0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views6 pagesECON 223 Class Test 2 Questions
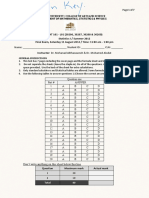
The document contains a 6 question test on statistics. It covers topics like distributions, confidence intervals, and probability. Students are asked to calculate probabilities, identify distributions, derive formulas, and interpret statistical values in various contexts.
Uploaded by
JAINAM JAINCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views6 pagesECON 223 Class Test 2 Questions
The document contains a 6 question test on statistics. It covers topics like distributions, confidence intervals, and probability. Students are asked to calculate probabilities, identify distributions, derive formulas, and interpret statistical values in various contexts.
Uploaded by
JAINAM JAINCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd