Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2
2
Uploaded by
Siow Shi XianCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2
2
Uploaded by
Siow Shi XianCopyright:
Available Formats
3/6/24, 8:41 AM Platform | Study Fetch
Functional Groups and Polymers
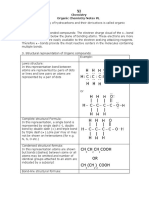
Functional groups add chemical character to carbon chains (Paragraph 1)
- Functional groups are groups of one or more atoms that have particular chemical properties regardless of what
they are attached to
- Common functional groups include:
- Amine (=NH)
- Amino (-NH2)
- Carboxyl (-COOH)
- Hydroxyl (-OH)
- Ketone (=O)
- Phosphate (-O-PO3H2)
- Sulfhydryl (-SH)
- Methyl (-CH3)
- Nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and sulfur atoms in functional groups are more electronegative than carbon
- Functional groups containing these atoms are polar
- Methyl group is nonpolar
Functional groups impact molecule polarity and solubility (Paragraph 2)
- Molecules containing polar functional groups become polar even if the carbon chain is nonpolar
- Polar molecules are soluble in aqueous environments like cells
- Polar molecules disperse throughout the cell
- Many functional groups are polar and reactive
- Reactions joining simpler molecules into polymers usually occur between functional groups
Proteins (Paragraph 3)
- Proteins do much of the cell's work as enzymes and structural components
- Enzymes accelerate chemical reaction rates
- Structural proteins provide cell shape and movement
- The human body contains thousands of distinct protein types performing diverse functions
- Proteins consist of amino acids covalently linked into chains
- Amino acid chemical features determine protein diversity and versatility
https://www.studyfetch.com/platform/studyset/65e7b8ed25d36a738a282618/material/65e7b941344c323a3b32fa6b/document 1/1
You might also like
- CHAPTER 4: Carbon - The Backbone of Biological MoleculesDocument1 pageCHAPTER 4: Carbon - The Backbone of Biological MoleculesClaire FilipekNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 A+ ss1 ProteinsDocument30 pagesLec 1 A+ ss1 Proteinsapi-287606445No ratings yet
- CH 4 Carbon and Molecular Diversity of LifeDocument3 pagesCH 4 Carbon and Molecular Diversity of Lifewil7ver100% (1)
- AcidsDocument7 pagesAcidsKelbzNo ratings yet
- OCR A-Level Basic Concepts and HydrocarbonsDocument20 pagesOCR A-Level Basic Concepts and HydrocarbonsWilliam TsuiNo ratings yet
- PART-1 - IUPAC Nomenclature of Saturated Hydrocarbons - AlkaneDocument17 pagesPART-1 - IUPAC Nomenclature of Saturated Hydrocarbons - AlkaneSankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Detailed Notes Topic 6 Organic Chemistry I Edexcel Chemistry A LevelDocument29 pagesDetailed Notes Topic 6 Organic Chemistry I Edexcel Chemistry A LevelttjjjNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Module Q2Week 7 8Document23 pagesGen Chem Module Q2Week 7 8Dan MacabingilNo ratings yet
- Module 9Document29 pagesModule 9Andrew Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- BiochimieDocument11 pagesBiochimieecosysNo ratings yet
- Theme 1 - Nature of Organic CompoundsDocument48 pagesTheme 1 - Nature of Organic CompoundsSiphelele SimelaneNo ratings yet
- In Nature Nothing Is Created, Nothing Is Lost, Everything ChangesDocument47 pagesIn Nature Nothing Is Created, Nothing Is Lost, Everything Changesboopathi_chemist3628No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - FundamentalsDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistry - FundamentalsMRUDULA HANNA REJINo ratings yet
- Introductory Organic Chemistry and AlkanesDocument15 pagesIntroductory Organic Chemistry and AlkanesBara' HammadehNo ratings yet
- 1.01 Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument6 pages1.01 Introduction To Organic ChemistryJackson NawezhiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - An Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument29 pagesChapter 14 - An Introduction To Organic ChemistrySahana KumarNo ratings yet
- CHM 112 Note On Functional Group Class and Nomen of Organic Compound - 2021Document28 pagesCHM 112 Note On Functional Group Class and Nomen of Organic Compound - 2021teamtruth50No ratings yet
- Bio Chem 1Document9 pagesBio Chem 1Darren ClemniansNo ratings yet
- Overview PDFDocument160 pagesOverview PDFJoy Mazo FaderagaoNo ratings yet
- Biology 109: Lab Handouts ($15) - Available in Biology Office - KC 231Document67 pagesBiology 109: Lab Handouts ($15) - Available in Biology Office - KC 231ronan2890No ratings yet
- Questions and Answers To Some Introductory Anatomy & Physiology QuestionsDocument4 pagesQuestions and Answers To Some Introductory Anatomy & Physiology Questionsskaliwigs16No ratings yet
- Functional FgroupDocument35 pagesFunctional FgroupAbdullah AmjadNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistryapi-233187566No ratings yet
- SCI4ASSDocument3 pagesSCI4ASSyimlurimlaNo ratings yet
- Organic Molecules Essential To LifeDocument4 pagesOrganic Molecules Essential To LifeEj AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Prelim, Chem.b.life. PPT 2Document27 pagesPrelim, Chem.b.life. PPT 2Lindley PareñoNo ratings yet
- Chem Notes 2Document12 pagesChem Notes 2Joanna PareñasNo ratings yet
- Natsci 02Document2 pagesNatsci 02Sofia Coleen Naluaran TemplonuevoNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules PDFDocument11 pagesMacromolecules PDFChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Biology Test 1 Review Chapters 3-6 Proteins, Nucleic Acids, Carbohydrates, Lipids + Review of Basic Biological ChemistryDocument7 pagesBiology Test 1 Review Chapters 3-6 Proteins, Nucleic Acids, Carbohydrates, Lipids + Review of Basic Biological ChemistryChad SinghNo ratings yet
- Anatomy CHP 2 Basic ChemistryDocument10 pagesAnatomy CHP 2 Basic ChemistryChristine Jenkins SimsNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: 1. Organic Chemistry Is The Study of Carbon CompoundsDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistry: 1. Organic Chemistry Is The Study of Carbon Compoundsreadsalot2012No ratings yet
- An Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument6 pagesAn Introduction To Organic ChemistrylettyNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument5 pagesAn Introduction To Organic ChemistryahumanbeinginearthNo ratings yet
- Bio Unit 3 Bioenergetics Unit PlanDocument6 pagesBio Unit 3 Bioenergetics Unit Planapi-376095456100% (1)
- 11 ChemistryDocument10 pages11 ChemistryABHISHEK SINGH THAKURNo ratings yet
- Chemical Basis of LifeDocument38 pagesChemical Basis of LifeFernadez RodisonNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document47 pagesModule 2Saalif RahmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Functional GroupsDocument25 pagesUnit 3 Functional GroupsrecopelacionanjayleNo ratings yet
- 1610assignment 1 ListDocument7 pages1610assignment 1 Listapi-341205347No ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Chem Notes Anil CH 12. Organic Chemistry Some Basic ConceptsDocument19 pagesHsslive Xi Chem Notes Anil CH 12. Organic Chemistry Some Basic ConceptsKrishnendu NairNo ratings yet
- Topic 2Document25 pagesTopic 2Talia Elan VickeryNo ratings yet
- Handouts in BiochemDocument46 pagesHandouts in BiochemJobeth MurcillosNo ratings yet
- Kimia Karbon Dan PolimerDocument12 pagesKimia Karbon Dan PolimerD'the QuiintLy MaskatNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument43 pagesNotesRubilyn OlaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: The Chemical Building Blocks of Life: Enantiomers . These Are Mirror Images of Each Other. MirroredDocument17 pagesChapter 3: The Chemical Building Blocks of Life: Enantiomers . These Are Mirror Images of Each Other. Mirroredapi-524244445No ratings yet
- Enzyme NomenDocument4 pagesEnzyme NomenSesilia Ursula EvalinatyNo ratings yet
- 8: A Classification of Linear Single-Strand Polymers (1988) : Rule 1.1Document11 pages8: A Classification of Linear Single-Strand Polymers (1988) : Rule 1.1swaroop_exlncNo ratings yet
- Chemistry s5 Full NoteDocument383 pagesChemistry s5 Full NotebravebahiziNo ratings yet
- Intro To Organic Chemistry PDFDocument64 pagesIntro To Organic Chemistry PDFYuen Kim100% (1)
- Chemistry For Engineers 4Document32 pagesChemistry For Engineers 4Audrey VicenteNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Chemistry Class NotesDocument44 pagesGrade 11 Chemistry Class NotesFurret MasterNo ratings yet
- Orgchem Module Edit 2Document74 pagesOrgchem Module Edit 2Nur-aine HajijulNo ratings yet
- 11chemistry - Organic chemistry-Notes&VLDocument14 pages11chemistry - Organic chemistry-Notes&VLPrashant SinghNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and Techniques - WatermarkDocument29 pagesOrganic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and Techniques - WatermarkPrathviraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Structural IsomerismDocument3 pagesStructural IsomerismKimberly IgbalicNo ratings yet
- Module 1. The Chemistry of Carbon Compounds TOPIC: Structure and FormulaeDocument38 pagesModule 1. The Chemistry of Carbon Compounds TOPIC: Structure and FormulaeOrlanda EllisNo ratings yet
- A-level Sciences Revision Boxset: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Sciences Revision Boxset: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeFrom EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNo ratings yet