Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Poverty, Inequality and Social Welfare
Poverty, Inequality and Social Welfare
Uploaded by
jonson balangon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageLesson about Poverty, Inequality and Social Welfare
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLesson about Poverty, Inequality and Social Welfare
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pagePoverty, Inequality and Social Welfare
Poverty, Inequality and Social Welfare
Uploaded by
jonson balangonLesson about Poverty, Inequality and Social Welfare
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Poverty, Inequality, and Social Welfare
(Monopoly Analogy)
What so bad about extreme inequality?
1. Income inequality -refers to the varying incomes of different socioeconomic groups in
an economy.
-also called as “Income Gap” – it highlights the gaps between those
with the highest and lowest incomes in a country, region, people, or the whole
world.
What TRIGGERS Income Inequality?
Male vs. Female workers
Young vs. Older workers
College Grad Vs. Undergrad
2. A person experienced extreme income can change his surroundings. If you experience
extreme income, it strengthens your political power.
3. Extreme Inequality is literally, obviously, clearly, visibly, undoubtedly, absolutely UNFAIR
period (.) and that is very disproportionate.
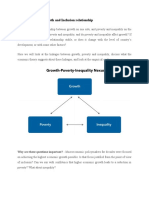
DUALISTIC DEVELOPMENT & SHIFTING LORENZ CURVES: SOME STYLIZED TYPOLOGY
1. The Modern Sector Enlargement Growth Typology (READ)
- L1 represents Lorenz curve, L2 represents the new one
- Each modern sector household receives the same absolute income as before, but
now the share received by the richest income group is smaller than before.
- It explains why the new Lorenz curve lies above the old one at the higher end of
income distribution scale.
- The Old and New Lorenz Curve must cross each other.
2. The Modern Sector Enrichment Growth Typology (READ)
- This aggravates inequality with households with lower scale of income which will either
have no effect or aggravate poverty.
- It actually trying to shift downward and further from the line of equality.
3. The Traditional Sector Enlargement Growth Typology (READ)
(EXPLAIN the graph)(line of equality, 0-100, Lorenz curve)
- It leads to a more equal relative distribution of income, and that culminates into
reduced poverty.
- It actually trying to shift closer toward the line of inequality.
Kuznet’s Inverted-U Hypothesis
- It was suggested by Simon Kuznets
- A curve which shows that as an economy develops, economic inequality first
increases and then decrease
Explanation as why inequality wight worsen
- The wages and productivity were high but employment is limited
- The need of educated workers increases but the supply of unskilled worker falls
You might also like
- Barclays Brazil A Guide To Local Markets - Finding Value in A Controlled EnvironDocument26 pagesBarclays Brazil A Guide To Local Markets - Finding Value in A Controlled Environmvidhya50No ratings yet
- CFA FlashcardsDocument258 pagesCFA FlashcardsBrook Rene Johnson71% (7)
- Venture Capital For Dummies Cheat Sheet - For DummiesDocument9 pagesVenture Capital For Dummies Cheat Sheet - For DummiesNasir Ali RizviNo ratings yet
- 1030GM Midterm SolutionDocument15 pages1030GM Midterm SolutionFelixEternityStabilityNo ratings yet
- Levelized Cost of Energy Calculation - BV - ENDocument16 pagesLevelized Cost of Energy Calculation - BV - ENOscar Iván TorresNo ratings yet
- Inequality, Poverty and DevelopmentDocument38 pagesInequality, Poverty and DevelopmentCresenciano MalabuyocNo ratings yet
- Econ Dev Chapter 5Document6 pagesEcon Dev Chapter 5Feizhen Mae RodelasNo ratings yet
- Ch05 Poverty Inequality DevelopmentDocument57 pagesCh05 Poverty Inequality DevelopmentE RVNo ratings yet
- Carti Pentru LicentaDocument16 pagesCarti Pentru LicentaRobertŞtefanNo ratings yet
- Assemble Smartphone Case SolutionDocument3 pagesAssemble Smartphone Case SolutionPravin Mandora50% (2)
- Kebijakan Tata Ruang Dan Pertanahan Dalam Kerangka InvestasiDocument0 pagesKebijakan Tata Ruang Dan Pertanahan Dalam Kerangka InvestasiPUSTAKA Virtual Tata Ruang dan Pertanahan (Pusvir TRP)No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 DeveeconomicsDocument75 pagesChapter 5 DeveeconomicsErmias AtalayNo ratings yet
- Unit Vi FinalDocument28 pagesUnit Vi FinalCatrina Joanna AmonsotNo ratings yet
- What Are The Four Properties Every Poverty Measures Must Satisfy?Document5 pagesWhat Are The Four Properties Every Poverty Measures Must Satisfy?Joshua johnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 & 6Document5 pagesChapter 5 & 6Cyrus ArmamentoNo ratings yet
- Unit VI. Poverty, Inequality, and Development: OutlineDocument11 pagesUnit VI. Poverty, Inequality, and Development: OutlinefghaNo ratings yet
- Proverty, Inequality, and Development: Group 5Document32 pagesProverty, Inequality, and Development: Group 5n. aisyahNo ratings yet
- Poverty, Inequality and Development Poverty, Inequality and DevelopmentDocument36 pagesPoverty, Inequality and Development Poverty, Inequality and DevelopmentARYATNo ratings yet
- Poverty in Equality and DevelopmentDocument25 pagesPoverty in Equality and DevelopmentASA PRATAMANo ratings yet
- Handouts Econ Final 1Document4 pagesHandouts Econ Final 1Lilian FredelucesNo ratings yet
- Global StratificationDocument4 pagesGlobal StratificationRonielyn CasullaNo ratings yet
- Poverty Inequality and Economic Growth: Presented By: Takesh LuckhoDocument14 pagesPoverty Inequality and Economic Growth: Presented By: Takesh LuckhoNikhil GungabissoonNo ratings yet
- Is Inequality All About The Tails The Palma Measure of Income InequalityDocument4 pagesIs Inequality All About The Tails The Palma Measure of Income InequalityHoBadalaNo ratings yet
- Chap4 Notes Econ-25Document9 pagesChap4 Notes Econ-25Erika May RamirezNo ratings yet
- Gap Between Rich and PoorDocument5 pagesGap Between Rich and PoorSayma HossainNo ratings yet
- What Is Poverty. Written ReportDocument3 pagesWhat Is Poverty. Written ReportzoeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2. Growth and Inclusion RelationshipDocument14 pagesLecture 2. Growth and Inclusion RelationshipAzər ƏmiraslanNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument4 pagesUntitled DocumentMA. REGINA MAI COMIANo ratings yet
- Apuntes Chapter 10Document10 pagesApuntes Chapter 10Jaime Ruiz-SalinasNo ratings yet
- Development Economics Assignment - 2: SUBMITTED BY-Shubham Gupta Roll No - 86 Semester - 5Document11 pagesDevelopment Economics Assignment - 2: SUBMITTED BY-Shubham Gupta Roll No - 86 Semester - 5Aditya KumarNo ratings yet
- 12:27 - Study Guide - MichaelaDocument4 pages12:27 - Study Guide - MichaelaMichaela TvrdíkováNo ratings yet
- Poverty: Measuring InequalityDocument7 pagesPoverty: Measuring InequalityTabraiz MarriNo ratings yet
- Questions To AddressDocument6 pagesQuestions To AddressAeron Rai RoqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Poverty, Inequality and Growth DevelopmentDocument187 pagesChapter 3-Poverty, Inequality and Growth DevelopmentLisaNo ratings yet
- Equity Distribuiton of IncomeDocument19 pagesEquity Distribuiton of IncomeAmy WuNo ratings yet
- Inequality Refer To The Phenomenon of Un Equal And/ or Unjust Distribution of Resources and Opportunities Among Member of Given SocietyDocument6 pagesInequality Refer To The Phenomenon of Un Equal And/ or Unjust Distribution of Resources and Opportunities Among Member of Given SocietyTECHNICAL SAMIULLAHNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 8: Income Distribution and Income InequalityDocument37 pagesLecture Notes 8: Income Distribution and Income InequalityMansab Raja KhanNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Concepts For The Perceptions of Poverty and Social ExclusionDocument10 pagesDefinitions of Concepts For The Perceptions of Poverty and Social ExclusionYoussef MpuhyousseNo ratings yet
- Summary Development Economics LecturesDocument32 pagesSummary Development Economics LecturesGishaNo ratings yet
- Poverty, Nutrition and Income InequalityDocument28 pagesPoverty, Nutrition and Income InequalityDarrr RumbinesNo ratings yet
- Rich and PoorDocument4 pagesRich and PoorJames SantosNo ratings yet
- Global Inequality: Submmitted byDocument12 pagesGlobal Inequality: Submmitted byKrizza Mae CanoneoNo ratings yet
- Economic Development Chapter 1 and 2Document2 pagesEconomic Development Chapter 1 and 2jay classroomNo ratings yet
- Definitions and GraphsDocument5 pagesDefinitions and GraphsAmgad ElshamyNo ratings yet
- The Economics of Poverty and The Poverty of Economics: A Christian PerspectiveDocument20 pagesThe Economics of Poverty and The Poverty of Economics: A Christian PerspectiveABCDNo ratings yet
- InequalityDocument10 pagesInequalityOns AlkhaliliNo ratings yet
- For Richer, For PoorerDocument14 pagesFor Richer, For Poorerletjes1603No ratings yet
- Income InequalityDocument12 pagesIncome InequalityEj LayconNo ratings yet
- Poverty and Poverty Reduction Strategies in UgandaDocument31 pagesPoverty and Poverty Reduction Strategies in UgandaBernard Francis MNo ratings yet
- Finals PPT Notes - Economic DevelopmentDocument6 pagesFinals PPT Notes - Economic DevelopmentGRACELINE JOY TOMENo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Poverty and InequalityDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Poverty and InequalityHyuna KimNo ratings yet
- Lec1 Spring 2019 DevDocument65 pagesLec1 Spring 2019 DevHai PhamNo ratings yet
- Income InequalityDocument5 pagesIncome InequalityAhtishamNo ratings yet
- The Price of Bliss Affluence Is A Double Edged Sword. On One Side, The Blade Is Dull and Embedded WithDocument2 pagesThe Price of Bliss Affluence Is A Double Edged Sword. On One Side, The Blade Is Dull and Embedded Withapi-296860658No ratings yet
- Nicolas Marié What Is The Relevance, Policy and Measurement Challenges Associated With Middle Classes (And Polarization) ?Document3 pagesNicolas Marié What Is The Relevance, Policy and Measurement Challenges Associated With Middle Classes (And Polarization) ?Nicolas MariéNo ratings yet
- 5 - Poverty, Inequality, and DevelopmentDocument17 pages5 - Poverty, Inequality, and DevelopmentJesie CuevasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - MicroeconomicsDocument7 pagesChapter 20 - MicroeconomicsFidan MehdizadəNo ratings yet
- Income Distribution - WikipediaDocument3 pagesIncome Distribution - WikipediaRajnikant BilungNo ratings yet
- Labor Migration TheoriesDocument9 pagesLabor Migration TheoriesR BNo ratings yet
- Globalization in The Contemporary WorldDocument14 pagesGlobalization in The Contemporary WorldEXTRA EXTRANo ratings yet
- Notes For Economics SubjectDocument5 pagesNotes For Economics SubjectSoleil SierraNo ratings yet
- Final 1.1 Poverty and Income DistributionDocument19 pagesFinal 1.1 Poverty and Income Distributionjayson deeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Debraj RayDocument21 pagesChapter 6 Debraj Raymuhammadsiddique99067% (3)
- Topic 3 NotesDocument7 pagesTopic 3 NotesjeremythamanNo ratings yet
- Origin of The Super-RichDocument19 pagesOrigin of The Super-RichJarlene Rodrigues ReisNo ratings yet
- Trends in Global and Regional Disparities: The Economy and Its Increasing DisparitiesDocument13 pagesTrends in Global and Regional Disparities: The Economy and Its Increasing Disparitiesmartin sirifaveNo ratings yet
- Globalization, Migration, and Welfare State: Understanding the Macroeconomic TrifectaFrom EverandGlobalization, Migration, and Welfare State: Understanding the Macroeconomic TrifectaNo ratings yet
- Nestle PresentationDocument32 pagesNestle PresentationNeoh WongNo ratings yet
- 3rd QuizDocument5 pages3rd QuizRyu Myrmidon100% (4)
- Econ 100c Syllabus Ssi13Document7 pagesEcon 100c Syllabus Ssi13other1991No ratings yet
- Ba in EconomicsDocument6 pagesBa in EconomicsShravani SalunkheNo ratings yet
- BTN T6Document54 pagesBTN T6Đỗ Hoàng Thu ThuỷNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16Document7 pagesChapter 16britt1611No ratings yet
- Kingfisher AirlinesDocument14 pagesKingfisher AirlinesGaurav Patel50% (2)
- Micro2 homw1postAY2022 23 T1Document2 pagesMicro2 homw1postAY2022 23 T1TAN CHUN LIN BOBBY DOWNo ratings yet
- Business Environment ProjectDocument9 pagesBusiness Environment ProjectAbdulNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Marketing: Ma. Anncel Panganiban-Spence, MBADocument14 pagesIntroduction To Marketing: Ma. Anncel Panganiban-Spence, MBAFevie Cates RamosNo ratings yet
- MRes Micro1 ProductionDocument10 pagesMRes Micro1 ProductionAarthi ShankarNo ratings yet
- Ankit Bagdi (Sec. B) Business AccountingDocument37 pagesAnkit Bagdi (Sec. B) Business AccountingANKIT BAGDINo ratings yet
- Dương Nguyễn - FIN 440 - Week 1 - Quiz 1Document3 pagesDương Nguyễn - FIN 440 - Week 1 - Quiz 1Dương NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Workplace Environment Management Syllabus (Ccmwm701)Document42 pagesWorkplace Environment Management Syllabus (Ccmwm701)MugishaNo ratings yet
- Role of Mncs in Indian Export CompetivenessDocument10 pagesRole of Mncs in Indian Export CompetivenessSunil SamratNo ratings yet
- Financial Management.... PGDocument17 pagesFinancial Management.... PGManali PatilNo ratings yet
- 2 TCW Chapter 2 Globalization of Markets and Economic RelationsDocument12 pages2 TCW Chapter 2 Globalization of Markets and Economic RelationsMiya LaideNo ratings yet
- 3i Final Part1Document35 pages3i Final Part1RS BuenavistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Transportation Planning ContextDocument22 pagesLecture 2 Transportation Planning ContextAkhmadRifaniNo ratings yet
- ProductDocument6 pagesProductHassanNo ratings yet
- Alya Tugas BinggrisDocument6 pagesAlya Tugas BinggrisMira SusantiNo ratings yet
- Twin Deficits HypothesisDocument3 pagesTwin Deficits HypothesisinnovatorinnovatorNo ratings yet