100% found this document useful (2 votes)
317 views67 pagesEPC Contracts
Uploaded by
ehs.ashutoshCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
317 views67 pagesEPC Contracts
Uploaded by
ehs.ashutoshCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction to EPC Contracts: Provides an introductory overview of EPC (Engineering, Procurement, and Construction) contracts.
- Contract Overview: Discusses what EPC contracts entail, including key issues and challenges.
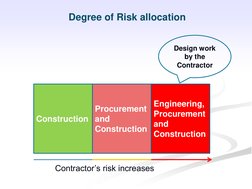
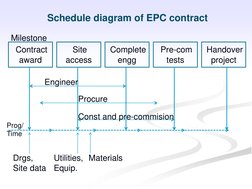
- EPC Contract Details: Outlines the scope, responsibilities, and risk allocation involved in EPC contracts.