second
to ways in patriarcha on, Sex”.
achieve which it l norms includin •Bell
gender intersect and g the Hooks.
equalit s with values, portraya (1984).
y and other which l of “Feminist
challen forms of perpetuate female Theory:
ge the oppressio gender characte From
patriar n. inequality rs as Margin to
chal •Highligh and passive Center”.
structu ts the discrimina or •Angela
res experienc tion. It subordin Davis.
that es and critiques ate to (1981).
oppress perspecti representa male “Women,
women. ves of tions of protagon Race &
It women, women in ists. Class”.
encompa particula popular •Examina •Laura
sses rly those culture, tion of Mulvey.
various marginali such as feminist (1975).
theoret zed based stereotype art and “Visual
ical on race, s, literatu Pleasure
perspec class, objectific re that and
tives, sexuality ation, and subverts Narrative
includi , etc. the traditio Cinema”.
ng •Critique underrepre nal •Judith
liberal s power sentation gender Butler.
feminis imbalance of women stereoty (1990).
m, s and in pes and “Gender
radical advocates positions explores Trouble:
feminis for of power. women's Feminism
m, and social, The experien and the
interse political implicatio ces. Subversio
ctional , and n of n of
feminis economic feminism Identity”
m. justice. is the .
•Recogniz promotion •Kimberlé
es the of Crenshaw.
importanc alternativ (1989).
e of e cultural “Demargin
intersect narratives alizing
ionality that the
in challenge Intersect
understan gender ion of
ding the norms and Race and
complexit empower Sex: A
ies of women. Black
oppressio Feminist
n. Critique
of
Antidiscr
imination
Doctrine,
Feminist
Theory
and
Antiracis
t
Politics”
.
Postmod Postmod •Critique Postmodern •Postmod •Storey,
ernism ernism s the ism views ern J.
is a notion of culture as literatu (2009).
philoso objective fluid, re that "Cultural
phical reality contingent employs Theory
and and , and in a metafict and
cultura universal state of ion, Popular
l truths, perpetual intertex Culture:
movemen emphasizi flux. It tuality, An
t that ng the rejects and Introduct
emerged subjectiv the idea pastiche ion."
in the ity of of a fixed , such •Kellner,
late experienc cultural as the D.
20th e. identity works of (1995).
century •Embraces or Jorge "Media
, fragmenta singular Luis Culture:
rejecti tion, interpreta Borges Cultural
ng the pastiche, tion, or Studies,
grand and irony advocating Thomas Identity
narrati as for Pynchon. and
ves and character plurality •Postmod Politics
absolut istic and ern art between
e features multiplici movement the
truths of ty of s like Modern
of postmoder meanings. Pop Art and the
moderni n The or Neo- Postmoder
ty. Key culture. implicatio Dada, n."
theoris •Challeng n of which
ts es postmodern appropri
include hierarchi ism is the ate
Jean- cal celebratio images
Françoi distincti n of from
s ons diversity popular
Lyotard between and the culture
, Jean high and recognitio and
Baudril low n of the challeng
lard, culture, contingent e
and blurring nature of traditio
Fredric boundarie knowledge nal
Jameson s between and truth. notions
. art and of
mass artistic
media. authenti
•Question city.
s the
stability
of
meaning
and the
authority
of
instituti
ons in
shaping
culture.
You might also like
- Traces of Humanism in China: Tradition and ModernityFrom EverandTraces of Humanism in China: Tradition and ModernityCarmen MeinertNo ratings yet
- Gec 12 Popular Culture Orolfo, Abegail 3aDocument5 pagesGec 12 Popular Culture Orolfo, Abegail 3aabegail.orolfoNo ratings yet
- Indigenous Peoples, Civil Society, and the Neo-liberal State in Latin AmericaFrom EverandIndigenous Peoples, Civil Society, and the Neo-liberal State in Latin AmericaNo ratings yet
- Gee2 Module 2Document6 pagesGee2 Module 2Marielle Grace PadilloNo ratings yet
- Pop Culture LessonDocument97 pagesPop Culture LessonVic Intia Paa100% (1)
- Popular Culture in SocietyDocument29 pagesPopular Culture in SocietyLoppyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Theories in Pop CultureDocument9 pagesChapter 2 - Theories in Pop CultureGreen GeekNo ratings yet
- Culture Is Ordinary Essay Plan EditedDocument3 pagesCulture Is Ordinary Essay Plan EditedsimonpolovakNo ratings yet
- Prelim Pop-TaylorDocument9 pagesPrelim Pop-Taylorbarangay threeNo ratings yet
- 6 3Document5 pages6 3Kiran kumarNo ratings yet
- PPC Midterm ModulesDocument8 pagesPPC Midterm ModulesYsduh GamingNo ratings yet
- The Concept of CultureDocument20 pagesThe Concept of CultureRamjit KumarNo ratings yet
- The Politicization of 'Culture'Document8 pagesThe Politicization of 'Culture'nicole quilangNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 What Is CultureDocument12 pagesLecture 1 What Is CulturedivyaNo ratings yet
- Cultural Studies, Multiculturalism, and Media Culture - D. KellnerDocument12 pagesCultural Studies, Multiculturalism, and Media Culture - D. KellnerSilvana TorresNo ratings yet
- Sujay Rao Mandavilli: ELK Asia Pacific Journal of Social Science Volume 4, Issue 2, 2018Document84 pagesSujay Rao Mandavilli: ELK Asia Pacific Journal of Social Science Volume 4, Issue 2, 2018Sujay Rao MandavilliNo ratings yet
- 240 Lecture NotesDocument17 pages240 Lecture Notesemmap.mooreNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Culture1Document8 pagesDefinitions of Culture1George L. CarinNo ratings yet
- Uscp Lesson 1 2 PDFDocument4 pagesUscp Lesson 1 2 PDFJessierhy Mae CanoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 and 8 Soc 1Document29 pagesLesson 7 and 8 Soc 1Reymark GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Journal Article (Group 5) - Cultural StudiesDocument4 pagesJournal Article (Group 5) - Cultural Studiesukmsemu.unibaNo ratings yet
- (Ucsp - Notes) Sociology, Anthropology, Political ScienceDocument3 pages(Ucsp - Notes) Sociology, Anthropology, Political ScienceMomoNo ratings yet
- CultureDocument12 pagesCultureSennahNo ratings yet
- Marxism, Political Economy, and Ideology.Document11 pagesMarxism, Political Economy, and Ideology.lalalovegoodNo ratings yet
- Spivak - 2006 - Culture AliveDocument2 pagesSpivak - 2006 - Culture AliveIsabela Umbuzeiro ValentNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Feb 26, 2024Document17 pagesAdobe Scan Feb 26, 2024hiroa6386No ratings yet
- 12 The Dynamics of Culture and Human EvolutionDocument21 pages12 The Dynamics of Culture and Human Evolutionhenry tulaganNo ratings yet
- Cultural Studies: Two Paradigms: Stuart Hall: in GeneralDocument4 pagesCultural Studies: Two Paradigms: Stuart Hall: in GeneralSithusha SNo ratings yet
- Disability Culture: Assimilation or Inclusion?Document20 pagesDisability Culture: Assimilation or Inclusion?Antwi VincentNo ratings yet
- COMM6502.Cultural Studies - November 2020.OURVLEDocument22 pagesCOMM6502.Cultural Studies - November 2020.OURVLENajae MurrayNo ratings yet
- Cultural Theory, Pr. MasfourDocument39 pagesCultural Theory, Pr. MasfourSennahNo ratings yet
- AS CultureDocument19 pagesAS CultureborahebangtanNo ratings yet
- Business As Unusual The Role of National Cultural Background in Corporate LifeDocument8 pagesBusiness As Unusual The Role of National Cultural Background in Corporate LifeHarsh SarafNo ratings yet
- IS Y1.1 - Cultural StudiesDocument18 pagesIS Y1.1 - Cultural StudiesShauna O'NeillNo ratings yet
- 6) Globalization and Culture - Chantal CrozetDocument8 pages6) Globalization and Culture - Chantal CrozetBea Nicole Estrada100% (1)
- Key Concepts in Cultural StudiesDocument11 pagesKey Concepts in Cultural StudiesarwalamouddanNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Cultural StudiesDocument34 pages1.introduction To Cultural StudiesSophia PapaNo ratings yet
- Socio AnthropologyDocument5 pagesSocio Anthropologyjoana.samsonNo ratings yet
- Full Download Sociology Pop Culture To Social Structure 3rd Edition Brym Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFull Download Sociology Pop Culture To Social Structure 3rd Edition Brym Solutions Manualjoseph8gfth100% (36)
- Culture, Identity and International RelationsDocument7 pagesCulture, Identity and International RelationsPranjal Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 CultureDocument43 pagesChapter 2 CultureShafaq RubabNo ratings yet
- Cultural Institution PresentationDocument17 pagesCultural Institution PresentationMichael Mao100% (1)
- Culture HandoutDocument4 pagesCulture HandoutGian Angela SancejaNo ratings yet
- Daenekindt, S (2018) High CultureDocument2 pagesDaenekindt, S (2018) High CultureElias Le GrandNo ratings yet
- Culture & Society - Lec. 10-14 - SNAdDocument37 pagesCulture & Society - Lec. 10-14 - SNAdTalha ZubayerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 The Growth of Anthropological Theories-1Document45 pagesChapter 4 The Growth of Anthropological Theories-1John Leif DanaoNo ratings yet
- UCSPDocument60 pagesUCSPMichelle TampoyNo ratings yet
- Cultural Properties and Types 11112022 022054pm 25102023 120854pmDocument33 pagesCultural Properties and Types 11112022 022054pm 25102023 120854pmhafizamanzoor44No ratings yet
- Key Concepts in Cultural StudiesDocument14 pagesKey Concepts in Cultural Studiessarayasmine1964No ratings yet
- Cultural Reader: Culture Industry - NotesDocument1 pageCultural Reader: Culture Industry - NotesJijinraj PulimathNo ratings yet
- Sociocultural GlobalizationDocument6 pagesSociocultural GlobalizationVianie Mae BagaoisanNo ratings yet
- Cultures of Circulation: The Imaginations of Modernity: Benjamin Lee and Edward LipumaDocument23 pagesCultures of Circulation: The Imaginations of Modernity: Benjamin Lee and Edward Lipumatoby_hobobyNo ratings yet
- Smith (1998) - NacionalismoDocument21 pagesSmith (1998) - NacionalismoDaniel AlecNo ratings yet
- Cultural Studies: Compiled By: Arif Widyanto Budi Nirwana SaktiDocument9 pagesCultural Studies: Compiled By: Arif Widyanto Budi Nirwana SaktiArif widya100% (1)
- SM 1cultureDocument128 pagesSM 1cultureshivam mishraNo ratings yet
- CultureDocument38 pagesCulturemarvel s. malaqueNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For LangIdent Sage Book Second QuizDocument3 pagesReviewer For LangIdent Sage Book Second Quizziaclyde.daguploNo ratings yet
- Chapter IVDocument19 pagesChapter IVBeverly CabuyadaoNo ratings yet
- Cultur E: Mr. Rene M. AnsaoDocument39 pagesCultur E: Mr. Rene M. AnsaoprecelynNo ratings yet
- Sow and Fattener ProductionDocument10 pagesSow and Fattener Productionabegail.orolfoNo ratings yet
- Broiler Record EvaluationDocument11 pagesBroiler Record Evaluationabegail.orolfoNo ratings yet
- Lab3 OrolfoDocument5 pagesLab3 Orolfoabegail.orolfoNo ratings yet
- Lab2 OrolfoDocument3 pagesLab2 Orolfoabegail.orolfoNo ratings yet
- Prototype - Lesson Plan - English 10 Q3 Week 7Document6 pagesPrototype - Lesson Plan - English 10 Q3 Week 7Lyke Therese Sungahid - BagsacNo ratings yet
- Freudian and Feminist Approaches To HamletDocument6 pagesFreudian and Feminist Approaches To HamletA Guy With A Very Long NameNo ratings yet
- Magoosh GRE Reading Comprehension Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesMagoosh GRE Reading Comprehension Questions and AnswersJai PhookanNo ratings yet
- Nepal's Women OrganizationDocument18 pagesNepal's Women OrganizationsuwashNo ratings yet
- Module 1 (Gender and Society)Document12 pagesModule 1 (Gender and Society)Elsie TabangcuraNo ratings yet
- NGOs and Imperialism - James Petras PDFDocument13 pagesNGOs and Imperialism - James Petras PDFXimonsNo ratings yet
- Daniela-Irina Darie, PHD Student, "Al. Ioan Cuza" University of IaşiDocument10 pagesDaniela-Irina Darie, PHD Student, "Al. Ioan Cuza" University of IaşiHouda BoursNo ratings yet
- How The East Took Over The West: Hippie Culture, Eastern Modernity and The Queer MovementDocument9 pagesHow The East Took Over The West: Hippie Culture, Eastern Modernity and The Queer MovementBrenn100% (1)
- Marie Antoinette: Fashion, Third Wave Feminism and Chick CultureDocument20 pagesMarie Antoinette: Fashion, Third Wave Feminism and Chick CultureinterkosmosNo ratings yet
- Darkside of FeminismDocument13 pagesDarkside of FeminismSahil MirNo ratings yet
- Topic-1: Role of Sociology in Social Problems:: AssignmentDocument12 pagesTopic-1: Role of Sociology in Social Problems:: AssignmentMOHAMAMD ZIYA ANSARINo ratings yet
- Labyrinth 2016Document116 pagesLabyrinth 2016danosarstedtNo ratings yet
- Aurat MarchDocument2 pagesAurat MarchUsman RajaNo ratings yet
- 4 SubalternStudiesDocument15 pages4 SubalternStudiesgarciaguionNo ratings yet
- Fourth Wave Feminism in Indonesia: Body Shaming Through Social Media PhenomenonDocument17 pagesFourth Wave Feminism in Indonesia: Body Shaming Through Social Media PhenomenonQuỳnh PhanNo ratings yet
- Heidi CronichlesDocument5 pagesHeidi CronichlesSteven Gregory MeyerNo ratings yet
- Votes For Women: The 19th Century The Suffragists and The SuffragettesDocument2 pagesVotes For Women: The 19th Century The Suffragists and The Suffragettesdalia HagryNo ratings yet
- Toxic MasculinityDocument8 pagesToxic MasculinityChristosNo ratings yet
- Group 2 ICT2MA RevisedDocument5 pagesGroup 2 ICT2MA RevisedRich BaguiNo ratings yet
- Feminism and Its WavesDocument6 pagesFeminism and Its WavesMuzna AliNo ratings yet
- A Feminist StandpointDocument9 pagesA Feminist StandpointMhabeni EzungNo ratings yet
- Linda Alcoff, The Problem of Speaking For OthersDocument9 pagesLinda Alcoff, The Problem of Speaking For OthersPepaSilvaNo ratings yet
- Is Feminism Bad For MulticulturalismDocument18 pagesIs Feminism Bad For MulticulturalismDavid Cruz FerrerNo ratings yet
- The Globalization of World PoliticsDocument248 pagesThe Globalization of World PoliticsRommel Rios Regala100% (3)
- Firebrand FeminismDocument46 pagesFirebrand FeminismUniversity of Washington PressNo ratings yet
- DRJK FloraNwapaDocument196 pagesDRJK FloraNwapaPrabhu KrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Feminist Theory - Hermeneutical Phenomenology - Human Environment SystemsDocument3 pagesFeminist Theory - Hermeneutical Phenomenology - Human Environment SystemsNathaniel Banes100% (1)
- The Problem and It'S Background: Dasmarinas)Document14 pagesThe Problem and It'S Background: Dasmarinas)wendy abulenciaNo ratings yet
- Modern History - Queen Victoria AssessmentDocument3 pagesModern History - Queen Victoria Assessmentapi-368761552No ratings yet
- Chapter IV The Inner Voice A Woman Speaks Out I ShodhgangaDocument63 pagesChapter IV The Inner Voice A Woman Speaks Out I ShodhgangaJelenaNo ratings yet