0% found this document useful (0 votes)
443 views13 pages4G Core Network Essentials
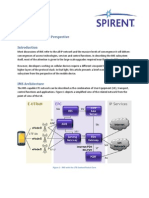
The document provides an overview of the 4G Core Network architecture, detailing key nodes such as the MME, SGW, PGW, HSS, and PCRF. It explains the functionalities of each component, including mobility management, user data handling, and policy enforcement. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of interconnectivity among various network technologies and the role of each node in ensuring efficient communication and service delivery.
Uploaded by
julescarrelCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
443 views13 pages4G Core Network Essentials
The document provides an overview of the 4G Core Network architecture, detailing key nodes such as the MME, SGW, PGW, HSS, and PCRF. It explains the functionalities of each component, including mobility management, user data handling, and policy enforcement. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of interconnectivity among various network technologies and the role of each node in ensuring efficient communication and service delivery.
Uploaded by
julescarrelCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd