Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Loop Impedance Testing For Electrical Safety
Uploaded by
Sunil KambleOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Loop Impedance Testing For Electrical Safety
Uploaded by
Sunil KambleCopyright:
Available Formats
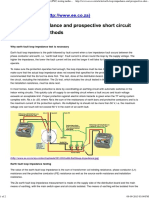
Earth Loop Impedance Testing
The testing of earthing pit alone cannot ensure the safety of man and machine during electrical faults.
The main reason for earth loop impedance testing is to verify that, if a fault occurs in an electrical
installation, sufficient current will flow to operate the circuit breaker protecting the faulty circuit within a
predetermined time to prevent accidents such as Electric Shock, Short Circuit, Fire etc.
The total impedance of the system can be measured at once by using a loop tester. This instrument
simulates a fault between a phase conductor and ground, and thereby measures the total impedance of
the entire ground loop, including conductors and the earth return path back to the transformer and its
winding. If any of these elements have too high a resistance, protective devices may be inhibited from
operating properly, resulting in damage, fire, and even fatal shocks. With an earth loop impedance test
from Dew Energy, you can avoid electrical hazards and ensure your worksite is safety compliant.
The following will affect the value of earth fault loop impedance:
▪ Earthing Resistance
▪ Resistance of Phase and Earthing Conductors/Cables
▪ Conductor Joints and Connections
▪ Transformer Impedance
▪ Type of Earthing System TT, TN or IT
Why earth fault loop Impedance test is necessary
Earth fault loop impedance testing can help us to evaluate the following:
▪ Safety of human beings from electric shock and fire.
▪ Tripping of protection equipment during earth faults.
▪ Absence of earthing or very high resistance of earthing.
▪ Combined values of protection and neutral earthing/Grid.
▪ Possibility of bad contacts present on the PE, neutral or line conductor.
▪ Continuity of Earthing conductors.
▪ The possible type of Earthing system TT / TN / IT.
▪ Accidental interconnection of neutral with equipment earthing.
Earth fault loop impedance testing
The value of the earth fault loop impedance is the sum of transformer coil winding resistance, phase
conductor resistance and the protective conductor (PE) resistance as well as the source earth resistance
and installation resistance.
The Zs impedance value, necessary for determining whether the protection is proper or not, must be
measured. During measurements of short-circuit current with the use of the technical method, an
"artificial short-circuit" is created. The unloaded voltage is measured first. Then the voltage drop caused
by the impedance is measured. These two values are compared, and the difference is used to calculate
total loop impedance. The test is performed so rapidly, within two half-cycles of the utility sine wave
(16millisec), that protective devices are not tripped, and no disruption of the electrical service occurs.
By testing a live circuit with utility power, rather than employing a battery source in the tester to merely
approximate a fault, the loop tester gives a genuine AC impedance reading under real-world conditions.
Dew Energy Services Pvt. Ltd.
HO: 2746, Sector-46, Gurugram, Haryana-122003
BO: 47E, NIT Ind. Area, Faridabad, Haryana-121001
Phone +91 9971690541
Email: deepak@dewenergy.com
You might also like
- Electrical Services-EarthingDocument61 pagesElectrical Services-EarthingArchitects Of BIT MesraNo ratings yet
- School of ElectricalDocument9 pagesSchool of ElectricalJeya KannanNo ratings yet
- Earth Loop Impedance and Prospective Short Circuit (PSC) Testing Methods - EE PublishersDocument2 pagesEarth Loop Impedance and Prospective Short Circuit (PSC) Testing Methods - EE PublishersRonak Rana100% (1)
- Philippine Electronics Code - Volume 1Document28 pagesPhilippine Electronics Code - Volume 1Ishimaru Thor100% (1)
- Grounding Methods and MeasurementDocument3 pagesGrounding Methods and MeasurementhotmailscribdNo ratings yet
- Philippine Electronics Code - Volume 1Document28 pagesPhilippine Electronics Code - Volume 1janaisha_bai7170100% (3)
- Philippine Electronics Code - Volume 1Document28 pagesPhilippine Electronics Code - Volume 1Eunice GeronaNo ratings yet
- "Fuse" "Earthing" "Short-Circuits"Document22 pages"Fuse" "Earthing" "Short-Circuits"Shalini YadavNo ratings yet
- Design of Electrical Power SystemsDocument36 pagesDesign of Electrical Power SystemsAhmed AwadenNo ratings yet
- L C R C L A e Y: Grounding SystemDocument45 pagesL C R C L A e Y: Grounding SystemAnonymous Jy6ASdQ45JNo ratings yet
- Tana 2018 Gruond LastDocument24 pagesTana 2018 Gruond LastTana AzeezNo ratings yet
- Earthing System: Presented By: Md. Noman Saber KhanDocument78 pagesEarthing System: Presented By: Md. Noman Saber Khansardarmkhan100% (2)
- Grounding System - NGRDocument22 pagesGrounding System - NGRChristopher WhitneyNo ratings yet
- Earthing SystemDocument25 pagesEarthing SystemVaneet Gupta100% (1)
- Eathing and Grounding 1 ProtectionDocument116 pagesEathing and Grounding 1 ProtectionAnees KhanNo ratings yet
- EarthingDocument10 pagesEarthingLionel Andreas ZweNo ratings yet
- Earth Potential RiseDocument5 pagesEarth Potential Risemyforum1No ratings yet
- Earthing PracticeDocument52 pagesEarthing PracticeSarah FrazierNo ratings yet
- Kosa Kata Dalam Bahasa Melayu Menjadi Asas Pembentukan Perpaduan Kaum - 2Document12 pagesKosa Kata Dalam Bahasa Melayu Menjadi Asas Pembentukan Perpaduan Kaum - 2Wendy TangNo ratings yet
- Concepts of EarthingDocument6 pagesConcepts of EarthingKonda SrinivasNo ratings yet
- System EarthingDocument43 pagesSystem EarthingaakashtrivediNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Earthing SystemsDocument4 pagesComparison of Earthing SystemsSiddesh RaneNo ratings yet
- Earthing and TestingDocument8 pagesEarthing and TestingTesfahun GirmaNo ratings yet
- Advice in Choosing The Right Neutral Earthing System For Your InstallationDocument10 pagesAdvice in Choosing The Right Neutral Earthing System For Your InstallationHaris MakrigiannakisNo ratings yet
- Protection TechnicalDocument44 pagesProtection TechnicalTarek MatarNo ratings yet
- Circuit Protection PrincipleDocument44 pagesCircuit Protection PrincipleNoli OtebaNo ratings yet
- GROUNDINGDocument43 pagesGROUNDINGmuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- Grounding Principles The Need To Ground: European American AustralianDocument10 pagesGrounding Principles The Need To Ground: European American Australianprasannakumar_rajaNo ratings yet
- Substation EarthingDocument5 pagesSubstation EarthingMidhun VargheseNo ratings yet
- Basics of Electrical Grounding Earthing and BondingDocument35 pagesBasics of Electrical Grounding Earthing and BondingSharad_B_Patel100% (3)
- Elec. PresnDocument50 pagesElec. Presnprovidence bizNo ratings yet
- The Earthing System: Sometimes Simply Called Earthing', Is The Total Set ofDocument10 pagesThe Earthing System: Sometimes Simply Called Earthing', Is The Total Set ofDaily FunNo ratings yet
- Civil Grounding System ReportDocument10 pagesCivil Grounding System ReportMessi ArabNo ratings yet
- Technical Notes - Earthed & Unearthed SystemDocument8 pagesTechnical Notes - Earthed & Unearthed SystemsiddharthangandhiNo ratings yet
- Ground Fault ProtectionDocument11 pagesGround Fault ProtectionJuan Espinoza100% (1)
- Safety AssignmentDocument2 pagesSafety AssignmentrhinoNo ratings yet
- Informe2 - Ing - ElectricaDocument24 pagesInforme2 - Ing - ElectricaCarlos Coral TaipeNo ratings yet
- Grounding System in Homes and BuildingsDocument4 pagesGrounding System in Homes and BuildingsCod Ry-angelNo ratings yet
- Special Ground Connection On Equipment and Metal StructuresDocument82 pagesSpecial Ground Connection On Equipment and Metal StructuresChRis dE LeonNo ratings yet
- What Is A ProtectionDocument54 pagesWhat Is A ProtectionmadhuNo ratings yet
- System Neutral EarthingDocument70 pagesSystem Neutral Earthingsorry2qazNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection For ESE ProposeDocument93 pagesPower System Protection For ESE ProposeYe GyiiiNo ratings yet
- Concepts of EarthingDocument9 pagesConcepts of EarthingJeya KannanNo ratings yet
- Earthing PracticesDocument58 pagesEarthing Practicessubbaiah54100% (1)
- Safety and Earthing DesignDocument61 pagesSafety and Earthing DesignEng-Al Raie SaadNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Earth ResistanceDocument12 pagesMeasurement of Earth ResistanceMuhammad Saif AmirNo ratings yet
- Power DistributionDocument46 pagesPower DistributionAdrian CamasosaNo ratings yet
- Earthing and LpsDocument32 pagesEarthing and LpsmohamedminnaNo ratings yet
- Earthing Concepts SummaryDocument9 pagesEarthing Concepts SummaryarinnotesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 & 15 System and Equipment EarthingDocument66 pagesLecture 14 & 15 System and Equipment Earthingmuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- Earthing Myths and FactsDocument67 pagesEarthing Myths and FactsPramode MishraNo ratings yet
- Earthing System - MaintenanceDocument22 pagesEarthing System - MaintenanceJuvencio Molina100% (1)
- 15.earthing TYPESDocument71 pages15.earthing TYPES16154996696No ratings yet
- Earthing System - Maintenance: Engineer Abid AzizDocument22 pagesEarthing System - Maintenance: Engineer Abid AzizTariq Mir100% (2)
- Power System Protection: Week-01Document63 pagesPower System Protection: Week-01faizanNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 4: Electromagnetic CompatibilityFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 4: Electromagnetic CompatibilityNo ratings yet
- Insulation Co-ordination in High-voltage Electric Power SystemsFrom EverandInsulation Co-ordination in High-voltage Electric Power SystemsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingFrom EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Notice Movidrive Compact MCF40ADocument64 pagesNotice Movidrive Compact MCF40AIván CascudoNo ratings yet
- Galleon One-RT-6-10K-manualDocument32 pagesGalleon One-RT-6-10K-manualevanilsonsantanaNo ratings yet
- r07320205 Switch Gear and ProtectionDocument6 pagesr07320205 Switch Gear and ProtectionandhracollegesNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Step and Touch PotentialDocument10 pagesCalculation of Step and Touch PotentialMeenakumari RamachandranNo ratings yet
- DEWA Instrumentation Cable SpecsDocument12 pagesDEWA Instrumentation Cable SpecsFlavioNo ratings yet
- I-Gard C-429em - Dsp-Ohmni - 2 - 12Document44 pagesI-Gard C-429em - Dsp-Ohmni - 2 - 12alvaro Lorca MoyaNo ratings yet
- Additional Design Documentation & Request For 11kV Services QuoteDocument3 pagesAdditional Design Documentation & Request For 11kV Services QuoteRonish ChandraNo ratings yet
- General Instruments SpecificationsDocument44 pagesGeneral Instruments Specificationsavinash1109No ratings yet
- Earthling System Electrical and Instruments Test ProcedureDocument23 pagesEarthling System Electrical and Instruments Test ProcedurejavadNo ratings yet
- Earth Fault Protection Guide 2022 Part 2Document54 pagesEarth Fault Protection Guide 2022 Part 2tomatoNo ratings yet
- FOX612 Installation 1KHW002462Document92 pagesFOX612 Installation 1KHW002462Netaxion CelularNo ratings yet
- Cahier Technique No 0: List and References of Cahiers Techniques Issued in EnglishDocument12 pagesCahier Technique No 0: List and References of Cahiers Techniques Issued in EnglisheliahudNo ratings yet
- PR Net NPL 001Document36 pagesPR Net NPL 001jaramib776No ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, and RCCBDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, and RCCBrod8silvaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Trade Theory N2: National CertificateDocument48 pagesElectrical Trade Theory N2: National CertificateAdriaan MyburghNo ratings yet
- Design of Wire Earth ReturnDocument77 pagesDesign of Wire Earth ReturnFredderick AzogueNo ratings yet
- MRJ4 Servo Manual PDFDocument580 pagesMRJ4 Servo Manual PDFĐỗ Tuấn BằngNo ratings yet
- SANS 3000-2!3!2008 - Railway Safety RegulatorDocument16 pagesSANS 3000-2!3!2008 - Railway Safety RegulatorBertus ChristiaanNo ratings yet
- Training Report 132/33 KV SubstationDocument42 pagesTraining Report 132/33 KV SubstationUmesh Kumar77% (30)
- Instruction ManualDocument276 pagesInstruction ManualSET SolucionesNo ratings yet
- Electrical Systems in A BuildingDocument30 pagesElectrical Systems in A Buildingpipeds100% (6)
- Antenna Feeder System InstallationDocument24 pagesAntenna Feeder System InstallationAbdul RahimNo ratings yet
- Schneider MV Design Guide Switchgear DefinitionDocument21 pagesSchneider MV Design Guide Switchgear DefinitionAdemEfeNo ratings yet
- LPI Earthing HandbookDocument68 pagesLPI Earthing Handbookgulatimanish1985No ratings yet
- Presentation Steca Solarix PliDocument27 pagesPresentation Steca Solarix PliMahalmadane ToureNo ratings yet
- Earthing Electrode CorporateDocument53 pagesEarthing Electrode CorporateRAVI KUMAR0% (1)
- Designing of HV Power Substation and LayoutDocument6 pagesDesigning of HV Power Substation and LayoutRagavanNo ratings yet
- Manual 9x55Document273 pagesManual 9x55Diego OrtizNo ratings yet
- Flair Catalogue FullDocument12 pagesFlair Catalogue FullEl Houcine KabdaNo ratings yet
- Aqua-Inverter ManualDocument32 pagesAqua-Inverter ManualmarcosNo ratings yet