Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar Disorder
Uploaded by
John Nine ErispeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar Disorder
Uploaded by
John Nine ErispeCopyright:
Available Formats
Bipolar Disorder
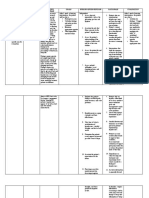
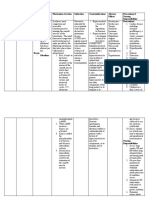
Mental Health "Psychiatric Care"
Pathophysiology
Bipolar is a mood disorder with cycling periods of lows with Depression followed by highs with Acute Mania.
During depression: clients have low mood, low energy, & motivation & high risk for suicide.
During acute mania: high energy, hyperactivity, elevated mood, & even aggression with violence.
HESI Question
Four or more mood MEMORY TRICK
Depression Acute Mania
episodes in a
12-month period, the Depression Mania
Declined mood More energy + Maniac
patient is said to be
Rapid cycling
ATI Question
Five acute manic
episodes in one year
Rapid cycling
Types of Bipolar Disorders
Bipolar 1 - 1 episode of mania that lasts over 1 week or need for hospitalization
Bipolar 2 - 2 episodes of milder high hypomania, which can last longer
Cyclothymia - milder lows & milder highs cycling over a period of 2 years
Rapid Cycling - 4 episodes of depression & mania within a 12 month period
Causes & Risk Factors
The cause is unknown but what does play a big part is:
• Genetics - having a family member with bipolar, clients are 10x more likely to have it.
• SSRIs (antidepressants) can trigger a manic episode
SSRIs can trigger a manic episode
Genetics SSRI
10x
Signs & Symptoms
M
More energy & Mood Swings
Euphoric energy, impulsive, grandiosity
ATI Question Kaplan Question
Hallucinations & delusions of grandeur
Q1: Acute manic phase: Which symptom
symptoms with manic behavior? does the nurse expect?
A Agitation
Set limits & structured environment
• More talkative than usual
• Easily distracted
• Hyperactivity & irritable
Q2: “I just bought myself a home
• Intense need for activity computer and a large screen TV for
N
the family.” Which interpretation is
Non-stop talking & Flight of ideas most accurate?
Colorful bizarre clothing choices
HESI Question • Mood disturbance and judgement
that is poor at this time
manic phase?
I Insomnia
Cannot sleep for days
Select all that apply.
• The client is quickly angered
• Flight of ideas
Saunders
Assessment finding that requires
A
• Going rapidly from one activity immediate intervention?
Attention span POOR to another • Nonstop physical activity and poor
Easily distracted = reduce stimuli
• Colorful & outlandish clothing nutritional intake
• Constant delusions
You might also like
- Chapter 13 Case Study 13.1Document2 pagesChapter 13 Case Study 13.1Bella mc100% (2)
- Why Am I Still Depressed? Recognizing and Managing the Ups and Downs of Bipolar II and Soft Bipolar DisorderFrom EverandWhy Am I Still Depressed? Recognizing and Managing the Ups and Downs of Bipolar II and Soft Bipolar DisorderRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- MSE - Bipolar (Manic Phase)Document3 pagesMSE - Bipolar (Manic Phase)Carla Tongson MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan HyperthyroidismDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Hyperthyroidismderic76% (17)
- Mental Status ExamDocument4 pagesMental Status Examscootaccess100% (1)
- Medical Treatment of Persistent Post Concussive Symptoms - Kuemmerle Neuro Boston Childrens Hospital HarvardDocument27 pagesMedical Treatment of Persistent Post Concussive Symptoms - Kuemmerle Neuro Boston Childrens Hospital HarvardRexDavidGidoNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Disorder: Presented By: Group 2Document19 pagesBipolar Disorder: Presented By: Group 2Pao DelossantosNo ratings yet
- 5 Prioritized Problems Bipolar 1Document18 pages5 Prioritized Problems Bipolar 1Joseph D. Wang100% (30)
- Mood Disorders: Depressive Disorders: Bipolar DisordersDocument4 pagesMood Disorders: Depressive Disorders: Bipolar DisordersWen Jie LauNo ratings yet
- Depression Nursing CareDocument1 pageDepression Nursing CareJohn Nine ErispeNo ratings yet
- Hopelessness NCPDocument5 pagesHopelessness NCPMatty JolbitadoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - What's This Mental Health Stuff 2023Document28 pagesModule 1 - What's This Mental Health Stuff 2023ShannonRichterNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Disease and DisordersDocument28 pagesMental Health Disease and DisordersCharleson OtubuNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry Revision E6.5 (Medicalstudyzone - Com)Document26 pagesPsychiatry Revision E6.5 (Medicalstudyzone - Com)Rohan RathoreNo ratings yet
- 04.psychiatry SamplesDocument50 pages04.psychiatry SamplesCherinet KibruNo ratings yet
- Bipolar DisorderDocument2 pagesBipolar DisorderChristel Mariz SantellaNo ratings yet
- PsychiatryDocument18 pagesPsychiatryWorld MedclickzNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry ManiaDocument2 pagesPsychiatry ManiaDevangkumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Brain Bee 2Document10 pagesBrain Bee 2dedhomosapien2No ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument1 pageAnxiety DisordersJohn Nine ErispeNo ratings yet
- Manic Depressive Disorder 2021-2022Document60 pagesManic Depressive Disorder 2021-2022ramiNo ratings yet
- Feature Dementia Delirium Depression: Onset and DurationDocument2 pagesFeature Dementia Delirium Depression: Onset and Durationwali mukadinmohamedNo ratings yet
- Universidad de Sta. Isabel: Vincentian Learning ModuleDocument17 pagesUniversidad de Sta. Isabel: Vincentian Learning ModuleYancy TingsonNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Disorder Symptoms: What The Fact Sheet CoversDocument4 pagesBipolar Disorder Symptoms: What The Fact Sheet CoversgugicevdzoceNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia: at The End of The Lecture You Should Be Able ToDocument18 pagesSchizophrenia: at The End of The Lecture You Should Be Able Toapi-3703352No ratings yet
- Management of Psychiatric Disorders Due To Another Medical ConditionDocument3 pagesManagement of Psychiatric Disorders Due To Another Medical ConditionCRUZ Jill EraNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry 101Document17 pagesPsychiatry 101Vaso Talakvadze0% (1)
- Panic AttackDocument1 pagePanic AttackJohn Nine ErispeNo ratings yet
- SIEGEL - Tailoring MindfulneDocument16 pagesSIEGEL - Tailoring Mindfulnejohannquesada100% (1)
- DSM 5 Made EasyDocument6 pagesDSM 5 Made EasyTesita100% (3)
- Delirium, Dementia, PsychosisDocument2 pagesDelirium, Dementia, PsychosisLagente EstalocaNo ratings yet
- PSYCHIATRYDocument12 pagesPSYCHIATRYSavanthi Carmaline de SilvaNo ratings yet
- 3a. Mood Disorder 2022Document101 pages3a. Mood Disorder 2022mirabel IvanaliNo ratings yet
- Psychotic Disorder PsychosisDocument3 pagesPsychotic Disorder PsychosisAhmad Syahmi YZNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument3 pagesINTRODUCTIONEj ChongNo ratings yet
- Abnormal PsychologyDocument12 pagesAbnormal Psychologyjayencee888No ratings yet
- Schizophrenia PDFDocument4 pagesSchizophrenia PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- AnxietyDocument2 pagesAnxietyikoiNo ratings yet
- Cognitive DisordersDocument4 pagesCognitive DisordersCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Identification of Psychological ProblemsDocument16 pagesIdentification of Psychological ProblemsMalachy ScullionNo ratings yet
- Dialectical Behavior TherapyDocument44 pagesDialectical Behavior TherapyRavitejaNo ratings yet
- 1 Page DSM - SubstanceDocument1 page1 Page DSM - SubstanceAlliyah Roma CadaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology, Twelfth Edition: SchizophreniaDocument40 pagesAbnormal Psychology, Twelfth Edition: SchizophreniaSheNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisorderDocument23 pagesAnxiety DisorderOliver Miguel ChavezNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document2 pagesNCP 1Camille SesaldoNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document2 pagesNCP 1Camille SesaldoNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia NCPDocument4 pagesSchizophrenia NCPDen-rashier M. Jamsuri100% (1)
- 1-01 Psychiatric History and Mental Status Examination Appendix CIC v1Document5 pages1-01 Psychiatric History and Mental Status Examination Appendix CIC v1Dane Mikhael CalicaNo ratings yet
- Affective Disorder Intro 2019-20Document15 pagesAffective Disorder Intro 2019-20fr4nc1s4ggr3yNo ratings yet
- NCP For Bipolar Risk For Injury Related To Extreme Hyperactivity As Evidenced by Excessive and Constant Motor ActivityDocument3 pagesNCP For Bipolar Risk For Injury Related To Extreme Hyperactivity As Evidenced by Excessive and Constant Motor Activitydana75% (4)
- Other Psychological Disorders: OCD and Personality DisorderDocument71 pagesOther Psychological Disorders: OCD and Personality DisorderAlessandra Dominique MarianoNo ratings yet
- NCP For BipolarDocument11 pagesNCP For BipolarFatima Medriza DuranNo ratings yet
- HypnosisDocument26 pagesHypnosisAsmita Dalvi100% (1)
- Human Behavior 12 2016Document15 pagesHuman Behavior 12 2016aalijahabbasNo ratings yet
- PERSONALITYDocument4 pagesPERSONALITYJustine BayabosNo ratings yet
- Case 6Document12 pagesCase 6Jovan TeopizNo ratings yet
- ANXIETY DISORDERS Pertemuan 3Document40 pagesANXIETY DISORDERS Pertemuan 3najwa prajna phalita kurniawanNo ratings yet
- Psychopatholgy of Bipolar DisorderDocument1 pagePsychopatholgy of Bipolar Disorderthr3adzNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia and Other Psychoses: Psychosis - Is A Disruptive Mental State inDocument7 pagesSchizophrenia and Other Psychoses: Psychosis - Is A Disruptive Mental State inDhen MarcNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing DemystifiedFrom EverandPsychiatric and Mental Health Nursing DemystifiedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- GamesDocument3 pagesGamesJohn Nine ErispeNo ratings yet
- Depression ProceduresDocument1 pageDepression ProceduresJohn Nine ErispeNo ratings yet
- Abuse & NeglectDocument1 pageAbuse & NeglectJohn Nine ErispeNo ratings yet
- Panic AttackDocument1 pagePanic AttackJohn Nine ErispeNo ratings yet
- Helping The Poor and DistressedDocument4 pagesHelping The Poor and DistressedJohn Nine ErispeNo ratings yet
- FlowerDocument2 pagesFlowerJohn Nine ErispeNo ratings yet
- Also Provider Manual 2023Document320 pagesAlso Provider Manual 2023John Nine ErispeNo ratings yet
- ALSO Mnemonic Laminate Cards 2023Document8 pagesALSO Mnemonic Laminate Cards 2023John Nine ErispeNo ratings yet
- JCI QuestionssDocument48 pagesJCI QuestionssJohn Nine ErispeNo ratings yet
- Thesis DDCDocument27 pagesThesis DDCJohn Nine ErispeNo ratings yet
- MMU Questions & AnswersDocument7 pagesMMU Questions & AnswersJohn Nine ErispeNo ratings yet
- HC - Assessment 2023Document4 pagesHC - Assessment 2023Bhanu Prasad SNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Kidney StoneDocument36 pagesCase Study On Kidney Stonemanojkumar200624No ratings yet
- Part 1 CD Mastery TestDocument15 pagesPart 1 CD Mastery TestRika MaeNo ratings yet
- EPI and HIV 1Document5 pagesEPI and HIV 1April Ivonne Claire BatoNo ratings yet
- Bradley J Monk First Line Pembrolizumab ChemotherapyDocument9 pagesBradley J Monk First Line Pembrolizumab ChemotherapyRaúl DíazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 41: Genitourinary Disorders Garzon Maaks: Burns' Pediatric Primary Care, 7th EditionDocument6 pagesChapter 41: Genitourinary Disorders Garzon Maaks: Burns' Pediatric Primary Care, 7th EditionHelen UgochukwuNo ratings yet
- What Is Newborn ScreeningDocument2 pagesWhat Is Newborn ScreeningroksanmiNo ratings yet
- Biochem Term PaperDocument5 pagesBiochem Term PaperVincent Philip DelavictoriaNo ratings yet
- A4 Metabolic and EndocrineDocument50 pagesA4 Metabolic and Endocrinemineb9631No ratings yet
- WCLC2017 Abstract Book WebDocument700 pagesWCLC2017 Abstract Book Webdavid.yb.wangNo ratings yet
- Standards of Care in Diabetes-2023: 10. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk ManagementDocument33 pagesStandards of Care in Diabetes-2023: 10. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Managementإكرام النايبNo ratings yet
- 10 Penyakit Terbanyak Di Rawat Jalan Di Puskesmas Provinsi Dki Jakarta TW I Tahun 2019Document9 pages10 Penyakit Terbanyak Di Rawat Jalan Di Puskesmas Provinsi Dki Jakarta TW I Tahun 2019Klinik pratama Iqra' medical centreNo ratings yet
- Academic Year: 2021/2022 Semester: Fall 2021Document27 pagesAcademic Year: 2021/2022 Semester: Fall 2021Marwa abbassNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Survival Guide McMaster 2020 07 01Document29 pagesCOVID-19 Survival Guide McMaster 2020 07 01MUHAMMAD09No ratings yet
- Central Nervous System Tumours: WHO Classification of Tumours - 5th EditionDocument584 pagesCentral Nervous System Tumours: WHO Classification of Tumours - 5th EditionSamira KhalilNo ratings yet
- NCM106-Cellular Aberrations-Module1-Lesson 1Document9 pagesNCM106-Cellular Aberrations-Module1-Lesson 1Esmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- DS ICS DuaventDecilone ForteDocument6 pagesDS ICS DuaventDecilone ForteThrinNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To Phlebotomy - Wimba DinutanayoDocument14 pages01 Introduction To Phlebotomy - Wimba Dinutanayojamalagus239No ratings yet
- Principles of Radiation OncologyDocument22 pagesPrinciples of Radiation OncologyGina RNo ratings yet
- Teachable Study PDF 1Document1 pageTeachable Study PDF 1Taif SalimNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - TPN PWDT FormpdfDocument22 pagesDokumen - Tips - TPN PWDT FormpdfRao SohaibNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument4 pagesCase StudyDaniel Angelo ArangoNo ratings yet
- Types of DeathDocument2 pagesTypes of DeathRamseena Udayakumar100% (1)
- EPI Lecture Note April 2005, YemaneDocument132 pagesEPI Lecture Note April 2005, YemaneGetahun TekleNo ratings yet
- Gynecological Exam: Preparation For Your ExamDocument2 pagesGynecological Exam: Preparation For Your ExamLotfyAdelNo ratings yet
- Med-Surg Ch25 Patient With Cancer Study Guide and NCLEX QuestionsDocument19 pagesMed-Surg Ch25 Patient With Cancer Study Guide and NCLEX QuestionsKyla Mae JumaritoNo ratings yet
- Gero Aging Review 2023-1Document41 pagesGero Aging Review 2023-1indo 5S100% (1)
- hemaطlogyDocument18 pageshemaطlogyHasan AlmomaniNo ratings yet
- CSB 341Document48 pagesCSB 341TessNo ratings yet