Notes in Physics for Engineers/m.a.
de salit
ELECTRIC POTENTIAL ENERGY and ELECTRIC POTENTIAL
Electrical Potential Energy
Electric potential energy is similar to gravitational potential energy – both involve field forces.
Analogy:
In a Gravitational field In an Electric field
- Energy is required to move an object against its - Movement of a positive test charge within an
gravitational field electric field is accompanied by changes in PE
- Objects naturally move from high PE under the - Going against nature requires work by an
influence of field force external force
-Work must be done to move an object against - Work would increase PE
nature
Electrical Potential Energy (U)
- is potential energy associated with a charge due to its position in an electric field.
The potential energy of a system of two point charges:
If more than two charges are present, get the sum of the energies of every pair of two charges
that are present to get the total potential energy.
for 3 charges
� Notes in Physics for Engineers/m.a. de salit
If the charges have the same sign, PE is positive
→ Positive work must be done to force the two charges near one another
→ The like charges would repel
If the charges have opposite signs, PE is negative
→The force would be attractive
→Work must be done to hold back the unlike charges from accelerating as they are
brought close together
Electric Potential
the amount of work needed to move a unit charge from a reference point to a specific point
against an electric field
also called potential difference or voltage.
the potential energy per unit charge in an electric field
Thus; 1 volt (V) = 1 Joule (J) / Coulomb (C)
*Notes:
- Electric potential is a scalar quantity
- the sign of V is the same as the sign of q
- a positively charged particle produces a positive electric potential and a negatively charged particle
produces a negative electric potential
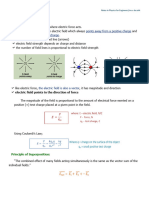
POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TWO POINTS
the potential difference V between two points in a uniform electric field E is equal to the product
of E and the distance r between the points in a direction parallel to E.
� Notes in Physics for Engineers/m.a. de salit
PROBLEMS/EXERCISES:
1. If a charge of magnitude 6.5 x 10-17 C is being held in place 2.0 x 10-8m from a charge of
- 8 x 10-19 C which is also being held in place, what is the electric potential energy of the system?
2. Find the electrical potential energy U for the array of three charges located at the vertices of an
equilateral triangle with side 12.5 m. q1 = +8 µC , q2 = q3 = - 9 µC
� Notes in Physics for Engineers/m.a. de salit
3. A potential difference of 10.0 volts exists between two points, A and B, within an electric field.
What is the magnitude of charge that requires 2.0 × 10–2 joule of work to move it from A to B?
4. Calculate the electric potential of q1 = 25.0 nC at (a) 1.00m, (b) 2.00m, and (c) infinite long
distance from it.
� Notes in Physics for Engineers/m.a. de salit
5. Three point charges are fixed in place as shown in the figure below. (a) Determine the electric
potential at point P (assuming V = 0 at infinity). (b) How much electric potential energy would an
electron placed at point P have? (4.6 x 105 V, -7.4 x 10-14J)
� Notes in Physics for Engineers/m.a. de salit
Try to solve:
6. Calculate the electric potential (a) at point A in the figure below due to charges shown and (b) at
point B
( Answer: 7.5 x 105V, 0)
5. A manufacturer claims that a carpet will not generate more than 5.0 kV of static electricity. What
magnitude of charge would have to be transferred between a carpet and a shoe for there to be a 5.0
kV potential difference between the shoe and the carpet, approximating the shoe and the carpet as
large sheets of charge separated by a distance of 1.0 mm?
( Answer: 1.1 x 10-6 C)