Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Structure of Indian Money Market
Structure of Indian Money Market
Uploaded by
Subhendu Jana0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageOriginal Title
structure of indian money market
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageStructure of Indian Money Market
Structure of Indian Money Market
Uploaded by
Subhendu JanaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
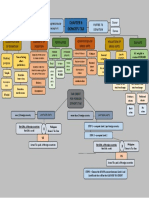
1.
Call Money Market:
o Deals in overnight funds lending and borrowing among banks and financial institutions.
o Regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to maintain liquidity and control short-term interest
rates.
2. Treasury Bills Market:
o Short-term government securities issued by the RBI to meet short-term financing needs.
o Available in three tenures: 91 days, 182 days, and 364 days.
o Mainly purchased by banks, financial institutions, and corporations.
3. Commercial Paper Market:
o Corporations issue unsecured short-term debt instruments to raise working capital.
o Maturities range from 7 days to 1 year.
o Provides companies an avenue to access short-term funds.
4. Certificate of Deposit Market:
o Banks and financial institutions issue time deposits with fixed maturities.
o Offered to individual and institutional investors.
o Enhances liquidity management and fund-raising for banks.
5. Repo and Reverse Repo Market:
o Involves the sale and repurchase of securities with a predetermined agreement.
o Repo: Used for short-term borrowing by banks and institutions.
o Reverse Repo: Used by investors to park excess funds temporarily.
6. Commercial Bills Market:
o Short-term credit instruments issued by businesses to meet working capital requirements.
o Typically bought and sold in secondary markets.
7. Money Market Mutual Funds (MMMFs):
o Investment funds that pool money to invest in money market instruments.
o Provides individuals and institutions with easy access to money market securities.
8. Foreign Exchange Market:
o Involves the exchange of one currency for another.
o Influences short-term interest rates and exchange rates.
9. RBI Operations:
o The Reserve Bank of India conducts Open Market Operations (OMOs) and Liquidity Adjustment
Facility (LAF) operations to manage liquidity and interest rates.
o Controls money supply and monetary policy.
10. Participants:
o Banks, financial institutions, corporations, mutual funds, NBFCs, and individual investors
participate in the money market.
o Each participant has specific roles in borrowing, lending, and investing.
11. Regulatory Framework:
o The RBI regulates and supervises the money market to ensure its smooth functioning.
o Sets guidelines for issuance, trading, and settlement of money market instruments.
12. Liquidity and Short-Term Focus:
o The money market is characterized by high liquidity and short maturities.
o Participants use money market instruments for short-term funding and liquidity management.
13. Interconnectedness with Other Markets:
o The money market is closely linked to the capital market and foreign exchange market.
o Movement in money market rates influences overall financial markets.
14. Risk Profile:
o Money market instruments are generally considered low-risk due to short-term nature and high
liquidity.
o Investors seek safety and stable returns in this market.
15. Role in Monetary Policy:
o The money market plays a vital role in the implementation of the central bank's monetary policy
objectives.
o Central bank actions affect money market rates and liquidity conditions.
You might also like
- Investment Banks Hedge Funds and Private Equity 3rd Edition Stowell Solutions ManualDocument6 pagesInvestment Banks Hedge Funds and Private Equity 3rd Edition Stowell Solutions Manualcourtneyvaughnkopeqrjwtd100% (20)
- Profit and LossDocument19 pagesProfit and LossVevianJavierCervantesNo ratings yet
- 5 SaaS+FinanceDocument47 pages5 SaaS+FinanceJay arNo ratings yet
- Money Market Participants & InstrumentsDocument24 pagesMoney Market Participants & InstrumentsManpreet SethiNo ratings yet
- Money Market InstrumentsDocument15 pagesMoney Market InstrumentsDharmendra Singh100% (1)
- CH 4 Money Market (Bharti Pathak)Document24 pagesCH 4 Money Market (Bharti Pathak)Mehak Ayoub0% (1)
- BFM Module C TREASURY MANAGEMENTDocument22 pagesBFM Module C TREASURY MANAGEMENTAnjuRoseNo ratings yet
- Progress Test QuestionsDocument11 pagesProgress Test QuestionsSophie ChopraNo ratings yet
- Features of Indian Money MarketDocument1 pageFeatures of Indian Money MarketSubhendu JanaNo ratings yet
- RM-C1: Unit - Xi: Treasury ManagementDocument16 pagesRM-C1: Unit - Xi: Treasury ManagementNikhila MuraleedharanNo ratings yet
- Money MarketDocument44 pagesMoney MarketReshma MaliNo ratings yet
- Arsh Advani - 1 Abhishek Dhariwal - 8 Pooja Jain - 17 Priyanka Majmundar - 32 Himanshu SanghviDocument14 pagesArsh Advani - 1 Abhishek Dhariwal - 8 Pooja Jain - 17 Priyanka Majmundar - 32 Himanshu SanghviArshAdvaniNo ratings yet
- Money MarketDocument8 pagesMoney MarketFaraz KhanNo ratings yet
- Kiran Gundaye (2029)Document55 pagesKiran Gundaye (2029)Kiran GundayeNo ratings yet
- Finance FatDocument28 pagesFinance Fatruchitac28No ratings yet
- Presentation On Indian Debt MarketDocument55 pagesPresentation On Indian Debt Marketpriya_12345632369100% (9)
- Ravindra A. Kamath: Document Name Version Number Approved by Approval Date Creator AudienceDocument44 pagesRavindra A. Kamath: Document Name Version Number Approved by Approval Date Creator AudienceRavindra A. KamathNo ratings yet
- Treasury ManagementDocument10 pagesTreasury ManagementSankar RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Money MarketDocument4 pagesMoney MarketivandimaunahannnNo ratings yet
- Money MarketDocument66 pagesMoney Marketchouhan.bharat849124No ratings yet
- 12 BST PDFDocument3 pages12 BST PDFAKHIL DuaNo ratings yet
- Money MarketDocument10 pagesMoney Marketswe1234No ratings yet
- Introduction of Financial MarketDocument11 pagesIntroduction of Financial Marketatul AgalaweNo ratings yet
- Name: Gundaye Kiran Pramod: Class: MMS Semester IIIDocument55 pagesName: Gundaye Kiran Pramod: Class: MMS Semester IIIKiran GundayeNo ratings yet
- FM ClipDocument16 pagesFM ClipNidhi SatvekarNo ratings yet
- Indian Economy by AshishDocument33 pagesIndian Economy by AshishBRAIN HUTNo ratings yet
- RBI - VI Sem B&F All FunctionsDocument10 pagesRBI - VI Sem B&F All FunctionsvinushriyuNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial System For BBADocument11 pagesIndian Financial System For BBARajat Pawan0% (2)
- Slide 1 (Definition) Yeye: Money MarketsDocument6 pagesSlide 1 (Definition) Yeye: Money MarketsCyeonjNo ratings yet
- Debt MarketsDocument46 pagesDebt MarketsDiv KabraNo ratings yet
- Indian Money MarketDocument72 pagesIndian Money MarketVinit RautNo ratings yet
- Financial SystemDocument32 pagesFinancial Systemneelabh1984No ratings yet
- The Foreign Exchange MarketDocument58 pagesThe Foreign Exchange MarketSHOBANA96No ratings yet
- Money MarketDocument16 pagesMoney MarketBelikovNo ratings yet
- Financial SystemDocument32 pagesFinancial Systemsaritasharma_sharmaNo ratings yet
- Money Market: Security Analysis and Portfolio ManagementDocument23 pagesMoney Market: Security Analysis and Portfolio Managementrahu007einstein56uNo ratings yet
- FM&BODocument17 pagesFM&BOvinaydevrukhkar2629No ratings yet
- BFM Module C SnapshotDocument8 pagesBFM Module C SnapshotVenkata Raman RedrowtuNo ratings yet
- Money Market InstrumentDocument30 pagesMoney Market Instrumentdont_forgetme2004No ratings yet
- Money MarketsDocument5 pagesMoney MarketsAbhay JoshiNo ratings yet
- MF0016 B1814 SLM Unit 02 PDFDocument18 pagesMF0016 B1814 SLM Unit 02 PDFBinnatPatelNo ratings yet
- CH 4 FMDocument13 pagesCH 4 FMTHRISHA JINKALANo ratings yet
- Money Market NotesDocument5 pagesMoney Market NotesNeelanjan MitraNo ratings yet
- Money MKT InstrDocument12 pagesMoney MKT Instrsagar77_lNo ratings yet
- Money MarketDocument34 pagesMoney MarketAshish TagadeNo ratings yet
- Assisgnment Forex BankingDocument17 pagesAssisgnment Forex BankingWaseem RajaNo ratings yet
- Money Market by TanishaDocument15 pagesMoney Market by TanishakirtikaNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument40 pagesFinancial Markets and InstitutionsAnZeerNo ratings yet
- Mgt-205: Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument78 pagesMgt-205: Financial Markets and InstitutionsBishal ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Money MarketsDocument27 pagesMoney MarketsMudabbir Azeez JamalNo ratings yet
- Money Market Simplified Easy PowerpointDocument17 pagesMoney Market Simplified Easy PowerpointNitin DawarNo ratings yet
- Study Notes - MMSDocument16 pagesStudy Notes - MMSAlok GoyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Research Methdology: Objective of The StudyDocument87 pagesChapter 1 - Research Methdology: Objective of The StudyRaman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Financial MarketsDocument7 pagesUnit-2 Financial MarketsArham JainNo ratings yet
- Call Money Market in IndiaDocument37 pagesCall Money Market in IndiaDivya71% (7)
- Money Market FinalDocument6 pagesMoney Market FinalPriyanka SharmaNo ratings yet
- Money Market InstrumentDocument40 pagesMoney Market InstrumentAkanksha ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Developing The Money Market in India: Dr. Muhammad ShafiDocument40 pagesDeveloping The Money Market in India: Dr. Muhammad ShafiPradeep KumarNo ratings yet
- The Indian Money Market: Prime AcademyDocument5 pagesThe Indian Money Market: Prime AcademyHardik KharaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ForexDocument10 pagesIntroduction To ForexVinit MehtaNo ratings yet
- BFM Treasury ManagementDocument11 pagesBFM Treasury ManagementH RajputNo ratings yet
- Role of Financial SystemDocument30 pagesRole of Financial SystemAhmed HabibNo ratings yet
- Marginal ProductivityDocument1 pageMarginal ProductivitySubhendu JanaNo ratings yet
- ANOVADocument1 pageANOVASubhendu JanaNo ratings yet
- Economics Module 2Document11 pagesEconomics Module 2Subhendu JanaNo ratings yet
- Data Analyst Vs Data SC Vs Data EngineerDocument2 pagesData Analyst Vs Data SC Vs Data EngineerSubhendu JanaNo ratings yet
- Strtegies For PLCDocument1 pageStrtegies For PLCSubhendu JanaNo ratings yet
- Techniques of Data Collection - BRMDocument2 pagesTechniques of Data Collection - BRMSubhendu JanaNo ratings yet
- Indusctrial Buying BehaviorDocument3 pagesIndusctrial Buying BehaviorSubhendu JanaNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument2 pagesProduct Life CycleSubhendu JanaNo ratings yet
- CB Vs IbDocument2 pagesCB Vs IbSubhendu JanaNo ratings yet
- Logic in Social ScienceDocument2 pagesLogic in Social ScienceSubhendu JanaNo ratings yet
- Distribution ChannelDocument2 pagesDistribution ChannelSubhendu JanaNo ratings yet
- Importance of Price in Marketing MixDocument1 pageImportance of Price in Marketing MixSubhendu JanaNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviorDocument2 pagesConsumer BehaviorSubhendu JanaNo ratings yet
- Management - Science, Theory & PracticeDocument30 pagesManagement - Science, Theory & PracticeSubhendu JanaNo ratings yet
- HMRCDocument22 pagesHMRCSubhendu JanaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Advanced Accounting 13Th Edition Beams Anthony Bettinghaus Smith 0134472144 9780134472140 Full Chapter PDFDocument30 pagesSolution Manual For Advanced Accounting 13Th Edition Beams Anthony Bettinghaus Smith 0134472144 9780134472140 Full Chapter PDFrose.carvin242100% (11)
- 26 - 27. IGCSE - Business Studies - Marketing Mix and Marketing Strategy - AssignmentDocument4 pages26 - 27. IGCSE - Business Studies - Marketing Mix and Marketing Strategy - Assignmentdung luongtuanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern World Reviewer.Document1 pageMathematics in The Modern World Reviewer.chrae0913No ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad WarningDocument2 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad WarningAbdullah ShahNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument17 pagesUntitledRonit SonawaneNo ratings yet
- ValuationDocument37 pagesValuationAJ SinghNo ratings yet
- 0450 - 1.5 Business Objectives and Stakeholder ObjectivesDocument11 pages0450 - 1.5 Business Objectives and Stakeholder ObjectivesCherylNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis AnswerDocument2 pagesRatio Analysis AnswerGenner RazNo ratings yet
- Price Ceiling Worksheet ANSWERSDocument3 pagesPrice Ceiling Worksheet ANSWERSAndrew WalkerNo ratings yet
- Age of Easy Money - FRONTLINE - TranscriptDocument85 pagesAge of Easy Money - FRONTLINE - TranscriptThe RearrangerNo ratings yet
- Future of Fintech CompaniesDocument8 pagesFuture of Fintech Companiesgaju619No ratings yet
- Operations Management For Mbas 5th Edition Meredith Test BankDocument25 pagesOperations Management For Mbas 5th Edition Meredith Test BankTonyaWilliamswejr100% (43)
- Midterm Examination 2Document5 pagesMidterm Examination 2Timbas TNo ratings yet
- Bep Problems Unit 2Document29 pagesBep Problems Unit 2CHENNAKESAVA MAMILLANo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Investments Concepts and Applications 5th Edition Heaney Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Investments Concepts and Applications 5th Edition Heaney Test Bank PDFbenlmkgray100% (10)
- Concept Map-Chap6Document1 pageConcept Map-Chap6Evonie Amor Arcillas HueteNo ratings yet
- Partnership DissolutionDocument8 pagesPartnership DissolutionEmmanNo ratings yet
- Installment SalesDocument2 pagesInstallment SalesadieNo ratings yet
- Financial Theory and Corporate Policy Copeland 4th Edition Solutions ManualDocument4 pagesFinancial Theory and Corporate Policy Copeland 4th Edition Solutions ManualShawnStewartadsb100% (36)
- Banking Awareness Mcqs PDF: Question:-1Document8 pagesBanking Awareness Mcqs PDF: Question:-1Ankit PradhanNo ratings yet
- Mmu Online Mba Syllabus For SpecializationsDocument5 pagesMmu Online Mba Syllabus For SpecializationsVimalesh YadavNo ratings yet
- 1922 B.com B.com Batchno 247Document66 pages1922 B.com B.com Batchno 247Mukesh SoniNo ratings yet
- About Us: WWW - Gupshup.ioDocument2 pagesAbout Us: WWW - Gupshup.ioSwati ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Chap 3Document29 pagesChap 3kimngan.nguyen8803No ratings yet
- 2nd Grading Exam-EntrepDocument4 pages2nd Grading Exam-EntrepronaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Operations and Supply Chain Management 13th Edition Jacobs Test BankDocument36 pagesFull Download Operations and Supply Chain Management 13th Edition Jacobs Test Bankpierswinkleblack100% (40)