Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IT Study Notes
Uploaded by
amarashah182Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IT Study Notes
Uploaded by
amarashah182Copyright:
Available Formats
Computer fundamentals
1. Explain the concept of information technology.
The concept of information technology is about using a computer to manipulate digital
data to create information. This information is used by people or sometimes machines
to complete a task.
2. distinguish among the major types of computer systems in terms of processing
speed, storage and portability.
i. Supercomputers
A super computer is designed to process more data at much higher speeds than other
computers. They must also store large amounts of data. They are very expensive. The
maintenance and running of the computer is much more costly. Super computers are
usually built for the government and large corporations. It usually costs around $50 to
$100m to build and the power needed to run a single supercomputer costs $5 to $10m
every year.
ii. Mainframe computers
Mainframes are housed in special rooms and have large amounts of storage. The
processes carried out by mainframes are usually quite simple so the processing speed
is less important than reliability.
iii. Desktop computers
Desktop computers are general use computers used in offices, schools and home. The
desktop computer can be customized to suit the needs of an individual needs you can
install a better graphics card or an extra disk drive.
iv. Mobile devices
This includes laptop computers, tablets and smartphones.
These devices either have a keyboard and screen built into the case or use a touch
screen.
v. embedded devices
Computer processors are now small and light they are built into many personal and
household devices from smart watches to cars.
An embedded microprocessor makes another device more powerful and useful.
( microprocessor the CPU of a modern computer. They are very small and it supports
small light mobile devices)
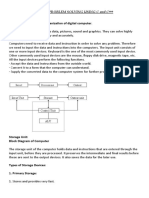
3. explain the functions of the major hardware components of a computer system
i. Input
It means turning data and instructions into electronic form so they can be processed by
the computer.
ii. Central processing unit
The computer processes input data according to input instructions this happens
electronically in the CPU
iii. RAM (random access memory)
The RAM stores the current instructions and data that the computer is using.
RAM is read-write memory which means it can store new data and RAM is volatile
which means if the computer is off the data stored will be lost.
iv. ROM (read only memory)
ROM stores the instructions to start up the computer system. Rom is read only which
means the instructions cannot be changed and its also non-volatile so these instructions
are not lost when the computer is off.
PROM (programmable read only memory)
PROM is blank when it leaves the factory and the instructions are added later by a
programmer but they are fixed and cannot be changed.
-EPROM (erasable programmable read-only memory)
If EPROM is exposed to ultraviolet is wiped clean, so it can be reused to store new
instructions.
v. Output
Usually means turning the results of the processing into a form that people can
understand or use.
4. Storage media
i. Magnetic tape
It stores data on magnetism on plastic tape. The features are sequential access is slow,
read-write access and removable from the computer. There are many sizes and types
of tape but tape is rarely used in modern computer systems.
ii. Hard disk
It stores data on magnetism on a stack of metal disks inside the computer case. The
feature are direct access read write access and usually fixed in on machine high
capacity they are HDD and SSD types of disks.
iii. Optical disks
It stores data on microscopic pits burned into a smooth surface by a lase they are
invisible to normal vision. The features are direct access, read only access unless you
have the software to burn new data on to the disk removable and high capacity. The
main types are CDs used to store music and large data flies.
DVDs have even higher capacity and are used to store very large amount of data such
as movies. Blu-ray is an optical disc format like CD and DVD. Blu-ray discs can hold
more information than other optical media, because of the blue lasers that the disc
drives use. A single Blu-ray disc can hold up to 25GB of data.
5. Units of storage
i. Bit
A single on and off signal (a single 1 or 0) is called a bit; this is short for binary digit.
ii. Byte
A group of bits big enough to store one letter is called a byte. And the exact value is 8
bits.
iii. Kilobyte
A group of bytes is enough to store a thousand characters and the storage value is
1024 bytes.
iv. Megabyte
A group of bytes is enough to store a million characters and storage value is 1048567
bytes.
v. Gigabyte
A group of megabytes is enough to store a billion characters and the storage value is
1000 mb
vi. Terabyte
A group of gigabytes is enough to store a trillion characters and the storage value is
1000gb
6. explain how the major hardware components of a computer system interrelate;
Input processing output storage (IPOS) cycle.
Input - processing - output - storage
Data is input to the computer —-- data is processed into information —-- information is
output to the user in various forms —- data or information is stored for a short or long
time.
7. evaluate the relative merits of cloud storage and local storage
Definition of cloud and local storage.Assessment criteria: capacity, cost,accessibility;
security issues.
Local storage allows quick access and large file processing, providing faster data
access and processing than cloud storage.
You might also like
- Job Description:: Phlebotomists DutiesDocument7 pagesJob Description:: Phlebotomists DutiesRajeev PareekNo ratings yet
- River CrossingDocument119 pagesRiver CrossingMohammad Shafaet JamilNo ratings yet
- BUCU002 Computer ApplicationsDocument83 pagesBUCU002 Computer ApplicationsjohnNo ratings yet
- Grade 7-Module 1: Computer Science Quarter 1-Week 3-4Document14 pagesGrade 7-Module 1: Computer Science Quarter 1-Week 3-4Leonie Cruz ReyesNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis Syallbus MG Univ KeralaDocument1 pagePower System Analysis Syallbus MG Univ KeralaChristy CyriacNo ratings yet
- Using Information TechnologyDocument4 pagesUsing Information TechnologyMg Tin OoNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument5 pagesClassification of ComputersSaranya VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument16 pagesComputer HardwareJane OrsalNo ratings yet
- Advances in Data Storage TechnologyDocument18 pagesAdvances in Data Storage TechnologySuresh31179No ratings yet
- Computer Storage Memory DeviceDocument21 pagesComputer Storage Memory DeviceOfficialbenny2No ratings yet
- Chapter3 SECONDARY STORAGE DEVICESDocument25 pagesChapter3 SECONDARY STORAGE DEVICESPrince kumarNo ratings yet
- Gabriel Com11Document14 pagesGabriel Com11Brooks RayNo ratings yet
- Computer Literracy-Assignment-1Document13 pagesComputer Literracy-Assignment-1Larry KnNo ratings yet
- Review Questions PDocument7 pagesReview Questions PRomeo GongobNo ratings yet
- Obilor Computer LiteracyDocument31 pagesObilor Computer LiteracybenobilorNo ratings yet
- Grade Nine (9) Computer Studies: Primary Storage: This Is The Direct Memory Which Is Accessible To TheDocument4 pagesGrade Nine (9) Computer Studies: Primary Storage: This Is The Direct Memory Which Is Accessible To TheChaiwa JustineNo ratings yet
- Figure 6-1.-C1assification System of Memory.: Time Destructive ReadoutDocument7 pagesFigure 6-1.-C1assification System of Memory.: Time Destructive ReadoutVijay Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- What Is The Computer System? Define Data and InformationDocument19 pagesWhat Is The Computer System? Define Data and InformationBikram TuladharNo ratings yet
- Magna College of EngineeringDocument9 pagesMagna College of Engineeringsoundharya03No ratings yet
- Year9 Ict 2ND Term NoteDocument42 pagesYear9 Ict 2ND Term NoteKeeping up with the durosaro DurosaroNo ratings yet
- Report in I.TDocument14 pagesReport in I.TNana LeeNo ratings yet
- Information: Communication TechnologyDocument120 pagesInformation: Communication TechnologyTusiimeNo ratings yet
- On Comprehensive Project: BCA (Session 2010-2013)Document74 pagesOn Comprehensive Project: BCA (Session 2010-2013)Yadwinder SinghNo ratings yet
- It101 Prelim Module1Document35 pagesIt101 Prelim Module1Karl John Jay ValderamaNo ratings yet
- CPNM NotesDocument153 pagesCPNM NotesRamanarayanSankriti100% (1)
- Coláiste Chiaráin IC3 NotesDocument19 pagesColáiste Chiaráin IC3 NotescchiarainNo ratings yet
- ICT Chapter 01Document8 pagesICT Chapter 01iltamasjaatNo ratings yet
- Os SelaDocument31 pagesOs SelaselaudinNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For MIS 7th Edition Bidgoli 1305667573 9781305667570Document36 pagesSolution Manual For MIS 7th Edition Bidgoli 1305667573 9781305667570daviddennissicrnqpxfz100% (22)
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To ComputersDocument9 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Computerszarinam94No ratings yet
- Bahria Foundation Colleges (North) Centralized Notes of Short Questions (F.B.I.S.E) Computer Science SSC - IDocument39 pagesBahria Foundation Colleges (North) Centralized Notes of Short Questions (F.B.I.S.E) Computer Science SSC - IZaheer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Student NotesDocument11 pagesStudent Noteskuldeep choudharyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document10 pagesChapter 3Xyza Faye RegaladoNo ratings yet
- Short Questions Other BoardsDocument50 pagesShort Questions Other BoardsZaheer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Week 1-Introduction To ComputersDocument8 pagesWeek 1-Introduction To ComputersJontex 254No ratings yet
- 11 CSS Week 2 Day 4Document4 pages11 CSS Week 2 Day 4mhelvinf.jimenezNo ratings yet
- ICT NOTES 2022 DiplomaDocument51 pagesICT NOTES 2022 DiplomaelishabagalwNo ratings yet
- Xia2 CH1 Lect4 Storage UnitsDocument4 pagesXia2 CH1 Lect4 Storage UnitsWhite 444No ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer TechnologyDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Computer TechnologyHanz Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- ICT Course 1Document52 pagesICT Course 1Ahmed KucherNo ratings yet
- ICT Notes 3Document6 pagesICT Notes 3komal_daoudNo ratings yet
- Notes 1Document9 pagesNotes 1Purity Kangogo100% (1)
- Programming For Problem Solving Using C and C++Document26 pagesProgramming For Problem Solving Using C and C++mallikarjunaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Computer SystemDocument48 pagesChapter - 1 Computer SystemVansh SainiNo ratings yet
- Class: BBA 1 Subject: IT in Business Name: Frooque Ahmed Chandio Assignment: OneDocument8 pagesClass: BBA 1 Subject: IT in Business Name: Frooque Ahmed Chandio Assignment: OneSky WolfNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Leveraging The Power ComputingDocument16 pagesUnit 3: Leveraging The Power ComputingMohd ShifanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: IT Infrastructure: After Completing This Topic, You Will Be Able ToDocument21 pagesLecture 1: IT Infrastructure: After Completing This Topic, You Will Be Able ToGabby OperarioNo ratings yet
- Sample For Computer Application CictDocument20 pagesSample For Computer Application CictJohn AyaraNo ratings yet
- It Skills LLB Part 2Document17 pagesIt Skills LLB Part 2Rana AnsNo ratings yet
- Problem Sloving Through C ProgrammingDocument51 pagesProblem Sloving Through C Programmingmanoj hmNo ratings yet
- Absrtact: 2011 DR - AIT, ECEDocument29 pagesAbsrtact: 2011 DR - AIT, ECESachin BhandariNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chapter 1 Computer SystemDocument34 pagesClass 11 Chapter 1 Computer Systemprasadnehra77No ratings yet
- Imd113 Final Exam ExerciseDocument5 pagesImd113 Final Exam ExercisenanaNo ratings yet
- Computer Application in Management Bba 2NDDocument22 pagesComputer Application in Management Bba 2NDFariha AbdulselamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Critical Thinking AnswersDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Critical Thinking Answersapi-347135684No ratings yet
- It101 Exam With AnswersDocument9 pagesIt101 Exam With AnswersMA. MICAH GIFT CALIBOSONo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - IT InfrastructureDocument26 pagesLecture 1 - IT InfrastructureMojica CalagueNo ratings yet
- Explanantion of ComputerDocument10 pagesExplanantion of Computernimra rafiNo ratings yet
- POPModule1 Part1Document45 pagesPOPModule1 Part1hchandrika116No ratings yet
- HardwareDocument26 pagesHardwarebaani22100% (1)
- AttachmentDocument8 pagesAttachmentManalAmerNo ratings yet
- Reducing Balance Method-9F258Document2 pagesReducing Balance Method-9F258amarashah182No ratings yet
- Jan 2020 P2 AnswersDocument24 pagesJan 2020 P2 Answersamarashah182No ratings yet
- E) THE CARBON, NITROGEN CYCLEDocument2 pagesE) THE CARBON, NITROGEN CYCLEamarashah182No ratings yet
- End of Term RevisionDocument12 pagesEnd of Term Revisionamarashah182No ratings yet
- AnansiDocument2 pagesAnansiamarashah182No ratings yet
- Provision For Bad-7B5D2Document7 pagesProvision For Bad-7B5D2amarashah182No ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis-1C135Document2 pagesRatio Analysis-1C135amarashah182No ratings yet
- CSEC Information Technology P1 2008Document12 pagesCSEC Information Technology P1 2008amarashah182No ratings yet
- B) THE EXCRETORY SYSTEMDocument5 pagesB) THE EXCRETORY SYSTEMamarashah182No ratings yet
- J) RespirationDocument3 pagesJ) Respirationamarashah182No ratings yet
- SFCSS SBA Problem Solving and Programming Assignment 2022Document1 pageSFCSS SBA Problem Solving and Programming Assignment 2022amarashah182No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 The Hamsa (Udhav Gita)Document7 pagesChapter 13 The Hamsa (Udhav Gita)Vishnu Prakash NangathNo ratings yet
- Lighting Global Standardized Specifications Book: Manufacturer: Component Family NameDocument4 pagesLighting Global Standardized Specifications Book: Manufacturer: Component Family NamemagaliNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Incidence and Risk Factors For Early Acute Kidney Injury in Nonsurgical Patients: A Cohort StudyDocument9 pagesResearch Article: Incidence and Risk Factors For Early Acute Kidney Injury in Nonsurgical Patients: A Cohort StudyAbdul RahimNo ratings yet
- Diklofenac DietilaminDocument12 pagesDiklofenac DietilaminAnnisa FitrianaNo ratings yet
- Us2-9a Study GuideDocument3 pagesUs2-9a Study Guideapi-517994178No ratings yet
- Lenskart DMDocument8 pagesLenskart DMmonu ShahNo ratings yet
- Phacoemulsification Made EasyDocument2 pagesPhacoemulsification Made EasymidoNo ratings yet
- Everything by David A. White: Week 5 Lesson Plan: What Is Fair? Day 1Document2 pagesEverything by David A. White: Week 5 Lesson Plan: What Is Fair? Day 1rerereNo ratings yet
- ZXCTN Seamless MPLS (BGP LU) Principles and Applications - R1.1Document24 pagesZXCTN Seamless MPLS (BGP LU) Principles and Applications - R1.1kyi lwinNo ratings yet
- Antiquiera, April Jonz, Morales: Sangley Point National High SchoolDocument5 pagesAntiquiera, April Jonz, Morales: Sangley Point National High SchoolMatthew HermanoNo ratings yet
- Charlie-Rose Evans ResumeDocument3 pagesCharlie-Rose Evans Resumeapi-309085679No ratings yet
- SDS 99121967 enDocument11 pagesSDS 99121967 enGray WangNo ratings yet
- PHP Architect - 2017 01 JanuaryDocument52 pagesPHP Architect - 2017 01 JanuaryRafi SMNo ratings yet
- Transition TheoryDocument36 pagesTransition TheoryMatty Jolbitado100% (1)
- Nepal Conference BrochureDocument20 pagesNepal Conference BrochureSuresh Kumar BhandariNo ratings yet
- Mar Apr 06Document34 pagesMar Apr 06Bot PsalmernaNo ratings yet
- Transmission Lines and Waveguides: UniversityDocument16 pagesTransmission Lines and Waveguides: UniversityRaj GaneshNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Time Dose Fractionation TDF ConceptsDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 - Time Dose Fractionation TDF Conceptsapi-299138743No ratings yet
- Operating and Maintenance Instructions On Tobul AccumulatorsDocument8 pagesOperating and Maintenance Instructions On Tobul AccumulatorszhenyupanNo ratings yet
- FFL - 0.15 FFL - 0.15: 1000 DoorDocument1 pageFFL - 0.15 FFL - 0.15: 1000 DoorAvanish SinghNo ratings yet
- KTPMDocument6 pagesKTPMBợmNo ratings yet
- Educ - 7 Assessment in Learning 2Document4 pagesEduc - 7 Assessment in Learning 2Rheame Quita DoriaNo ratings yet
- ALS - Pysical ScienceDocument7 pagesALS - Pysical ScienceMarcial MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Avesta Finishing Solutions For Petrochemicals IndustryDocument92 pagesAvesta Finishing Solutions For Petrochemicals IndustryHAKANNo ratings yet
- Railway Recruitment Board: Employment Notice No. 3/2007Document4 pagesRailway Recruitment Board: Employment Notice No. 3/2007hemanth014No ratings yet
- Agency Theory EssayDocument2 pagesAgency Theory EssayAnggi KartikaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System NotesDocument8 pagesRespiratory System NotesKomalesh TheeranNo ratings yet