0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views9 pagesAirflow Fundamentals and Duct Systems
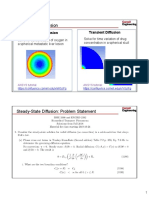
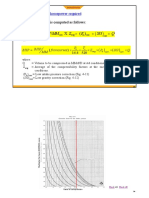
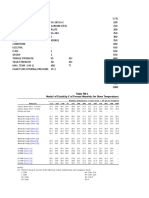
The document discusses the fundamentals of air including standard air properties, air velocity, volumetric flow rate, air pressure, air flow, noise and airflow. It then covers all-air HVAC systems including large commercial and small residential systems. The document also discusses ductwork materials, layouts, arrangements and basic HVAC equipment like fans, dampers and air terminals.
Uploaded by
Rosita Talde DalupangCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views9 pagesAirflow Fundamentals and Duct Systems
The document discusses the fundamentals of air including standard air properties, air velocity, volumetric flow rate, air pressure, air flow, noise and airflow. It then covers all-air HVAC systems including large commercial and small residential systems. The document also discusses ductwork materials, layouts, arrangements and basic HVAC equipment like fans, dampers and air terminals.
Uploaded by
Rosita Talde DalupangCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd