Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assessment - Recuenco
Uploaded by
John Kenneth RecuencoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assessment - Recuenco
Uploaded by
John Kenneth RecuencoCopyright:
Available Formats
ACTIVITY ON ASSESSMENT
Name: JOHN KENNETH Q. RECUENCO
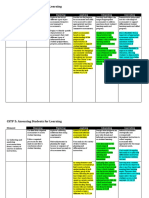
1. Illustrate using Venn diagram the similarity and differences between
a. Assessment of Learning vs. Assessment for Learning
ASSESSMENT OF LEARNING ASSESSMENT FOR LEARNING
Assessment of learning refers to
an approach to teaching and
strategies designed to confirm
learning that creates feedback
what students know,
Both are geared which is then used to improve
demonstrate whether or not
towards providing students' performance. Students
they have met curriculum
fair and sound become more involved in the
outcomes or the goals of their
assessment strategy learning process and from this
individualized programs, or to
for varied learners. gain confidence in what they are
certify proficiency and make
expected to learn and to what
decisions about students' future
standard.
programs or placements.
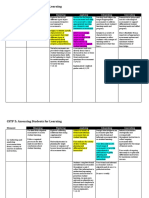
b. Assessment of learning vs. Assessment in Learning
ASSESSMENT OF LEARNING ASSESSMENT AS LEARNING
Assessment of learning refers to
strategies designed to confirm involves students monitoring
what students know, Both are geared and gathering information about
demonstrate whether or not towards providing their own learning. They do this
they have met curriculum fair and sound through self and/or peer-
outcomes or the goals of their assessment strategy assessments to help understand
individualized programs, or to for varied learners. how they are progressing in their
certify proficiency and make learning, and what, if anything,
decisions about students' future they can do to improve.
programs or placements.
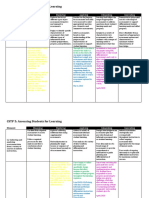
c. Assessment for learning vs. Assessment as Learning
ASSESSMENT FOR LEARNING ASSESSMENT AS LEARNING
an approach to teaching and
involves students monitoring
learning that creates feedback Both are geared
and gathering information about
which is then used to improve towards
their own learning. They do this
students' performance. Students providing fair
through self and/or peer-
become more involved in the and sound
assessments to help understand
learning process and from this assessment
how they are progressing in their
gain confidence in what they are strategy for
learning, and what, if anything,
expected to learn and to what varied learners.
they can do to improve.
standard.
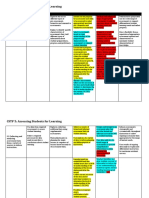
d. Assessment of Learning vs. Assessment for Learning vs. Assessment in Learning.
ASSESSMENT OF LEARNING
Assessment of learning refers to strategies
designed to confirm what students know,
demonstrate whether or not they have met
curriculum outcomes or the goals of their
individualized programs, or to certify proficiency
and make decisions about students' future
programs or placements.
ASSESSMENT FOR LEARNING ASSESSMENT AS LEARNING
These forms of assessment are constructed
in order to determine various types of
learning of learners before, during and
after the process of assessment. Leads to
holistic development of learners through
an efficient and suitable assessment.
an approach to teaching and learning that involves students monitoring and gathering
creates feedback which is then used to improve information about their own learning. They do
students' performance. Students become more this through self and/or peer- assessments to
involved in the learning process and from this help understand how they are progressing in
gain confidence in what they are expected to their learning, and what, if anything, they can
learn and to what standard. do to improve.
2. Using Venn diagram, Illustrates the distinction between Traditional Assessment and
modern assessment (technology aid-based assessment).
TRADITIONAL ASSESSMENT MODERN ASSESSMENT
“tests” taken with paper and powerful way to assess learners'
pencil that are usually true/false, knowledge, skills, and attitudes.
matching, or multiple choice. Examples of such methods
Both types of assessment are
These assessments are easy to include online quizzes and tests,
efficient when used on
grade, but only test isolated digital portfolios, e-portfolios,
various types of learning and
application, facts, or memorized simulations and games, and
assessment situations.
data at lower-level thinking multimedia projects. deals with
skills. There are forms of innovative survey techniques
The most widely used traditional assessment requiring and testing methods—for
assessment tools are multiple- traditional approach whilst example, computer- and
choice tests, true/false tests, others require a more internet-based competence
short answers, and essays. modern or technology-based testing.
True/false tests: True/false assessment.
items require students to make
a decision and find out which of
two potential responses is true.
3. Differentiates Basic Assessment from Advanced Educational assessment and cite some
instances.
BASIC ASSESSMENT ADVANCE EDUCATIONAL ASSESSMENT
the systematic basis for making
inferences about the learning the systematic process of
and development of students. It documenting and using
is the process of defining, Basic and advance educational empirical data on the
selecting, designing, collecting, assessment goes together. Basic knowledge, skill, attitudes,
analyzing, interpreting, and assessment takes precedence aptitude and beliefs to refine
using information to increase over advance educational programs and improve student
students' learning and assessment. A good mastery of learning. he systematic process
development. There are three the basic types of assessment of finding out about a student's
types of assessment: diagnostic, will be helpful towards knowledge, experience, skills,
formative, and summative. practicing advance educational and beliefs using empirical data.
Although are three are generally assessments. The ultimate goal is to quantify
referred to simply as and document how much a
assessment, there are distinct student knows.
differences between the three.
4. Make a timeline/step on how assessment inside your classroom being done as a
teacher.
SALIENT STEPS ON HOW ASSESSMENT IS DONE INSIDE THE CLASSROOM:
The basic steps in the classroom assessment process are:
1. Choose a learning goal to assess and identify possible learning outcomes.
2. Choose an assessment technique or method of assessment.
3. Determine and set criteria or standard
4. Apply the technique.
5. Gather evidence
6. Analyze and interpret the data and share the results with students.
7. Respond to the data.
8. Review results and implement change based on results.
9. Execute improvement actions
10. Document assessment process and cycle
11. Go back to step 1 and never stop helping and improving learners.
5. Discuss briefly in your own words the following and give some instances:
a. Measurement theory.
It is the thought process and interrelated body of knowledge that form the basis of valid
measurements. Translation of measurement theory to behaviors helps to ensure the integrity
and relevancy of tests and the data that result from them.
This theory seeks to represent a latent (unobserved) construct with one or more observable
indicators (operational measures or variables) that accurately capture a theoretically
intended concept.
b. Reliability and validity.
Reliability - A measure of consistency. It is the degree to which student results are the same
when they take the same test on different occasions, when different scorers score the same
item or task, and when different but equivalent tests are taken at the same time or at different
times.
Validity - Educational assessment should always have a clear purpose, making validity the
most important attribute of a good test. The validity of an assessment tool is the extent to
which it measures what it was designed to measure, without contamination from other
characteristics. For example, a test of reading comprehension should not require
mathematical ability.
c. Item response theory.
It is also known as the latent response theory refers to a family of mathematical models that
attempt to explain the relationship between latent traits (unobservable characteristic or
attribute) and their manifestations (i.e. observed outcomes, responses or performance).
They establish a link between the properties of items on an instrument, individuals
responding to these items and the underlying trait being measured. IRT assumes that the
latent construct (e.g. stress, knowledge, attitudes) and items of a measure are organized in
an unobservable continuum. Therefore, its main purpose focuses on establishing the
individual’s position on that continuum.
6. Using Venn Diagram, illustrates the following
a. Formative and summative assessment.
FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT
a planned, ongoing process used
an assessment administered at
by all students and teachers
These two types of the end of an instructional unit
during learning and teaching to
assessment complete in a course. These assessments
elicit and use evidence of
the teaching learning are intended to evaluate student
student learning to improve
process. After a series learning by comparing
student understanding of
of formative performance to a standard or
intended disciplinary learning
assessments, and benchmark. They are often high-
outcomes and support students
innovations in teaching, stakes, meaning they have a
to become self-directed
comes the summative high point value. evaluate
learners. Formative
assessment that assess student learning at the end of an
assessments have low stakes
the level of mastery of instructional unit by comparing
and usually carry no grade,
learners. it against some standard or
which in some instances may
benchmark.
discourage the students from
doing the task or fully engaging
with it.
b. Performance-based assessment and authentic assessment.
PERFORMANCE-BASED ASSESSMENT AUTHENTIC ASSESSMENT
Performance-based assessment Focuses on students using and
requires students to applying knowledge and skills in
demonstrate or apply their real-life settings. For example,
knowledge, skills, and strategies Performance based you might have students take
by creating a response or assessment goes beyond part in: a simulation or role play
product or doing a task. just assessment using of a scenario. completion of a
Performance-based learning is paper and pencil test and real-world task. assessment in a
when students participate in utilizes higher level of workplace setting. the idea of
performing tasks or activities thinking and domain and using creative learning
that are meaningful and authentic assessment experiences to test students'
engaging. The purpose of this provides an environment skills and knowledge in realistic
kind of learning is to help where they can be situations. Authentic assessment
students acquire and apply assessed authentically and measures students' success in a
knowledge, practice skills, and genuinely. way that's relevant to the skills
develop independent and required of them once they've
collaborative work habits. finished your course or degree
You might also like
- Art of Developing Positive AttitudeDocument48 pagesArt of Developing Positive AttitudeShafak MahajanNo ratings yet
- 41 Harmful Manipulation TacticsDocument12 pages41 Harmful Manipulation TacticsKimberly StanfordNo ratings yet
- Psychology For PhysiotherapistsDocument211 pagesPsychology For PhysiotherapistsAkshaya Mistry89% (18)
- Asperger Syndrome and Psychotherapy Understanding Asperger PerspectivesDocument173 pagesAsperger Syndrome and Psychotherapy Understanding Asperger PerspectivesCindy Ramona FaluvegiNo ratings yet
- Passing Exams with Confidence Strategies for Study Habit ImprovementFrom EverandPassing Exams with Confidence Strategies for Study Habit ImprovementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Is It Working in Your Middle School?: A Personalized System to Monitor Progress of InitiativesFrom EverandIs It Working in Your Middle School?: A Personalized System to Monitor Progress of InitiativesNo ratings yet
- Educational ObjectivesDocument15 pagesEducational Objectivesmadhurima kundu100% (2)
- FS 1 Episode 9Document10 pagesFS 1 Episode 9Diane Lyn D. Sindo IINo ratings yet
- MECHANICS AND RUBRIC For MonologueDocument1 pageMECHANICS AND RUBRIC For MonologueLee Nico Emiliano0% (1)
- ASSESSMENT IN LEARNING FinalDocument62 pagesASSESSMENT IN LEARNING FinalLance Go LlanesNo ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Clift 5Document8 pagesCSTP 5 Clift 5api-622179254No ratings yet
- Assessment - SaberdoDocument5 pagesAssessment - SaberdoJohn Kenneth RecuencoNo ratings yet
- Terminologies in Graphic OrganizersDocument4 pagesTerminologies in Graphic OrganizersChery-Ann GorospeNo ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Matuchniak 0423Document8 pagesCSTP 5 Matuchniak 0423api-572629820No ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Moser 3Document9 pagesCSTP 5 Moser 3api-572147191No ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Nguyen 9Document8 pagesCSTP 5 Nguyen 9api-492431821No ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Callahan0921Document8 pagesCSTP 5 Callahan0921api-573026598No ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Camp Updated 5:6:23Document10 pagesCSTP 5 Camp Updated 5:6:23Nancy CampNo ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Bernstein Semester 3Document8 pagesCSTP 5 Bernstein Semester 3api-483682821No ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Howell 3Document9 pagesCSTP 5 Howell 3api-622177304No ratings yet
- D 63 Aaaa 8 B 36 FBDocument7 pagesD 63 Aaaa 8 B 36 FBapi-468780445No ratings yet
- Guiding Principles For CBE AssessmentDocument8 pagesGuiding Principles For CBE AssessmentfleurmodafemininaNo ratings yet
- CSTP 5: Assessing Students For Learning: Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating InnovatingDocument10 pagesCSTP 5: Assessing Students For Learning: Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating InnovatingNancy CampNo ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Nersesian-4Document10 pagesCSTP 5 Nersesian-4api-699871570No ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Stack 9Document8 pagesCSTP 5 Stack 9api-528653613No ratings yet
- AL 1.1 - Concepts and Relevance of AssessmentDocument3 pagesAL 1.1 - Concepts and Relevance of AssessmentJessa ParedesNo ratings yet
- cstp5 Sarah Clingan 7Document8 pagescstp5 Sarah Clingan 7api-679242917No ratings yet
- CSTP 5: Assessing Students For Learning: Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating InnovatingDocument10 pagesCSTP 5: Assessing Students For Learning: Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating InnovatingNancy CampNo ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Sullivan 7Document8 pagesCSTP 5 Sullivan 7api-621945476No ratings yet
- CSTP 5: Assessing Students For Learning: Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating InnovatingDocument8 pagesCSTP 5: Assessing Students For Learning: Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating InnovatingLacey WoolstonNo ratings yet
- cstp5 EspalinDocument9 pagescstp5 Espalinapi-573214664No ratings yet
- 5 CSTPDocument8 pages5 CSTPapi-432388156No ratings yet
- CTSP 5 Urziklove 5Document8 pagesCTSP 5 Urziklove 5api-468542718No ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Williams-Hackman F19Document12 pagesCSTP 5 Williams-Hackman F19Lauren Williams-HackmanNo ratings yet
- CSTP 5 MacLachlan 9.20.22Document8 pagesCSTP 5 MacLachlan 9.20.22James MacLachlanNo ratings yet
- CSTP 5 DiazTrejoDocument8 pagesCSTP 5 DiazTrejoMelissa Diaz-TrejoNo ratings yet
- PDF CSTP 5 Timm 04Document10 pagesPDF CSTP 5 Timm 04api-678539949No ratings yet
- Cstp5 Mark BricenoDocument8 pagesCstp5 Mark BricenoMark BricenoNo ratings yet
- SS14 ReviewerDocument13 pagesSS14 ReviewerAnthony Jovan Munoz Tan IINo ratings yet
- cstp5 Ramos 7Document7 pagescstp5 Ramos 7api-679112611No ratings yet
- Name: Nayab Amjad ROLL NO: MCF1900609 Program: Ma Education (Morning)Document27 pagesName: Nayab Amjad ROLL NO: MCF1900609 Program: Ma Education (Morning)Nayab Amjad Nayab AmjadNo ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Meyer 12Document8 pagesCSTP 5 Meyer 12api-572185051No ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Salamone 12.10.23Document7 pagesCSTP 5 Salamone 12.10.23taylornsalamoneNo ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Mackie 4Document9 pagesCSTP 5 Mackie 4api-542739600No ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Roth 10Document8 pagesCSTP 5 Roth 10api-557225182No ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Glass 10-1-22 1Document8 pagesCSTP 5 Glass 10-1-22 1api-557253004No ratings yet
- cstp5 2009Document7 pagescstp5 2009api-557045107No ratings yet
- cstp5 1 Newman 12Document8 pagescstp5 1 Newman 12api-622511939No ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Goodman 11.28.22Document8 pagesCSTP 5 Goodman 11.28.22Samantha GoodmanNo ratings yet
- Ed7 ReviewerDocument11 pagesEd7 ReviewerMarbelyn BarbosaNo ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Camp Updated 12:5:22Document10 pagesCSTP 5 Camp Updated 12:5:22Nancy CampNo ratings yet
- ASL Module 1 Assessment WITH ANSWERSDocument14 pagesASL Module 1 Assessment WITH ANSWERSAeron Chester DinoNo ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Hopson 535Document7 pagesCSTP 5 Hopson 535api-557172309No ratings yet
- CSTP 5Document4 pagesCSTP 5api-701835949No ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Salamone 4.30.24Document7 pagesCSTP 5 Salamone 4.30.24taylornsalamoneNo ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Kaczmarek 12Document8 pagesCSTP 5 Kaczmarek 12api-528489480No ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Aoki 9Document8 pagesCSTP 5 Aoki 9api-572429129No ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Kvale 9Document8 pagesCSTP 5 Kvale 9api-637091703No ratings yet
- Assessment in Learning 1 DietherDocument18 pagesAssessment in Learning 1 DietherMery Rose AdelanNo ratings yet
- Gumpal Asynch 1 KWL ChartDocument1 pageGumpal Asynch 1 KWL Chartapi-712266337No ratings yet
- W8.pentaksiran PembelajaranDocument54 pagesW8.pentaksiran PembelajaranEyka YanaNo ratings yet
- CSTP 5 Steiss 7Document8 pagesCSTP 5 Steiss 7api-678983495No ratings yet
- READING GUIDE Chapter 7-Assessment (Shin & Crandall, 2014)Document3 pagesREADING GUIDE Chapter 7-Assessment (Shin & Crandall, 2014)Julian BarreroNo ratings yet
- All REVIEWER in ASLDocument10 pagesAll REVIEWER in ASLydolem940No ratings yet
- Empowering Growth - Using Proficiency Scales for Equitable and Meaningful Assessment: Quick Reads for Busy EducatorsFrom EverandEmpowering Growth - Using Proficiency Scales for Equitable and Meaningful Assessment: Quick Reads for Busy EducatorsNo ratings yet
- Who Packed Your Parachute? Why Multiple Attempts on Assessments Matter: Quick Reads for Busy EducatorsFrom EverandWho Packed Your Parachute? Why Multiple Attempts on Assessments Matter: Quick Reads for Busy EducatorsNo ratings yet
- The Power of MindDocument20 pagesThe Power of MindDane KylieNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 CBDocument13 pagesUnit 4 CBAnilBahugunaNo ratings yet
- Interview For Employers HotelDocument2 pagesInterview For Employers HotelKurnia SandiNo ratings yet
- Outline and Evaluate Infradian And/or Ultradian Rhythms (16 Marks)Document2 pagesOutline and Evaluate Infradian And/or Ultradian Rhythms (16 Marks)HumaNo ratings yet
- The Wiley Blackwell Handbook of Childhood Social Development 3Rd Edition Peter K Smith All ChapterDocument67 pagesThe Wiley Blackwell Handbook of Childhood Social Development 3Rd Edition Peter K Smith All Chapterveronica.reaver962100% (8)
- 35.4 Uses Principles of Effective Speech Writing Focusing On Facial Expressions, Gestures and MovementsDocument4 pages35.4 Uses Principles of Effective Speech Writing Focusing On Facial Expressions, Gestures and MovementsWayne Dolorico MillamenaNo ratings yet
- Meta-Analysis of Comparative Studies of Depression in Mothers of Children With and Without Developmental DisabilitiesDocument15 pagesMeta-Analysis of Comparative Studies of Depression in Mothers of Children With and Without Developmental DisabilitiesLudmila MenezesNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Aspects of Goal-Setting and Motivation in RehabilitationDocument24 pagesTheoretical Aspects of Goal-Setting and Motivation in RehabilitationcrisNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in Mapeh HealthDocument2 pagesSummative Test in Mapeh HealthEthel Marie Casido BurceNo ratings yet
- Jahoda Salud Mental PositivaDocument14 pagesJahoda Salud Mental PositivaDavid Ponce HernandezNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal Wajdi-ReadyDocument4 pagesResearch Proposal Wajdi-ReadyNadia KhanNo ratings yet
- Emdr Research Evaluated Clinical ApplicationsDocument19 pagesEmdr Research Evaluated Clinical ApplicationsVivian RiveraNo ratings yet
- Literature Review 2Document8 pagesLiterature Review 2api-511258439No ratings yet
- Spiritual Intelligence and Resilience Among Christian Youth in KeralaDocument1 pageSpiritual Intelligence and Resilience Among Christian Youth in KeralaCristina Teixeira PintoNo ratings yet
- Self DevelopmentDocument21 pagesSelf DevelopmentNovie Jane HontiverosNo ratings yet
- Problems Faced by Partime Job StudentsDocument2 pagesProblems Faced by Partime Job StudentsAbbasi Arshad HussainNo ratings yet
- Siena College, Inc.: Passion For Truth and Compassion For HumanityDocument10 pagesSiena College, Inc.: Passion For Truth and Compassion For HumanityBrave MitraNo ratings yet
- I Like What She's #Endorsing The Impact of PDFDocument40 pagesI Like What She's #Endorsing The Impact of PDFBasitAliJadoonNo ratings yet
- Survey ResultDocument6 pagesSurvey ResultAbdul RahimNo ratings yet
- Book Structure: Taha KarramDocument13 pagesBook Structure: Taha KarramI'MOTOTAHANo ratings yet
- Running Head: INSIDE OUT 1Document4 pagesRunning Head: INSIDE OUT 1Breanna ThomsenNo ratings yet
- Culminating Activity PR 1Document3 pagesCulminating Activity PR 1andrew0% (1)
- Addictive TradingDocument4 pagesAddictive TradingmanickNo ratings yet