Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Release 2004
Release 2004
Uploaded by
jhbmlee0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views106 pagesAP physics
Original Title
Release_2004
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAP physics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views106 pagesRelease 2004
Release 2004
Uploaded by
jhbmleeAP physics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 106
The College Board: Connecting Students to College Success
‘The College Board is a not-for-profit membership association whose mission is to connect,
students to college success and opportunity. Founded in 1900, the association is composed
of more than 4700 schools, colleges, universities, and other educational organizations. Each
yar, the College Board serves over three and a half million students and their parents, 23,000
high schools, and 3,500 colleges through major programs and services in college admissions,
guidance, assessment, financial aid, enrollment, and teaching and learning, Among its best:
Jknown programs are the SAT®, the PSAT/NMSOT®, and the Advanced Placement Program®
(AP®). The College Board is committed to the principles of excellence and equity, and that
‘commitment is embodied in all of its programs, services, activities, and concerns,
‘or further information, visit www.collegeboard.com.
The College Board and the Advanced Placement Program encourage teachers, AP Coordinators,
and school administrators to make equitable access a guiding principle for their AP programs.
‘The College Board is committed to the principle that all students deserve an opportunity to
participate in rigorous and academically challenging courses and programs. All students who
are willing to accept the challenge of a rigorous academic curriculum should be considered fo
admission to AP courses, The Board encourages the elimination of barriers that restrict act
to AP courses for students from ethnic, racial, and socioeconomic groups that have been
traditionally underrepresented in the AP Program. Schools should make every effort to ensure
that their AP classes reflect the diversity of their student population,
For more information about equity and access in principle and practice, contact the
National Office in New York,
Copyright © 2006 by College Entiance Examination Hoard Al rights reserved. Collage Board, AP Cental, APCD, Advanced
Placement Program, AP, AP Vertical Teams, Pe-AP. SAT, and the arn logo ave registered todematks of the Cole
nance Examination Board. Admitted Cass Evaluation Sewvice, ACES, CallegaBd, connect to cllage success, MyRoad,
‘SAT Profesional Development. SAT Readiness Program, and Soting the Cornersiones are traders owned by the Coleg
Entrance Examination Bosrd, PSAT/NMSQT is a rogistered trademal cf the Clloge Euan Examination Boa and
National Mesit Schlatship Carporaticn. Other products and dovieas may be trademark of ther reepectve nets,
‘Visit Calogo Board onthe Web: www cologeboard.com
For further information, visit apcentral.collegeboard.com.
‘The Physics B Exam
PHYSICS B
You must take the entire B Exam as follows:
First 90 minutes Section I— Multiple Choice
70 Questions
‘This booklet, pp. 3-19
No calculators allowed
Percent of Total Grade — 50
2-minute interval Survey Questions
6 Questions (101-106)
‘This booklet, pp. 20-21
Second 90 minutes Section II— Free Response
6 Questions
Pink Booklet
Any battery-operated, hand-held calculator allowed
Percent of Total Grade — 50
‘Each multiple-choice quéstion has equal weight, Rulers or straightedges may be used in both sections. However,
calculators may be used in Section II only, NOT in Section I. Calculators may not be shared.
Section I of this examination contains 70 multiple-choice questions. Therefore, please be careful to fill in only the
‘ovals that are preceded by numbers 1 through 70 on your answer sheet. Also, please be careful to fill in the ovals,
preceded by the numbers 101 through 106 when answering the survey questions. A table of information that may be
|helpfal is found on page 2 of this book.
General Instructions
DONOTOPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE INSTRUCTED TO DOSO.
INDICATE ALL YOUR ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS IN SECTION I ON THE SEPARATE ANSWER SHEET.
‘No credit will be given for anything written inthis examination booklet, but you may use the booklet for notes or
seratchwork. After you have decided which of the suggested answers is best, COMPLETELY fill inthe corresponding
oval on the answer sheet. Give only one answer to each question. If you change an answer, be sure that the previous mark
is erased completely.
Example: Ss wer
Chicago is a DE®oO
(A) state
(B) city
(©) country
@) continent
©) village
Many candidates wonder whether or not to guess the answers to questions about which they are not certain. In this section
of the examination, as a correction for haphazard guessing, one-fourth of the number of questions you answer incorrectly
‘will be subtracted from the number of questions you answer correctly. It is improbable, therefore, that mere guessing will
improve your score significantly; it may even lower your score, and it does take time. If, however, you are not sure of the
‘correct answer but have some knowledge of the question and are able to eliminate one or more of the answer choices as
‘wrong, your chance of getting the right answer is improved, and it may be to your advantage to answer such a question.
Use your time effectively, working as rapidly as you can without losing accuracy. Do not spend too much time on
{questions that are too difficult. Go on to other questions and come back to the difficult ones later if you have time. It is
rot expected that everyone will be able to answer all the multiple-choice questions.
15
The following conventions are used in this examination.
1. Unless otherwise stated, the frame of reference of any problem is assumed to be inertial
UL. The direction of any electric current is the direction of flow of positive charge (conventional current).
II. For any isolated electric charge, the electric potential is defined as zero at an infinite distance from the charge.
TV. For mechanics and thermodynamics equations, W represents the work done on a system.
Physics B
TABLE OF INFORMATION FOR 2004 and 2005
‘CONSTANTS AND CONVERSION FACTORS UNITS PREFIXES
» Name Symbol | Factor Prefix Sumbol
1 united atomic mass unit 1 = 1665 5107 ig
mete m oe i G
= 931 Mevie? 7 7 ee
Proton mas, 167 x10 kg a oie oe
Newton mass, rm, = 167 10g — s ] ido x
etron mass, m= 941 x10 eg ampere A cat
“Magnituse ofthe eecton cree, = 160 x10"C islvin K ili om
Avogadro's number, 602 x 10° mot* vot : =
‘Universal gas constant, R= 831 5/(@01-K) : "
Boltzmann's constant, fy = 13810? 1K ne ”
Speedf tight, 00 x 108 m/s ee _ Pico oP
: * cal Pa
Planck's constant, f= 663% 105-5 ie ‘VALLES OF TRIGONOMETRIC
ea pny 1 _| FUNCTIONS FoR COMMON ANGLES
he 199 107m wat w @ | sino | cos@ | tan @
= 124. 10%eV-am coulomb alae lea
2 cynemt | volt v
Vacuum peritivity, = 885 10 C/N 5
= a so | 12 | Br | 3a |
Coulomb's laveconstant, —& = 14g = 90 x 10" Nem?/Cc?
‘Vacuum permeability, dee ae xiorremsa | Men re | ores | ease |e
Magnetic constant, Hole = OCT IA on a |
“ree? | ul 4s | V22 | V2] 1 t
‘Universal gravitational constant, 6 = 667 x10 wings | |
‘Aveeleration due to gravity Celsius °C sx | 4s | 35 | 43 |
he Bar's surface, 298ml |
slecron-
1 mosphere pressre, 1 atm = 10 « 10° N/a? rh wv | olgol mle |
= 0% 10° Pe i
1 electon vol, Lev = 160x105 go | 4 0 |
i
i
|
16
Physics B
PHYSICS B
Section 1
‘Time—90 minutes
70 Questions
Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or
‘completions. Select the one that is best in each case and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet.
Note: To simplify calculations, you may use g = 10 m/s? in all problems.
1. For which of the following motions of an object
must the acceleration always be zero?
I. Any motion in a straight line
I. Simple harmonic motion
IIL. Any motion in a circle
(A) Tonly
(B) Monly
(© Wonly
(D) Either I or I, but not 1
(B) None of these motions guarantees zero
acceleration.
2. A rope of negligible mass supports a block that,
weighs 30 N, as shown above. The breaking
strength of the rope is 50 N. The largest accelera-
tion that can be given to the block by pulling up
‘on it with the rope without breaking the rope is
most nearly
(A) 6 mys?
@) 6.7 m/s?
(C) 10mvs?
(D) 15 mis?
() 16.7 m/s?
[Unauthorized copying or reuse of
any part of is page toga GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. 7
Top View
3. A compressed spring mounted on a disk can
project a small ball. When the disk is not rotating,
as shown in the top view above, the ball moves
radially outward. The disk then rotates in a
counterclockwise direction as seen from above,
and the ball is projected outward at the instant the
disk is inthe position shown above. Which of the
following best shows the subsequent path of the
ball relative to the ground?
an
CY
oe
CH
CY
©
[Unauthorized copying of rouse a]
any part of tis page fo toga.
Physics B
|. A ball is thrown straight up in the air. When
the ball reaches its highest point, which of the
following is true?
(A) Itis in equilibrium,
(B) Ithas zero acceleration.
(© Ithas maximum momentum.
(D) Ithas maximum kinetic energy.
(B) None of the above
&
‘The figure above shows an object of mass 0.4 kg
that is suspended from a scale and submerged in a
liquid. Ifthe reading on the scale is 3 N, then the
‘buoyant force that the fluid exerts on the object is,
‘most nearly
(A) 13N
(B) LON
© 075N
(D) 033N
© 025N
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE.
B
Physics B
Questions 6-7
os __ Point of
KA Release
Equilibrium ——| Equilibrium
Position Position
Point of ——————{_}
Release =
A sphere of mass ,, which is attached to a spring, is displaced downward from its equilibrium position as shown
above left and released from rest. A sphere of mass m,, which is suspended from a string of length £, is displaced to
the right as shown above right and released from rest so that it swings as a simple pendulum with small amplitude,
‘Assume that both spheres undergo simple harmonic motion
6. Which of the following is true for both spheres? 7. If both spheres have the same period of oscillation,
which of the following is an expression for the
(A) The maximum kinetic energy is attained as spring constant?
the sphere passes through its equilibrium
position, w
(B) The maximum kinetic energy is attained as me
the sphere reaches its point of release.
(C) The minimum gravitational potential energy (B) ad
is attained as the sphere passes through its m
equilibeium position. me
(D) The maximum gravitational potential energy o>
is attained when the sphere reaches its point
of release. ms
(E) The maximum total energy is attained only as o>
the sphere passes through its equilibrium
osition,
. @ 7
[Gnsuthorzed copying or rouse of]
ary part of ns ae sega GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. 19
8. A block attached to the lower end of a vertical
spring oscillates up and down. Ifthe spring obeys
Hooke’ law, the period of oscillation depends on
which of the following?
1. Mass of the block
IL. Amplitude of the oscillation
IIL Force constant of the spring
(A) Lonly
(B) Honly
(© Monty
(D) Tand
© land
9. An empty sled of mass M moves without friction
across a frozen pond at speed vp. Two objects are
dropped vertically into the sled one at a time: first
an object of mass m and then an object of mass
2m. Afterward the sled moves with speed v,.
‘What would be the final speed of the sled ifthe
objects were dropped into it in reverse order?
4
3
4
B® >
© %
D) 2%,
©) 3u;
(A)
10. A new planet is discovered that has twice the
Earth’s mass and twice the Earth’s radius. On the
surface of this new planet, a person who weighs
500 N on Barth would experience a gravitational
force of
(A) 125N
(B) 250N
(©) SOON
(D) 1000N
(©) 2000N
as
Sanna
ML.
12,
Physics B
xm)
20:
18
16
14
12
veEAwS
18)
i 2
‘The graph above represents position x versus
time t for an object being acted on by a constant
force. The average speed during the interval
between I s and 2 s is most nearly
(A) 2mis
(B) 4 m/s
© Sms
(©) 6 m/s
© 8m/s
Two blocks of steel, the first of mass 1 kg and the
second of mass 2 kg, are in thermal equilibrium
with a third block of aluminum of mass 2 kg that
has a temperature of 400 K. What are the respec-
tive temperatures of the first and second steel
blocks?
(A) 400 K and 200 K
(B) 200 K and 400 K
(©) 400 K and 400 K
(D) 800 K and 400 K
() None of the above
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE.
Physics B
13, Am ideal gas may be taken from one state to
another state with a different pressure, volume,
and temperature along several different paths.
(Quantities that will always be the same for this
process, regardless of which path is taken, include
which of the following?
I. The change in internal energy of the gas
I. The heat exchanged between the gas and its
surroundings
IML. The work done by the gas
(A) only
(B) Tonly
(© Vand Mf only
(D) Mand Mf only
© 1,0 and
14, Two parallel wires, each carrying a current J,
repel each other with a force F. If both currents
are doubled, the force of repulsion is
(A 2F
(B) W2F
© 4F
©) WEF
© 8F
15, The hollow metal sphere shown above is positively
charged, Point C is the center of the sphere and
point P is any other point within the sphere,
‘Which of the following is true of the electric
field at these points?
(A) Itis zero at both points,
(B) Itis zero at C, but at P it is not zero and is
directed inward.
(© Itis zero at C, but at P it is not zero and is
directed outward,
(D) Itis zero at P, but at C it
() Itis not zero at either point.
not zero.
Unauharsed copying or rou a
sry art of tls page egal.
16. The total capacitance of several capacitors in
parallel is the sum of the individual capacitances
for which of the following reasons?
(A) The charge on each capacitor depends on its
capacitance, but the potential difference
across each is the same.
(B) The charge is the same on each capacitor, but
the potential difference across each capac~
itor depends on its capacitance.
(©) Equivalent capacitance is always greater than
the largest capacitance.
(D) Capacitors in a circuit always combine like
resistors in series.
©) The parallel combination increases the effec
tive separation of the plates.
17. A wire of length L and radius r has a
resistance R. What is the resistance of a second
wire made from the same material that has a
length L/2 and a radius 1/2?
(A) 4R
(B) 2k
© R
(D) RR
Ris
18. The operating efficiency of a 0.5 A, 120 V electric
motor that lifts a 9 kg mass against gravity at an
average velocity of 0.5 m/s is most nearly
(A) 1%
(B) 13%
© 25%
(©) 53%
©) 75%
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. 21
Questions 19.20
a
-2
ova
Charges -Q and +9 are located on the x- and
y-axes, respectively, each at a distance d from the
origin 0, as shown above.
19. What is the direction of the electric field at the
origin 07
(A) —
@) -—
© \
© \
® Sf
20. What is the magnitude of the electric field at the
origin 07
kQ
© oa?
kO
py 2
® Tae
[Grauthorzed copying ote
any pat tis page oH
a4
22,
23.
Physics B
2D
Anelectron ¢ and a proton p are simultaneously
released from rest in a uniform electric field E, as
shown above. Assume that the particles are suf-
ficiently far apart so that the only force acting on
each particle after it is released is that duc to the
electric field. At a later time when the particles
are still inthe field, the electron and the proton
will have the same
(A) direction of motion
(B) speed
(©) displacement
(D) magnitude of acceleration
(E) magnitude of force acting on them
A square steel plate with sides of length 1.00 m
has a hole in its center 0-100 m in diameter. If the
entire plate is heated to such a temperature that its
sides become 1.01 m long, the diameter of the
hole will be
(A) 0.090 m
(B) 0.099 m
(© 0.100 m
(D) 0.101 m
® 0.110m
Which of the following will occur if the average
speed of the gas molecules in a closed rigid
container is increased?
(A) The density of the gas will decrease
(B) The density of the gas will increase.
(©) The pressure of the gas will increase.
(D) The pressure of the gas will decrease.
(E) The temperature of the gas will decrease.
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE.
BY Physice
28, Which of the following is characteristic of both
abe d ¢ sound and light waves?
(A) They are longitudinal waves.
(B) They are transverse waves
(© They travel with the same velocity.
24. The spherical mirror shown above has a center of (D) They
-y can be easily polarized.
curvature at point c. Which point is nearest to the @) They give rise to interference effects.
focal point?
a
(B) b
q Oc Questions 29-30
| @)d
@®e Force (N)
25. The frequencies of the first two overtones (second
and third harmonics) of a vibrating string are f 25
and 3f/2. What is the fundamental frequency of
this string? 20
(A) £/3
®) £2 2 T
OF 10
(D) 2
() if e)
26. An object is placed in front of a converging thin
lens at a distance from the center of the lens equal 1 2 3 4
to half the focal length. Compared to the object, Time (s)
the image is
(A) upright and larger A student obtains data on the magnitude of force
(B) upright and smaller applied to an object as a function of time and displays,
(C) inverted and larger the data on the graph above.
(D) inverted and smaller
(©) inverted and the same size 29. The slope of the “best fit” straight line is most
nearly
27. A radio station broadcasts on a carrier frequency (A) 5s
of 100 MHz. The wavelength of this radio wave is ®) 6Ns
‘most nearly (©) 7s
(A) 3.0 10 m . ) 8Nis
(B) 1.0m (©) 10N/s
(©) 3.0m
(D) 33m 30. The increase in the momentum of the object
©) 30x 108m between t = 0s and r= 45s is most nearly
(A) 40Nss
(B) 50Nss
© ONs
(D) 80Nes
) 100N's
[Snasthorzed copying or ause a]
any art of tis page siege GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. 23
24
31. How does an air mattress protect a stunt person
landing on the ground after a stunt?
(A) Itreduces the kinetic energy loss of the stunt
person.
(B) It reduces the momentum change of the stunt
person.
(C) Itincreases the momentum change of the
stunt person.
(D) It shortens the stopping time of the stunt
person and inereases the force applied
during the landing,
(©) Itlengthens the stopping time of the stunt
person and reduces the force applied during
the landing,
Questions 32-33
‘A horizontal, uniform board of weight 125 N and
length 4 m is supported by vertical chains at each end
A person weighing 500 N is sitting on the board. The
‘tension in the right chain is 250 N.
32, What is the tension in the left chain?
(A) 250
(B) 375N
(© SOON
(D) 625N
® 875N
33. How far from the left end of the board is the
person sitting?
(a) 04m
@B) 15m
© 2m
(D) 25m
© 3m
Gnautharzed copying o ours
any pat of tis page egal
Physics B
Questions 34-35 relate to the photoelectric effect.
For each question, choose an answer from the
following graphs.
(A) (B)
© (D)
34. Which graph shows the maximum Kinetic energy
of the emitted electrons versus the frequency of
the light?
(AA
(B) B
oc
@)D
®E j
35. Which graph shows the total photoelectric
current yersus the intensity of the light for a
fixed frequency above the cutoff frequency?
(A) A
(B) B
oc
(@) D
®E
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE.
Physics B
36. Which of the following statements about the
number of protons Z and the number of neutrons
N in stable nuclei is true?
(A) All stable nuclei have Z= N.
(B) Only heavy stable nuclei have Z= N.
(©) Heavy stable nuclei tend to have ZN.
37. Each of the beakers shown above is filled to
the same depth h with liquid of density . The
area A of the flat bottom is the same for each
beaker. Which ofthe following ranks the beakers
according to the net downward force exerted by
the liquid on the flat bottom, from greatest to least
force?
(A) 1,101, 0, 1V
@®) LIV, 0
(© 0, 0, 1V,1
(D) Iv, I, 1,
(B) None of the above; the force on each is the
same.
38. A T-shaped tube with a constriction is inserted
in a vessel containing a liquid, as shown above.
‘What happens if air is blown through the tube
from the left, as shown by the arrow in the
diagram?
(A) The liquid level in the tube rises to a level
above the surface of the liquid surrounding
the tube.
(B) The liquid level in the tube falls below the
level of the surrounding liquid.
(© The liquid level in the tube remains where
itis.
(D) The air bubbles out at the bottom of the tube.
() Any of the above depending on how hard the
air flows.
39. A spring scale calibrated in kilograms is used to
determine the density of a rock specimen. The
reading on the spring scale is 0.45 kg when the
specimen is suspended in air and 0.36 kg when
the specimen is fully submerged in water. If the
density of water is 1000 kg/m?, the density of the
rock specimen is
(A) 2.0.x 10? kg/m?
(B) 8.0.x 10? kg/m?
(© 1.25 x 10? kein?
(D) 4.0.x 10° kg/m?
(B) 5.0.x 10° kg/m?
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. 25
40. Two objects, A and B, initially at rest, are
“exploded” apart by the release of a coiled
spring that was compressed between them.
As they move apart, the velocity of object A
is 5 m/s and the velocity of object B is ~2 m/s.
The ratio of the mass of object A to the mass of
object B, mg/m, is
(A) 4225
(B) 25
©
(D) 5/2
(B) 25/4
41. The cart of mass 10 kg shown above moves
‘without frictional loss on a level table. A 10 N
force pulls on the cart horizontally to the right.
At the same time, a 30 N force at an angle of 60°
above the horizontal pulls on the cart to the left,
What is the magnitude of the horizontal
acceleration of the cart?”
(A) 05 mis?
(B) 16 mis?
© 20 m/s?
(D) 25 mis?
© 26m
42. A child has a toy tied to the end of a string and
whirls the toy at constant speed in a horizontal
circular path of radius R. The toy completes each
revolution of its motion in a time period 7. What
is the magnitude of the acceleration of the toy?
(A) Zero
4R
oa
aR
© Pp
)g
© 2m
nstioread coving ane of
Ee ary part of tis page a egal
Physics B
43. A simple pendulum and a mass hanging on a
spring both have a period of 1 s when set into
small oscillatory motion on Earth. They are taken
to Planet X, which has the same diameter as Earth
‘but twice the mass. Which of the following state-
ments is true about the periods of the two objects
on Planet X compared to their periods on Earth?
(A) Both are shorter,
(B) Both are the same.
(C) Both are longer.
(D) The period of the mass on the spring is
shorter; that of the pendulum is the same.
(B) The period of the pendulum is shorter; that of
the mass on the spring is the same.
44, A steel ball supported by a stick rotates in a
circle of radius r, as shown above. The direction
of the net force acting on the ball when itis in
the position shown is indicated by which of the
following?
(A) |
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE.
Physics B
Questions 45-46
TOT
0.04 m
0.01 m Ay
‘Two large, flat, parallel, conducting plates are
0.04 m apart, as shown above. The lower plate is at a
potential of 2 V with respect to ground. The upper
plate is at a potential of 10 V with respect to ground.
Point P is located 0.01 m above the lower plate.
45. The electric potential at point P is
(a) 10V
@) 8Vv
© 6v
@) 4v
® 2v
46. The magnitude of the electric field at point P is
(A) 800 Vim.
(B) 600 Vin
(C) 400 Vim
(D) 200 Vim
©) 100 Vim
47. Two conducting wire loops move near a very
long, straight conducting wire that carties a
current 7. When the loops are in the positions
shown above, they are moving in the directions
shown with the same constant speed v . Assume
that the loops are far enough apart that they do
not affect each other. Which of the following is
‘rue about the induced electric currents, if any,
in the loops?
Loopt Loop2
(A) No current No current
(B) No current Counterclockwise
direction
(©) Clockwise direction No current
(D) Clockwise direction Clockwise direction
(©) Counterclockwise Clockwise direction
direction
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE.
a7
Questions 48-49 relate to the following circuit
diagram.
R,= 20002
R, = 25009 h
wh
€=12V
48, What is the current /, ?
(A) 08mA
(B) LOmA
(© 20maA
(D) 3.0mA
(B) 60mA
49, How do the currents /,, Ip, and J; compare?
(A h>h>h
® h>h>h
Ohhh
O) h>h>h
® h>hrh
a
», «EERE
Physics B
‘Questions 50-51
moo Bk
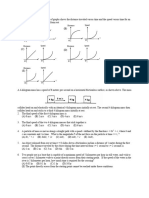
A light ray R in medium I strikes a sphere of
medium Il with angle of incidence @ , as shown
above. The figure shows five possible subsequent
paths for the light ray.
50. Which path is possible if medium I is air and
medium Is glass?
(A) A
(B) B
oc
(@)D
®E
51. Which path is possible if medium I is glass and
medium His air?
(AA
(B) B
mc
@)D
®@eE
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE.
‘BE physics B
52. Two fire trucks have sirens that emit waves of
the same frequency. As the fire trucks approach
a person, the person hears a higher frequency
from truck X than from truck ¥. Which of the
following statements about truck X can be
correctly inferred from this information?
| 1 Itis traveling faster than truck Y.
II. Itis closer to the person than truck ¥.
| INL It is speeding up, and truck Y is slowing
down,
(A) Lonly
(B) IMonly
(© Land I only
(D) Mand If only
©) 1,0 and
Light
mh
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- AP Calculus AB 2008 With AnswersDocument33 pagesAP Calculus AB 2008 With AnswersjhbmleeNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry 2008 With AnswersDocument19 pagesAP Chemistry 2008 With AnswersjhbmleeNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry 1994 With AnswersDocument22 pagesAP Chemistry 1994 With AnswersjhbmleeNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry 1984 With AnswersDocument22 pagesAP Chemistry 1984 With AnswersjhbmleeNo ratings yet
- Release 1998 DiaDocument18 pagesRelease 1998 DiajhbmleeNo ratings yet
- Release 1998Document92 pagesRelease 1998jhbmleeNo ratings yet
- AP Physics B 1974 With AnswersDocument11 pagesAP Physics B 1974 With AnswersjhbmleeNo ratings yet
- Release 1998 2sidedDocument92 pagesRelease 1998 2sidedjhbmleeNo ratings yet
- AP Physics C 1988 With AnswersDocument18 pagesAP Physics C 1988 With AnswersjhbmleeNo ratings yet
- AP Physics C 1984 With AnswersDocument15 pagesAP Physics C 1984 With AnswersjhbmleeNo ratings yet
- AP Physics B 1998 With AnswersDocument18 pagesAP Physics B 1998 With AnswersjhbmleeNo ratings yet
- AP Physics C 1974 With AnswersDocument16 pagesAP Physics C 1974 With AnswersjhbmleeNo ratings yet