Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Beige Minimalist Elegant Daily Notes Planner
Beige Minimalist Elegant Daily Notes Planner
Uploaded by
ADDISON PONICH0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesbiology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentbiology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesBeige Minimalist Elegant Daily Notes Planner
Beige Minimalist Elegant Daily Notes Planner
Uploaded by
ADDISON PONICHbiology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
NOTES
taxonomy date: April 27
Genetic Diversity: It's not just important for adaptation but also for ensuring
the long-term survival of a species by providing the raw material for natural
selection.
Importance of Biodiversity: It's highlighted through various aspects such as
the provision of resources like fresh water and food, regulation of services
like erosion, and the support of multiple life forms through nutrient cycling
and habitat availability.
Syilx siwik™ Strategy: It emphasizes the importance of water (siwik) and
equality among all forms of life, reflecting a holistic approach to biodiversity
conservation.
Taxonomy: It's crucial for organizing the vast diversity of life on Earth,
enabling scientists to understand relationships between organisms and
study their characteristics
Aristotle, an ancient Greek thinker, is known for his early attempts at
categorizing living organisms into plants and animals. His classifications
were based on observable characteristics and habitat, setting the stage for
future advancements in taxonomy.
Carolus Linnaeus, an 18th-century Swedish botanist, is credited as the
"father of taxonomy" for introducing binomial nomenclature and a
hierarchical classification system based on structural similarities.
Taxonomy is a system that categorizes and organizes living organisms
based on their shared characteristics and evolutionary relationships. It
involves hierarchical groupings, from broad categories like domains and
kingdoms to specific classifications like genus and species.
Species Concept: The text discusses the challenges of defining a species,
especially in cases of asexual reproduction or fossil records, highlighting
the complexity of biological classification.
Binomial Nomenclature: Besides accurately naming organisms, it also
prevents confusion and misnomers, ensuring consistency in scientific
communication.
Classification Principles: They're based not only on structural similarities
but also on biochemical composition, behaviour, and reproductive
isolation, providing insights into evolutionary relationships.
Dichotomous Keys: These keys are practical tools used by scientists to
identify organisms based on observable characteristics, facilitating
classification and taxonomy.
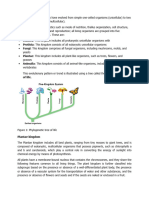
Kingdoms and Domains: The classification system has evolved to include
kingdoms and domains, reflecting advancements in our understanding
of the diversity of life and its evolutionary history.
The Tree of Life: It serves as a visual representation of the evolutionary
relationships among all living organisms, illustrating the
interconnectedness and shared ancestry of life on Earth.
domain
kingdom
phylum
class
order
family
genus
species
You might also like
- Systematics Based On Evolutionary Relationship 1Document13 pagesSystematics Based On Evolutionary Relationship 1Keith Penaso100% (3)
- Joining Kit - Editable V3Document30 pagesJoining Kit - Editable V3yash khitouliaNo ratings yet
- Education: ScienceDocument14 pagesEducation: ScienceLamiche EdalNo ratings yet
- GooglepreviewDocument35 pagesGooglepreviewTricia Mae ReyesNo ratings yet
- Risk Based Auditing Ebook PDFDocument11 pagesRisk Based Auditing Ebook PDFAsepWahyuPrabowo100% (1)
- Ethics and Politics Aristotle PDFDocument2 pagesEthics and Politics Aristotle PDFTimNo ratings yet
- Systematic BiologyDocument42 pagesSystematic BiologyYlane Lee100% (1)
- Classification: Essential Question Why Is It Important To Place Living Things Into Categories?Document45 pagesClassification: Essential Question Why Is It Important To Place Living Things Into Categories?Martin TisherNo ratings yet
- Biology and EcologyDocument5 pagesBiology and EcologykarennNo ratings yet
- Classification of OrganismDocument35 pagesClassification of OrganismJnll JstnNo ratings yet
- Ex29007-Pdf BDDocument155 pagesEx29007-Pdf BDsereptNo ratings yet
- PH-Electric-Rope-Shovel-Components (Splited)Document3 pagesPH-Electric-Rope-Shovel-Components (Splited)Oscar JimenezNo ratings yet
- Aerosols in AyurvedaDocument13 pagesAerosols in AyurvedaDr ajayNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy 1Document27 pagesTaxonomy 1Rouie john dizonNo ratings yet
- Research 1Document16 pagesResearch 1Ivan Dave Peralta AsiongNo ratings yet
- Cladistics and Phylogeny - NotesDocument6 pagesCladistics and Phylogeny - NotesEllah Iracielli TevesNo ratings yet
- B7 Classification ReadingDocument3 pagesB7 Classification ReadingMatt StromNo ratings yet
- Evolutionaryaazzqq: Evolutionary Research SpeciesDocument4 pagesEvolutionaryaazzqq: Evolutionary Research Speciesterran2020No ratings yet
- Wwevolutionaryaazzqqaa: Evolutionary Research SpeciesDocument4 pagesWwevolutionaryaazzqqaa: Evolutionary Research Speciesterran2020No ratings yet
- 3 CompevDocument13 pages3 CompevAm'alia Jassey TristyNo ratings yet
- Week 34 ScienceDocument3 pagesWeek 34 ScienceKittie EliseNo ratings yet
- ClassificationDocument39 pagesClassificationAl-Bien TadoNo ratings yet
- Purpose of Taxonomy in BiologyDocument7 pagesPurpose of Taxonomy in BiologytboylingweNo ratings yet
- Classification of BiodiversDocument2 pagesClassification of Biodiverssathish1992No ratings yet
- General-Biology II Q3 Week - 6Document8 pagesGeneral-Biology II Q3 Week - 6Charles Dion MilanNo ratings yet
- Systematics Based On Evolutionary RelationshipsDocument33 pagesSystematics Based On Evolutionary Relationshipskaren milloNo ratings yet
- Species: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesSpecies: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaLali HajzeriNo ratings yet
- 0Ent0fFYaIym8VoHWgBl-1 SSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSPDFDocument11 pages0Ent0fFYaIym8VoHWgBl-1 SSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSPDFDigraj Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- Diversity of LifeDocument28 pagesDiversity of LifeMa. Krizia Tiny ParconNo ratings yet
- MCB100 - Module 1Document50 pagesMCB100 - Module 1ReginaNo ratings yet
- Earl Eugene Castro - Bio 32 Learning Activity 1Document2 pagesEarl Eugene Castro - Bio 32 Learning Activity 1EARL CASTRONo ratings yet
- Taxonomy PDFDocument15 pagesTaxonomy PDFSwarup MondalNo ratings yet
- What Is BiodiversityDocument4 pagesWhat Is BiodiversityJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy and SystematicsDocument22 pagesTaxonomy and SystematicsHyun JiNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument45 pagesHepatitisReza MajidiNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Biology Organisms and Adaptations Media Update Enhanced Edition 1st Edition Noyd Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Biology Organisms and Adaptations Media Update Enhanced Edition 1st Edition Noyd Solutions Manual PDFcodle.flasher26qf5100% (12)
- Carolus LinnaeusDocument30 pagesCarolus Linnaeusummu atiqah maisaraNo ratings yet
- SYSTEMATICTAXONOMYmainDocument26 pagesSYSTEMATICTAXONOMYmainRachel BiagNo ratings yet
- Wepik The Taxonomic Framework Unveiling The Classifications of Life Forms 20240104115413CGBiDocument11 pagesWepik The Taxonomic Framework Unveiling The Classifications of Life Forms 20240104115413CGBiroyavishek685No ratings yet
- Tree of Life and SystematicsDocument37 pagesTree of Life and SystematicsFaith MagluyanNo ratings yet
- m5 - Classification of AnimalsDocument30 pagesm5 - Classification of AnimalsDaisy RamaNo ratings yet
- Wa0000Document19 pagesWa0000Muzammil LiaketNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Lesson 2 BIODIVERSITYDocument8 pagesModule 3 Lesson 2 BIODIVERSITYRobert VasquezNo ratings yet
- TaxonomyDocument46 pagesTaxonomyJorell lapatingNo ratings yet
- Biological Diversity and Habitat Diversi PDFDocument9 pagesBiological Diversity and Habitat Diversi PDFLuis Angel Aguirre MendezNo ratings yet
- Defining BiodiversityDocument14 pagesDefining BiodiversityjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Food Web - Wikipedia PDFDocument4 pagesFood Web - Wikipedia PDFNadja SoleilNo ratings yet
- Full Download Biology Organisms and Adaptations Media Update Enhanced Edition 1st Edition Noyd Solutions ManualDocument27 pagesFull Download Biology Organisms and Adaptations Media Update Enhanced Edition 1st Edition Noyd Solutions Manualantonynolleus2645100% (39)
- Biological DiversityDocument25 pagesBiological DiversityDonna RemitarNo ratings yet
- CladeDocument1 pageCladeLeticiaNo ratings yet
- The Living WorldDocument14 pagesThe Living WorldNalla Raghuram ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Miners AssignmentDocument17 pagesChemistry For Miners AssignmentmpwemboNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy (Biology) - WikipediaDocument89 pagesTaxonomy (Biology) - WikipediaNaniNo ratings yet
- Widyasatwaloka Reseacrh Center For Biology - LIPI, Cibinong: Introduction To TaxonomyDocument4 pagesWidyasatwaloka Reseacrh Center For Biology - LIPI, Cibinong: Introduction To TaxonomyFarhana ReNo ratings yet
- A3.1 Diversity of OrganismsDocument36 pagesA3.1 Diversity of OrganismsGeorge KoukouvesNo ratings yet
- Conceito de EspéciesDocument23 pagesConceito de EspéciesLuiz HenriqueNo ratings yet
- 1 - Taxonomy Vs SystematicsDocument19 pages1 - Taxonomy Vs SystematicsHADI WIBOWONo ratings yet
- Concepts of SpeciesDocument19 pagesConcepts of SpeciesAcosta Gerardo100% (2)
- Microbial Taxonomy Mcba p1 TDocument119 pagesMicrobial Taxonomy Mcba p1 TShikha GuptaNo ratings yet
- 3 Evolv PDFDocument13 pages3 Evolv PDFprasannandaNo ratings yet
- TaxonomyDocument1 pageTaxonomyJarel MarabutNo ratings yet
- Principles of Systematic Zoology TaxonomyDocument19 pagesPrinciples of Systematic Zoology TaxonomyKhadija IkramNo ratings yet
- BIODIVERSITYDocument24 pagesBIODIVERSITYGlysemie TecsonNo ratings yet
- Disha NEET Biology FinalDocument336 pagesDisha NEET Biology Finalsubham ghoshNo ratings yet
- M - 1.6 - Training EvaluationDocument15 pagesM - 1.6 - Training EvaluationLGED ManikganjNo ratings yet
- Analysis of To Autumn.Document5 pagesAnalysis of To Autumn.M JaanNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics I (8.04) Spring 2016 Assignment 2: Problem Set 2Document5 pagesQuantum Physics I (8.04) Spring 2016 Assignment 2: Problem Set 2Fabian M Vargas FontalvoNo ratings yet
- QM Assignment July 22 by Permal Sajjad - SolutionDocument7 pagesQM Assignment July 22 by Permal Sajjad - SolutionZeeshan Bakali100% (1)
- WBLFFDocument10 pagesWBLFFMohd IzatNo ratings yet
- DQSHolding - 812E1 - High Level Structure ISO 27001Document1 pageDQSHolding - 812E1 - High Level Structure ISO 27001MTOLLERNo ratings yet
- 3cce171c-d4d7-49b0-8dda-425b225fb1f5 (1)Document2 pages3cce171c-d4d7-49b0-8dda-425b225fb1f5 (1)j4606074No ratings yet
- MQ-9 Reaper Armed Unmanned Aircraft System (UAS)Document2 pagesMQ-9 Reaper Armed Unmanned Aircraft System (UAS)joma11No ratings yet
- Domain Name System - Internet PDFDocument8 pagesDomain Name System - Internet PDFp-jornNo ratings yet
- HW 5Document3 pagesHW 5Mansi JainNo ratings yet
- RFC 1337Document13 pagesRFC 1337NickyNETNo ratings yet
- Sony 19wt400Document110 pagesSony 19wt400Bittu sainiNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security: Threats, Vulnerabilities and Countermeasures - A Perspective On The State of Affairs in MauritiusDocument15 pagesCyber Security: Threats, Vulnerabilities and Countermeasures - A Perspective On The State of Affairs in MauritiusliezelleannNo ratings yet
- Monitor Control Board Specification: MODEL: M.NT68676.2ADocument9 pagesMonitor Control Board Specification: MODEL: M.NT68676.2AHuynh ChauNo ratings yet
- Researching Alzheimer's Medicines - Setbacks and Stepping StonesDocument20 pagesResearching Alzheimer's Medicines - Setbacks and Stepping StonesOscar EspinozaNo ratings yet
- I.T Unit 1Document9 pagesI.T Unit 1Gowtham R GowthamNo ratings yet
- Conditional TYPE 3 ExerciseDocument2 pagesConditional TYPE 3 ExercisejamalfthhNo ratings yet
- Vibrating Wire Strain GaugeDocument2 pagesVibrating Wire Strain GaugejilofeNo ratings yet
- The Gifted StudentsDocument6 pagesThe Gifted StudentsHoàng BùiNo ratings yet
- DCM Part Shots December 2002Document1 pageDCM Part Shots December 2002sobheysaidNo ratings yet
- Market Analysis of Isopropyl AlcoholDocument4 pagesMarket Analysis of Isopropyl AlcoholhasanulfiqryNo ratings yet
- Factor Analysis SPSSDocument6 pagesFactor Analysis SPSSNeelima Varma NadimpalliNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: MAT 243 Project Three Summary ReportDocument8 pagesThis Study Resource Was: MAT 243 Project Three Summary ReportnellyNo ratings yet