Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Knowledge Organiser 2.3
Uploaded by
Moises SantosCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Knowledge Organiser 2.3
Uploaded by
Moises SantosCopyright:
Available Formats
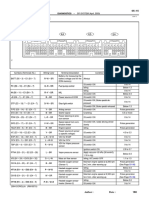
Subject: Economics Topic: Productive efficiency Year Group: 12
What is productivity? Why is productivity important? Ways to increase capacity
Consequences of working at full
Productivity measures the efficiency with which Lower unit costs: These cost savings might
be passed onto consumers in lower prices,
utilisation capacity
inputs are converted into outputs. encouraging higher demand, more output 1 Production is rushed
Increase workforce hours – Staff could be encourage to
and an increase in employment. work overtime or temporary staff could be employed
Labour productivity for example measures the 2 Less time for quality control
output per worker per hour (or per day, per Improved competitiveness and trade thus increasing the businesses current output.
performance: Productivity growth and 3 Added workloads & stress
month, etc)
lower unit costs are key determinants of Outsource some of production – by outsourcing some
4 De-motivating if sustained
Capital productivity would measure the output the competitiveness of firms in global of the production process it allows the business to
markets. for too long
per machine per period of time increase its current output.
Higher profits: Efficiency gains are a source 5 Less able to meet sudden or
of larger profits for companies which unexpected increases in
How is productivity might be re-invested to support the long demand
term growth of the business.
Reduce machine maintenance – This will reduce the
calculated? time at which machines are not producing goods. 6 Production equipment may
Higher wages: Businesses can afford Therefore, although it may be unsustainable, in the require repair
Productivity = total output / total input higher wages when their workers are more
efficient.
short run output will increase.
Let's say your company generated £80,000 Economic growth: If an economy can raise
worth of goods or services (output) utilizing the rate of growth of productivity then the
1,500 labour hours (input). To calculate your trend growth of national output can pick
company's labour productivity, you would divide up. Consequences of working under capacity
80,000 by 1,500, which equals 53. Productivity improvements mean that
labour can be released from one industry 1 Inefficiency – By not producing at maximum capacity it may mean that the
and be made available for another – for business is unable to full exploit economies of scale. As a result of this, the
What is capacity utilisation? example, rising efficiency in farming will business is likely to experience an increase in their average costs.
increase production yields and provide
Capacity utilisation is a measure of the extent to more food either to export or to supply a 2 Flexibility – By not producing at full capacity it allows the business some slack. This
which the productive capacity of a business is growing urban population. means that if new or unexpected orders were to be demanded the business would
being used. If the size of the economy is bigger, higher be able to increase their current output and match the increase in demand.
wages will boost consumption, generate 3 Loss of market share – If the business is operating at less than full capacity then it
Capacity utilisation can be calculated by : Actual more tax revenue to pay for public goods
output / maximum output x 100 is likely to result in a reduction in the sales of the business. As a result of this, their
and perhaps give freedom for tax cuts on
people and businesses. percentage market share is likely to decrease.
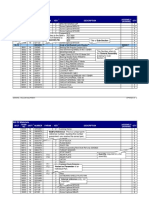
Subject: Economics Topic: Productive efficiency Year Group: 12
Lean production strategies
Ways to increase Ways of improving capacity Lean production
1 Quality control refers to the traditional method of
capacity utilisation utilisation: checking that products are of a good enough 1Lean production is about minimising waste at
standard. Inspection of products takes place during every stage of production or service delivery to
Increase workforce hours – Competitors exiting the market – This is likely to result and at the end of the operations process. minimise costs. Various strategies are used in lean
Staff could be encouraged to in an increase in demand for the current business’s production, most of which are now commonly
goods/ services. This is because customers of 2 Quality assurance (QA) implies a commitment to used in manufacturing.
work overtime or temporary collaboration between the
competitors that have exited the market will switch
staff could be employed thus over to businesses that are still in the market. This will people responsible for design, production and
increasing the businesses allow the business to increase its current output in marketing. They will work
current output. order to match the increase in demand. As a result of together towards increased quality and reliability. Competitive advantage from lean
this it is likely to improve their percentage of capacity Everyone in the business has production
Outsource some of production utilisation,
to become more aware of the need for quality.
– by outsourcing some of the A reduction in costs, which may allow firms to
3 Total Quality Management (TQM) is a philosophy
Balancing seasonal demand – Businesses could balance spend more on product development or
production process it allows that tries to generate both an
their seasonal demand by reducing their inputs e.g. marketing or can allow the firm to reduce prices
the business to increase its individual and a collective responsibility for quality
which, depending on PED for the product, could
staff in periods of low demand then increasing them at every level. Each
current output. again when demand increases. This will cause potential increase market share and sales
department or team is seen as having responsibility
output to fall as current output does (low demand) and revenue for the firm.
Reduce machine maintenance for quality in both products
• Improved quality and therefore greater
potential output to increase as current output does and services.
– This will reduce the time at customer satisfaction.
(high demand). This will allow the business to work at a
which machines are not higher percentage of capacity utilisation throughout 4 Kaizen is a Japanese word meaning ‘continuous • Labour becomes more involved, therefore
producing goods. Therefore, improvement’ and it emphasises getting things right more motivation and less staff
the year.
first time. turnover.
although it may be
Improved marketing – By increasing marketing when in
unsustainable, in the short run 6 Just in time (JIT) is simply an application of lean
periods of low demand, it is likely to result in an
output will increase. increase in demand. This will help to increase current
production to stock control.
output thus increasing the percentage of capacity that
The JIT process focuses on frequent reordering of Impact on costs and sales revenue
relatively small quantities of
is being utilised. stock thus reducing the costs of holding stock and Any steps a firm takes to increase productivity can
relies on a strong working serve to reduce average unit costs. This can result in
higher profits which may be re-invested to further
relationship between a firm and its suppliers.
Labour intensive vs capital intensive improve efficiency or in product development.
A labour-intensive business is one in which the business Capacity utilisation Firm may develop a growing reputation for quality and
hence see an increase in sales revenue
utilises a lot of labour in its production process Capacity utilisation is a measure of the extent to which the
productive capacity of a business is being used. Reduced lead times (the time delay between making a
A capital-intensive business is one in which the business decision and implementing the decision) may make a
employs a greater proportion of capital relative to other Capacity utilisation can be calculated by : Actual output / firm more market orientated.
inputs in the production process maximum output x 100
You might also like
- The Profit Zone (Review and Analysis of Slywotzky and Morrison's Book)From EverandThe Profit Zone (Review and Analysis of Slywotzky and Morrison's Book)No ratings yet
- Production PlanningDocument11 pagesProduction PlanningDiana Camily Mesias BahamondeNo ratings yet
- Key Term: 1 Business Organisation and EnvironmentDocument1 pageKey Term: 1 Business Organisation and EnvironmentLissa MontielNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Definitions 1Document1 pageMicroeconomics Definitions 1070_tomNo ratings yet
- Economics, 19th Edition by Samuelson, ReviewerDocument13 pagesEconomics, 19th Edition by Samuelson, ReviewerDo Kyungsooooo100% (1)
- Business Studies Production Year 11Document35 pagesBusiness Studies Production Year 11Juliser DublasNo ratings yet
- Eritriya Mam's NotesDocument12 pagesEritriya Mam's NotesAbhimanyuNo ratings yet
- Captura de Pantalla 2023-06-21 A La(s) 13.43.19Document57 pagesCaptura de Pantalla 2023-06-21 A La(s) 13.43.19Molly WeasleyNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Business Edxcel NotesDocument18 pagesIGCSE Business Edxcel NotesYasmin YehiaNo ratings yet
- BusinessDocument16 pagesBusinessRoaa EidNo ratings yet
- Capacity & Economies of ScaleDocument26 pagesCapacity & Economies of ScaleOckouri BarnesNo ratings yet
- Capacity UtilisationDocument21 pagesCapacity UtilisationTyler IlesNo ratings yet
- The Production ProcessDocument4 pagesThe Production ProcessOh MyNo ratings yet
- Principles of Business: Topic: ProductionDocument31 pagesPrinciples of Business: Topic: ProductionMujah ClarkeNo ratings yet
- Efficiency Production & Operations: Production Efficiency: ProductivityDocument1 pageEfficiency Production & Operations: Production Efficiency: Productivityapi-110990005No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document4 pagesChapter 7Melody BautistaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Uts Aggregate Planning - Nadira LaksitaDocument12 pagesTugas Uts Aggregate Planning - Nadira LaksitaMahdi Latief DamsirNo ratings yet
- 23 The Nature of Operations ASCNDocument12 pages23 The Nature of Operations ASCNKalsoom SoniNo ratings yet
- 7 The Production ProcessDocument4 pages7 The Production ProcessOh MyNo ratings yet
- Economies of ScaleDocument2 pagesEconomies of ScaleKharaKarisiaDimpudusNo ratings yet
- Production of Goods & ServicesDocument35 pagesProduction of Goods & ServicesShahannah DOOKHAN100% (1)
- Efficiency: Vesile Gaye ÖZGENCİL 2009503075 Industrial Engineering DepartmentDocument26 pagesEfficiency: Vesile Gaye ÖZGENCİL 2009503075 Industrial Engineering DepartmentNabiha AzadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Operations Management AS and A LevelDocument43 pagesChapter 4 Operations Management AS and A LevelLiam NyakudyaNo ratings yet
- Theoriy of ProductionDocument8 pagesTheoriy of ProductionArnab PaulNo ratings yet
- 3 6+firms+and+productionDocument19 pages3 6+firms+and+productionZati Zhafarina Che RazaliNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Operations Lesson 1 & 2Document12 pagesThe Nature of Operations Lesson 1 & 2Koshla RentonNo ratings yet
- Ekonomi Bisnis: Materi 2 Matrikulasi Ekonomi Bisnis & Manajerial MMSI Univ. Gunadarma 2007-2008Document26 pagesEkonomi Bisnis: Materi 2 Matrikulasi Ekonomi Bisnis & Manajerial MMSI Univ. Gunadarma 2007-2008Shucy SihombingNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics: Activity # 7Document9 pagesManagerial Economics: Activity # 7Vienna MamarilNo ratings yet
- OMGT 1013 Module 8Document8 pagesOMGT 1013 Module 8Maria YelleNo ratings yet
- Assessing A Change in Scale : Unit 9-Strategic Methods - How To Pursue StrategiesDocument10 pagesAssessing A Change in Scale : Unit 9-Strategic Methods - How To Pursue StrategiesOlu MichaelNo ratings yet
- Danshui Plant No. 2Document10 pagesDanshui Plant No. 2AnandNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Business Studies 0450 Theory v1Document47 pagesCaie Igcse Business Studies 0450 Theory v1smNo ratings yet
- 2 Mo-EanDocument2 pages2 Mo-EanEnny NguyenNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Production of Goods and ServicesDocument8 pages4.1 Production of Goods and Servicesgeneva conventionsNo ratings yet
- AS Business Unit 4 Production HandoutDocument19 pagesAS Business Unit 4 Production HandoutUrafa NoamanNo ratings yet
- A-Levels Business Studies - Unit 4, NotesDocument12 pagesA-Levels Business Studies - Unit 4, NotesRafay Mahmood88% (8)
- Long Run Production Function & Economies of ScaleDocument14 pagesLong Run Production Function & Economies of ScaleAbhi0669No ratings yet
- Operations Management Methods of Production: Advantages DisadvantagesDocument27 pagesOperations Management Methods of Production: Advantages Disadvantagesincomingimprint BRNo ratings yet
- Economies of ScaleDocument3 pagesEconomies of ScaleEthan-Dale BrownNo ratings yet
- 4.1 - Production of Goods and Services - IGCSE AIDDocument1 page4.1 - Production of Goods and Services - IGCSE AIDAdam NoorNo ratings yet
- ProductivityDocument6 pagesProductivityAk AlNo ratings yet
- Economies of Scale and Diseconomies of ScaleDocument22 pagesEconomies of Scale and Diseconomies of ScaleHafizul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.6. Growth and Evolution (Notes)Document9 pagesChapter 1.6. Growth and Evolution (Notes)S RameshNo ratings yet
- Cambridge A-Level Business - CHP 25Document15 pagesCambridge A-Level Business - CHP 25SitayeshNo ratings yet
- Micro - Economies and Diseconomies of ScaleDocument9 pagesMicro - Economies and Diseconomies of ScaleTanvi ShahNo ratings yet
- The Theory of The FirmDocument23 pagesThe Theory of The FirmEj MacadatuNo ratings yet
- Eco Dev Chapter 3 - Growth and The Asian ExperienceDocument69 pagesEco Dev Chapter 3 - Growth and The Asian ExperienceAlyssaNo ratings yet
- Growth and EvolutionDocument5 pagesGrowth and EvolutionVeronika RaichevaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Cost and ProfitsDocument17 pagesTheory of Cost and ProfitsLyn Mae GonzalesNo ratings yet
- SC T9Document28 pagesSC T9Zi En AngNo ratings yet
- Management Advisory Services-Ho1Document4 pagesManagement Advisory Services-Ho1kehlaniNo ratings yet
- Capacity and Location PlanningDocument5 pagesCapacity and Location PlanningJoana TorresNo ratings yet
- Delivering Long Term Value in e and PDocument24 pagesDelivering Long Term Value in e and PTekena FubaraNo ratings yet
- Capacity PlanningDocument21 pagesCapacity PlanningAvi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 EconomicsDocument3 pagesChapter 21 EconomicsJanvi JainNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Economies of Scale in Large BusineDocument7 pagesDeterminants of Economies of Scale in Large BusineRudi IryantoNo ratings yet
- Past Papers (9-3-2021)Document2 pagesPast Papers (9-3-2021)May OsmanNo ratings yet
- Cbme - Midterm-Examination-Reviewer EditedDocument7 pagesCbme - Midterm-Examination-Reviewer EditedGemini LibraNo ratings yet
- 003 03economicDocument5 pages003 03economiceyoboldairNo ratings yet
- Youth Camp Registration Form-2022Document1 pageYouth Camp Registration Form-2022FlerkNo ratings yet
- BITS Pilani: Determination of Extreme Pressure, Wear Preventive Characteristics of Lubricants Using Four Ball TesterDocument10 pagesBITS Pilani: Determination of Extreme Pressure, Wear Preventive Characteristics of Lubricants Using Four Ball Testerakash chNo ratings yet
- RD Sharma Class8 SolutionsDocument2 pagesRD Sharma Class8 Solutionsncertsoluitons100% (2)
- Colour FastnessDocument37 pagesColour FastnessSivakumar K100% (1)
- SOPDocument16 pagesSOPjerome marquezNo ratings yet
- Cold Regions Science and TechnologyDocument8 pagesCold Regions Science and TechnologyAbraham SilesNo ratings yet
- Vanish Magic Magazine VANISH MAGIC MAGAZINE 58 May 2019Document118 pagesVanish Magic Magazine VANISH MAGIC MAGAZINE 58 May 2019mick byrnes100% (1)
- EXAMPLE 8.6 Veneer Grades and RepairsDocument2 pagesEXAMPLE 8.6 Veneer Grades and RepairsnickNo ratings yet
- ARK - Intel® Core™ I3-370m Processor (3M Cache, 2Document3 pagesARK - Intel® Core™ I3-370m Processor (3M Cache, 2Delzi Guindra AdriNo ratings yet
- CulvertsDocument18 pagesCulvertsAmmar A. Ali100% (1)
- Types of Loads Considered For Design of BridgeDocument45 pagesTypes of Loads Considered For Design of BridgeAbhishek100% (1)
- Sample Appellant BriefDocument6 pagesSample Appellant BriefKaye Pascual89% (9)
- LinkageDocument9 pagesLinkageHarshu JunghareNo ratings yet
- Bulk Material/Part Ppap Process Checklist / Approval: Required?Document32 pagesBulk Material/Part Ppap Process Checklist / Approval: Required?krds chidNo ratings yet
- Coding DecodingDocument21 pagesCoding DecodingAditya VermaNo ratings yet
- c270 KW NTA855G2 60 HZDocument31 pagesc270 KW NTA855G2 60 HZAhmad El KhatibNo ratings yet
- Terminals of Ecm: E3 E4 E5 E6Document2 pagesTerminals of Ecm: E3 E4 E5 E6jeremih alhegn100% (1)
- Asme Code Sec Ix Ma Appe 2004Document3 pagesAsme Code Sec Ix Ma Appe 2004Guillermo CamachoNo ratings yet
- Volvo Penta GensetDocument4 pagesVolvo Penta GensetafandybaharuddinNo ratings yet
- Quartile1 PDFDocument2 pagesQuartile1 PDFHanifah Edres DalumaNo ratings yet
- Javanese PeopleDocument22 pagesJavanese PeopleDenisaNo ratings yet
- The Spirit Controlled Life Ebook PDF 1Document184 pagesThe Spirit Controlled Life Ebook PDF 1Okesola AbayomiNo ratings yet
- Bravo MRI II Operation ManualDocument45 pagesBravo MRI II Operation ManualLuis100% (1)
- 2017 Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. Decision Making Algorithms For Clinical PracticeDocument40 pages2017 Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. Decision Making Algorithms For Clinical PracticebbNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Páginas-509-580Document72 pagesMaintenance Páginas-509-580Alexandra Gabriela Pacheco PrietoNo ratings yet
- Atomic St. Package PDFDocument28 pagesAtomic St. Package PDFSatvik RaoNo ratings yet
- BIO 201 Chapter 11 LectureDocument34 pagesBIO 201 Chapter 11 LectureDrPearcyNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Diabetic FootDocument7 pagesAssessment of Diabetic FootChathiya Banu KrishenanNo ratings yet
- Influence of Aesthetics Attributes of Brand Web Pages On Customer Brand EngagementDocument22 pagesInfluence of Aesthetics Attributes of Brand Web Pages On Customer Brand EngagementNOOR AKMA AIDANo ratings yet
- ASME Pressue Vessel ExampleDocument271 pagesASME Pressue Vessel ExamplesavanchandranNo ratings yet