Professional Documents
Culture Documents
გრამატიკა
Uploaded by
gio9033710 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesg
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentg
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesგრამატიკა
Uploaded by
gio903371g
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
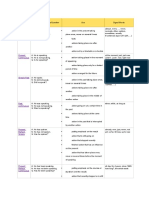
able of English Tenses
tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words
always, every …,
Simple A: He speaks. action in the present taking never, normally,
Present N: He does not speak. place regularly, never or several often, seldom,
Q: Does he speak? sometimes, usually
times if sentences type I (If
facts I talk, …)
actions taking place one after
another
action set by a timetable or
schedule
Present A: He is speaking. at the moment, just,
Progressive N: He is not speaking. action taking place in the moment just now, Listen!,
Q: Is he speaking? of speaking Look!, now, right now
action taking place only for a
limited period of time
action arranged for the future
Simple Past A: He spoke. yesterday, 2 minutes
N: He did not speak. action in the past taking place once, ago, in 1990, the other
Q: Did he speak? never or several times day, last Friday
if sentence type II (If
actions taking place one after I talked, …)
another
action taking place in the middle of
another action
Past A: He was speaking. while, as long as
Progressive N: He was not speaking. action going on at a certain time in
Q: Was he speaking? the past
actions taking place at the same
time
action in the past that is interrupted
by another action
Present A: He has spoken. already, ever, just,
Perfect N: He has not spoken. putting emphasis on the result never, not yet, so far,
Simple Q: Has he spoken? action that is still going on till now, up to now
action that stopped recently
finished action that has an influence
on the present
action that has taken place once,
never or several times before the
moment of speaking
Present A: He has been speaking. all day, for 4 years,
Perfect N: He has not been speaking. putting emphasis on the course or since 1993, how
Progressive Q: Has he been speaking? duration (not the result) long?, the whole week
action that recently stopped or is
still going on
finished action that influenced the
present
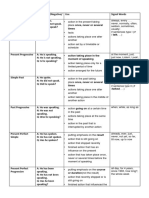
Past A: He had spoken. already, just, never,
Perfect N: He had not spoken. action taking place before a certain not yet, once, until
Simple Q: Had he spoken? time in the past that day
if sentence type III (If
sometimes interchangeable with I had talked, …)
past perfect progressive
putting emphasis only on
the fact (not the duration)
Past A: He had been speaking. for, since, the whole
Perfect N: He had not been speaking. action taking place before a certain day, all day
Progressive Q: Had he been speaking? time in the past
sometimes interchangeable with
past perfect simple
putting emphasis on the duration
or course of an action
Future I A: He will speak. in a year, next …,
Simple N: He will not speak. action in the future that cannot be tomorrow
Q: Will he speak? influenced If-Satz Typ I (If you
ask her, she will
spontaneous decision helpyou.)
assumption: I think,
assumption with regard to the probably, perhaps
future
Future I A: He is going to speak. in one year, next
Simple N: He is not going to speak. decision made for the future week, tomorrow
Q: Is he going to speak? conclusion with regard to the future
(going to)
Future I A: He will be speaking. in one year, next
Progressive N: He will not be speaking. action that is going on at a certain week, tomorrow
Q: Will he be speaking? time in the future
action that is sure to happen in the
near future
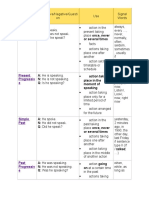
Future II A: He will have spoken. by Monday, in a week
Simple N: He will not have spoken. action that will be finishedat a
Q: Will he have spoken? certain time in the future
Future II A: He will have been speaking. for …, the last couple
Progressive N: He will not have been action taking place before a certain of hours, all day long
speaking. time in the future
Q: Will he have been speaking?
putting emphasis on the course of
an action
Conditional A: He would speak. if sentences type II
I Simple N: He would not speak. action that might take place (If I were you,
Q: Would he speak? I would go home.)
Conditional A: He would be speaking.
I N: He would not be speaking. action that might take place
Progressive Q: Would he be speaking? putting emphasis on
thecourse / duration of the action
Conditional A: He would have spoken. if sentences type III
II Simple N: He would not have spoken. action that might have taken place (If I had seen that,
Q: Would he have spoken? in the past Iwould have helped.)
Conditional A: He would have been speaking.
II N: He would not have been action that might have taken place
Progressive speaking. in the past
Q: Would he have been speaking?
puts emphasis on
the course / duration of the action
You might also like
- The Fun Way To Learn EnglishDocument7 pagesThe Fun Way To Learn EnglishPatrascu CristiNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: GrammarDocument2 pagesTable of English Tenses: GrammarGenesis Belen0% (1)
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument2 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentClaudiaNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsMarko MillaNo ratings yet
- Kirkwood School District Directory 2014-15Document32 pagesKirkwood School District Directory 2014-15timesnewspapersNo ratings yet
- Rejoinder On Sedan Corrected - Doc 5.29.17Document4 pagesRejoinder On Sedan Corrected - Doc 5.29.17Hoven Macasinag100% (1)
- Valuation in The Airline Industry Excel FileDocument12 pagesValuation in The Airline Industry Excel FilevivekNo ratings yet
- BELSONDRA - BT Retail Case AnalysisDocument4 pagesBELSONDRA - BT Retail Case AnalysisSim BelsondraNo ratings yet
- General Hospital Level 3Document3 pagesGeneral Hospital Level 3Cloe Dianne SillaNo ratings yet
- Persian EnglishDocument802 pagesPersian Englishshoaibahmed_1933% (3)
- Iwo Jima Amphibious Ready Group/24TH Marine Expeditionary Unit (IWOARG/24 MEU) NDIA Post-Deployment BriefDocument13 pagesIwo Jima Amphibious Ready Group/24TH Marine Expeditionary Unit (IWOARG/24 MEU) NDIA Post-Deployment Briefthatguy96No ratings yet
- Tenses PDFDocument2 pagesTenses PDFgeraskewesNo ratings yet
- Tenses - Ready Reckoner: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument7 pagesTenses - Ready Reckoner: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRajalakshmi Gajapathy100% (2)
- Ortopedie Traumatologie Schite Examen PracticDocument46 pagesOrtopedie Traumatologie Schite Examen PracticMarcela BucicăNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Amirul Asyraaf Bin Zainuddin MKT 558 Group Assignment 1 CookieslyciousDocument9 pagesMuhammad Amirul Asyraaf Bin Zainuddin MKT 558 Group Assignment 1 CookieslyciousMohd HarithNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument2 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentBogdan ChișcababiiNo ratings yet
- Eng Grammar Parts of SpeechDocument3 pagesEng Grammar Parts of Speechsami karemNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument2 pagesSimple Present: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsAdailton SamuelNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: I Talked, )Document2 pagesSimple Present: I Talked, )Seminarski Radovi Iz IstorijeNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordslovely innocentNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument10 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsMina SamyNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Simple PresentNorvin TreminioNo ratings yet
- Tiempos Verbales Cuadro ColegioDocument2 pagesTiempos Verbales Cuadro ColegioelisaNo ratings yet
- Times: I Talk, )Document11 pagesTimes: I Talk, )mugiNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRanjit KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.tense Table (At Start of Tenses)Document3 pages1.tense Table (At Start of Tenses)Adeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsGiannina Ailén MusacchioNo ratings yet
- Tense TABLE DE PE NET - BUNDocument2 pagesTense TABLE DE PE NET - BUNMirela MarinNo ratings yet
- Verbos, Adjetivos y Sustanfivos en InglésDocument242 pagesVerbos, Adjetivos y Sustanfivos en InglésVioleta Patricia Molet100% (1)
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsInga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses Chart: Tense Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesVerb Tenses Chart: Tense Use Signal WordsmllorenteNo ratings yet
- Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesAffirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsKavitha RajendranNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument3 pagesInglesazoljamiaidounNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Simple PresentSofiene GuedriNo ratings yet
- Guia de Ingles 11 de Informatica Semana 5 Ii PartialDocument5 pagesGuia de Ingles 11 de Informatica Semana 5 Ii PartialLizzy Yessenia Torres 11- 8 BCHNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jul 15, 2023Document2 pagesAdobe Scan Jul 15, 2023sumanta biswasNo ratings yet
- My English Grammar Guide CompressDocument39 pagesMy English Grammar Guide CompressBenny LeeNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentCristina ArdeleanNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Key WordsDocument2 pagesSimple Present: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Key Wordsyadhi20No ratings yet
- English TensesDocument4 pagesEnglish TensesLucaNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument2 pagesTable of English TensesRasta FariNo ratings yet
- TenseDocument2 pagesTenseKlaudia TerjékNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAngi BraileanuNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words Simple PresentDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words Simple Presentmanchiraju raj kumarNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument3 pagesEnglish Tensescoquin8816No ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument7 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAnonymous vqzyDYXkNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDahliya DwitaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentMarinela AnghelNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument2 pagesTable of English TensesOscar LunaNo ratings yet
- Tenses Cuadro ResumenDocument4 pagesTenses Cuadro ResumenGuillermo NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDiego GrañenaNo ratings yet
- Cours 2bac L en 04Document2 pagesCours 2bac L en 04hkuuiNo ratings yet
- English Grammar OnlineDocument6 pagesEnglish Grammar OnlineNasir IqbalNo ratings yet
- Tenses Chart With Examples Use and Signal WordsDocument1 pageTenses Chart With Examples Use and Signal WordsMustapha ElNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument5 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAlfi Ramdhani PNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/ USE Signal WordsDocument2 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/ USE Signal WordsradivojerNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument3 pagesTable of English TensesMelinaNo ratings yet
- Chart of English TensesDocument2 pagesChart of English TensesMaria ArtilesNo ratings yet
- Tenses Chart Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument2 pagesTenses Chart Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsanamariaNo ratings yet
- ÖzetDocument2 pagesÖzetEnes PolatNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Italk, )Document2 pagesSimple Present: Italk, )Enes PolatNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument4 pagesTensesLiliia RakNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument2 pagesTable of English TensesElmi Zulkarnain OsmanNo ratings yet
- All TensesDocument3 pagesAll TenseskarenNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument7 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAnonymous vqzyDYXkNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument2 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentJosé LiraNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument6 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentMarkoNo ratings yet
- English Course: Like I, Me (Personal Pronouns) or My, Mine (Possessive Pronouns)Document12 pagesEnglish Course: Like I, Me (Personal Pronouns) or My, Mine (Possessive Pronouns)Luis AlejandroNo ratings yet
- English 3Document114 pagesEnglish 3Pang TartarusNo ratings yet
- Rating Methodologies List of Rating Methodologies 03mar23Document31 pagesRating Methodologies List of Rating Methodologies 03mar23malingaNo ratings yet
- Tarea 6. ICT - Guide 2Document9 pagesTarea 6. ICT - Guide 2Jennifer Cardozo cruzNo ratings yet
- Likisha Ticket - TR8N15003825Document5 pagesLikisha Ticket - TR8N15003825Pratik PatilNo ratings yet
- Statutory Construction TanedoDocument3 pagesStatutory Construction TanedoRidmd TresNo ratings yet
- Q1. Explain The Need For Corporate Governance. Discuss Its Role and Importance in Improving The Performance of Corporate SectorDocument3 pagesQ1. Explain The Need For Corporate Governance. Discuss Its Role and Importance in Improving The Performance of Corporate SectorAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- Pulse PolioDocument27 pagesPulse PolioAbigail MelendezNo ratings yet
- After BrexitDocument7 pagesAfter Brexityosmeilys.ramirezNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Construction ContractDocument109 pagesChapter Three Construction ContractHayelom Tadesse GebreNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5-Computer 9th ClassDocument8 pagesChapter-5-Computer 9th ClassMudassar NaseemNo ratings yet
- Tcs Bancs Webservice Repository Document - InwarddirectcreditcorrectiontransactionDocument8 pagesTcs Bancs Webservice Repository Document - InwarddirectcreditcorrectiontransactionMuhammad Sheharyar MohsinNo ratings yet
- Positivism, The Separation of Law and MoralsDocument6 pagesPositivism, The Separation of Law and MoralsRifa adillahNo ratings yet
- Principles of Business Sba - Rachael BrownDocument23 pagesPrinciples of Business Sba - Rachael BrownRachael BrownNo ratings yet
- KRA 1. Maternal, Neonatal, Child Health and Nutrition (MNCHN)Document7 pagesKRA 1. Maternal, Neonatal, Child Health and Nutrition (MNCHN)Tmo BosNo ratings yet
- Pulalun Gets Recognition - Quo Vadis Other SultansDocument2 pagesPulalun Gets Recognition - Quo Vadis Other SultansIcas PhilsNo ratings yet
- Sources PageDocument4 pagesSources Pageapi-106353803No ratings yet
- Begining of A New Era Unit-IiDocument14 pagesBegining of A New Era Unit-IiANJU ASHOKANNo ratings yet
- Homeless Serving Land Use Overnight Shelter Parcel DataDocument14 pagesHomeless Serving Land Use Overnight Shelter Parcel DataAbhishekh GuptaNo ratings yet
- YB1941Document504 pagesYB1941Brendan Paul Valiant100% (1)
- Armory v. DelamirieDocument1 pageArmory v. DelamiriePerez_Subgerente01No ratings yet
- Provisional Answer KeyDocument11 pagesProvisional Answer KeyFreshflowerNo ratings yet