Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CIV428 HW2 Spring2023 2024
Uploaded by
Hala MOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CIV428 HW2 Spring2023 2024
Uploaded by
Hala MCopyright:
Available Formats
CIV428: Slopes and Earth Structures O. S.
Mughieda
Due on: 24/3/2024 HW # 2 Spring 2023-2024
1. An undisturbed sample of a soft clay is set up in the triaxial cell and normally consolidated in the
lab. under an equal all round pressure of 50 kPa. Then the drainage lines are turned off, and axial
stress is increased until failure is reached at (1 - 3)f = 30 kPa, uf 15 kPa. Compute:
a. Undrained shear strength of the soil. Su = ……………………….(kPa)
b. , assume c= 0.0, = …………………….(degrees)
c. cu, assume c = 0.0 cu,= ………………………(degrees)
d. Af Af = ………………………..
2. An undisturbed sample of clay is set up in the triaxial test, and normally consolidated in the lab.
Under equal all round pressure of 20 kPa. Then, while drainage lines are turned on the axial stress is
increased until failure is reached. If c= 25 kPa and = 20o compute:
a. The major effective principal stress at failure, 1f =…………………… (kPa)
b. The drained shear strength of the soil, S = …………………………(kPa)
c. The inclination of the plane of failure, = ………………………… (degrees)
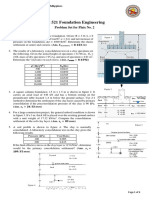
3. A soil profile consists of 4 ft of peat ( = 75 pcf) over a uniform soft clay layer. For the clay = 100
pcf and , p/vo = 1.0. the water table is at the ground surface. For a clay element at the depth of 10
feet (6 feet into the soft clay) compute the following:
a. Unconfined compressive strength. qu = …………………(psf)
b. Undrained shear strength. Su = ………………………….(psf)
Assume a wide fill, thickness 7 feet, = 120 pcf is placed over the surface of the peat.
c. Undrained shear strength immediately after the fill is placed S u = ……………(psf)
d. Undrained shear strength after all of the excess pore water pressures are dissipated. S u =………(psf)
You might also like
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Direct Shear TestDocument18 pagesDirect Shear TestJemuel FloresNo ratings yet
- Shear Strength of Soil Student HandoutDocument32 pagesShear Strength of Soil Student HandoutlohitsnNo ratings yet
- StressDocument14 pagesStressFrank PingolNo ratings yet
- SettlementDocument45 pagesSettlementMuhammad Imam MumtazNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics II ProblemDocument67 pagesSoil Mechanics II ProblemAliMuhammedTekinNo ratings yet
- Mata Deseree Plate 7Document9 pagesMata Deseree Plate 7Diecon Irish ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Settlement of Loaded Ground - Immediate and Consolidation SettlementDocument4 pagesSettlement of Loaded Ground - Immediate and Consolidation SettlementDiana CiurteNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document5 pagesTutorial 2WHfamilyNo ratings yet
- Final Exam-Advanced Soil MechanicsDocument2 pagesFinal Exam-Advanced Soil MechanicsBikaZee100% (1)
- CE363 Old Homework Solutions Part2Document21 pagesCE363 Old Homework Solutions Part2Irmak ÜnalNo ratings yet
- CEN 512 Shear Strength of SoilsDocument5 pagesCEN 512 Shear Strength of SoilsRustom RemorozaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7Document4 pagesTutorial 7Seanam DMNo ratings yet
- Assignment-3: CE3350 (Shear Strength of Soils) : Due Date: For Self-Learning, No Need To Submit The SolutionsDocument6 pagesAssignment-3: CE3350 (Shear Strength of Soils) : Due Date: For Self-Learning, No Need To Submit The SolutionsAddandi AshrithNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet - 5 - CE 1403 Geotechnical Engineering - 230426 - 092421Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet - 5 - CE 1403 Geotechnical Engineering - 230426 - 092421imamadnan69No ratings yet
- UU CD TestsDocument24 pagesUU CD TestsDenver James RabaraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1EYU Eyuel Abrham ArbaNo ratings yet
- Consolidated-Undrained Tri-Axial Test (Cu - Test) : Problem 1Document14 pagesConsolidated-Undrained Tri-Axial Test (Cu - Test) : Problem 1Jemuel FloresNo ratings yet
- CE Review Geotech Set ProbsDocument1 pageCE Review Geotech Set ProbsJella DulatreNo ratings yet
- Pnge 218 Midterm I Spring 2023Document4 pagesPnge 218 Midterm I Spring 2023Mohammed MilanNo ratings yet
- 3.2 University of Glasgow Geotechnical Exam Question ExamplesDocument5 pages3.2 University of Glasgow Geotechnical Exam Question ExamplesFırat PulatNo ratings yet
- ch7 Deep Foundation Piles PDFDocument24 pagesch7 Deep Foundation Piles PDFJonathan SantosNo ratings yet
- ContabilidadDocument14 pagesContabilidadMiqueas SantosNo ratings yet
- Part 2nd CH Lect 10 Consolidation Settlement in FoundationsDocument33 pagesPart 2nd CH Lect 10 Consolidation Settlement in FoundationsKhichi LifeNo ratings yet
- Assnmt 11Document2 pagesAssnmt 11RK MEHTANo ratings yet
- HKU Advance Soil MechanicsDocument7 pagesHKU Advance Soil MechanicsRafi SulaimanNo ratings yet
- ALL Questions.: 3ki 3ki 3kiDocument2 pagesALL Questions.: 3ki 3ki 3kiZack FengNo ratings yet
- ASM Assignment 4Document2 pagesASM Assignment 4rockyNo ratings yet
- Geotech FoundationsDocument17 pagesGeotech FoundationsHoney ApariceNo ratings yet
- Branch: Civil Engineering: No. of Pages: 2 Apj Abdul Kalam Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesBranch: Civil Engineering: No. of Pages: 2 Apj Abdul Kalam Technological UniversityHari RamNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument2 pagesPhysicsMomina UsmanNo ratings yet
- 04 Geotechnical Engineering - IIDocument2 pages04 Geotechnical Engineering - IIMURALI KRISHNANo ratings yet
- 2016 - HW3 - Bearing CapacityDocument3 pages2016 - HW3 - Bearing Capacitychargers777No ratings yet
- FDN Eng'g - Plate No. 2Document2 pagesFDN Eng'g - Plate No. 2Jaycee CuarteroNo ratings yet
- Shear Strenght ExampleDocument11 pagesShear Strenght ExamplealvinNo ratings yet
- Strength 4Document15 pagesStrength 4Yen Ling NgNo ratings yet
- DEEP FOUNDATIONS - Pile Foundations: A. Static ApproachDocument24 pagesDEEP FOUNDATIONS - Pile Foundations: A. Static ApproachRafi Mahmoud SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Review Session 2 - Midterm 2 - SolutionDocument7 pagesReview Session 2 - Midterm 2 - Solutiontyler bradfordNo ratings yet
- CECA 2 - Problem Set No. 06Document3 pagesCECA 2 - Problem Set No. 06carldomingoNo ratings yet
- University of Nairobi Department of Civil and Construction EngineeringDocument9 pagesUniversity of Nairobi Department of Civil and Construction EngineeringLovian MagandaNo ratings yet
- SheetsDocument14 pagesSheetsMohamed TarekNo ratings yet
- Read Each Statement Carefully. Then, Circle Either T (True) or F (False) As Your AnswerDocument10 pagesRead Each Statement Carefully. Then, Circle Either T (True) or F (False) As Your AnswerOsama Al MazrouaiNo ratings yet
- ConsolSett CPTDocument6 pagesConsolSett CPTFajar MardiantoNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios - Esfuerzo Efectivo y ConsolidaciónDocument1 pageEjercicios - Esfuerzo Efectivo y ConsolidaciónVerónica CastroNo ratings yet
- Pre Boards Tutorial 1Document59 pagesPre Boards Tutorial 1vandiazvanNo ratings yet
- Assignment GeoEQDocument11 pagesAssignment GeoEQKamalKishorKumarNo ratings yet
- Pile Load Capacity-Cohesive-Lec-3 (Compatibility Mode)Document24 pagesPile Load Capacity-Cohesive-Lec-3 (Compatibility Mode)Humza ShahidNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5, 6Document4 pagesAssignment 5, 6Tim ChongNo ratings yet
- Foundation Engg Modal Question BDocument3 pagesFoundation Engg Modal Question Bmahil1234No ratings yet
- Ce6101 Problem Sheet 3Document4 pagesCe6101 Problem Sheet 3HT BinhNo ratings yet
- Kuat Geser Tanah (Shear Strength) : Triaxial TestDocument47 pagesKuat Geser Tanah (Shear Strength) : Triaxial TestKhoirul IkhwanNo ratings yet
- CVX4343 2022-23 Tma2Document1 pageCVX4343 2022-23 Tma2shani anneNo ratings yet
- CE602 MockboardQuiz2Document8 pagesCE602 MockboardQuiz2Najib A. CasanNo ratings yet
- GEO 2 Prob Set Take 2 Chap 9Document3 pagesGEO 2 Prob Set Take 2 Chap 9John Pierce GumapacNo ratings yet
- 16 Model Question 1 (Feb 2020) WoaDocument28 pages16 Model Question 1 (Feb 2020) WoakhaledNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics PP 2013Document4 pagesSoil Mechanics PP 2013Zack FengNo ratings yet
- Serkalem Walle BDU0800341Document18 pagesSerkalem Walle BDU0800341Bogale SenayNo ratings yet
- NTU - Mechanical Engineering - MP 4J02 - MArine and Offshore Structural Integrity - Sem 2 06-07Document4 pagesNTU - Mechanical Engineering - MP 4J02 - MArine and Offshore Structural Integrity - Sem 2 06-07awy02No ratings yet
- Pressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910From EverandPressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910No ratings yet
- Presentation 13 ModDocument21 pagesPresentation 13 ModHala MNo ratings yet
- Presentation 16 ModDocument13 pagesPresentation 16 ModHala MNo ratings yet
- Presentation 12 - ModDocument17 pagesPresentation 12 - ModHala MNo ratings yet
- BearingDocument2 pagesBearingHala MNo ratings yet
- HW6 Strength and Reinforcement of Shear WallsDocument2 pagesHW6 Strength and Reinforcement of Shear WallsHala MNo ratings yet
- CIV428-Shear Strength2 SecondDocument77 pagesCIV428-Shear Strength2 SecondHala MNo ratings yet
- WindLoadsASCE7 16Document45 pagesWindLoadsASCE7 16Hala MNo ratings yet
- 77882-Brainstorming Powerpoint TemplateDocument1 page77882-Brainstorming Powerpoint TemplateHala MNo ratings yet
- 2 Wind On Steel BuildingsDocument23 pages2 Wind On Steel BuildingsHala MNo ratings yet
- 2020 AnnualreporttemplateDocument15 pages2020 AnnualreporttemplateHala MNo ratings yet
- Neural Networks - AnnotatedDocument21 pagesNeural Networks - AnnotatedHala MNo ratings yet
- Convolutional Neural Networks - AnnotatedDocument83 pagesConvolutional Neural Networks - AnnotatedHala MNo ratings yet
- AI Performance Evaluation - AnnotatedDocument52 pagesAI Performance Evaluation - AnnotatedHala MNo ratings yet
- Chap5b1 1Document69 pagesChap5b1 1Hala MNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 Block Shear Bearing TearoutDocument59 pagesChap 3 Block Shear Bearing TearoutHala MNo ratings yet
- Chap5b2 - Winter 2023Document58 pagesChap5b2 - Winter 2023Hala MNo ratings yet
- 30 - Lecture 3 - CIV 321 - Spring 2011 (Compatibility Mode)Document35 pages30 - Lecture 3 - CIV 321 - Spring 2011 (Compatibility Mode)Hala MNo ratings yet
- Business ProposalDocument12 pagesBusiness ProposalHala MNo ratings yet
- Chapt4CompMembers2 - 1Document45 pagesChapt4CompMembers2 - 1Hala MNo ratings yet
- Culture by RafikDocument30 pagesCulture by RafikHala MNo ratings yet