Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hypothesis Testing Seminar
Uploaded by
Jacky C.Y. HoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hypothesis Testing Seminar
Uploaded by
Jacky C.Y. HoCopyright:
Available Formats
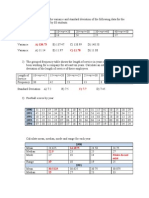
Let the random variable Z follow a standard normal distribution, and let z1 be a possible value of Z that is unknown but
identifiable by position and area. Find z1 if the area to the right of z1 is 0.0869: a) -1.36. b) 1.71. c) 1.36. d) 1.80 Let the random variable X follow a normal distribution with a mean and a standard deviation . Let m1 and m2 be the means of samples of sizes 35 and 35, respectively, randomly and independently selected from this population. Consider the following expressions: (1) Pr(-0.2<m1<+), and (2) Pr(-<m2<+0.2). Which of the following statements is true? a) Value of expression 1 is equal to value of expression 2. b) Value of expression 1 is greater than value of expression 2. c) Value of expression 1 is smaller than value of expression 2. d) Unable to determine the relationship between expression 1 and expression 2. In a recent survey of college professors, it was found that the average amount of money spent on entertainment each week was normally distributed with a mean of $95.25 and a standard deviation of $27.32. What is the probability that the average spending of a sample of 30 randomly-selected professors will exceed $102.50? a) 0.0730 b) 0.1064 c) 0.3936 d) 0.4082 In examining the invoices issued by a company, an auditor finds that the dollar amounts of invoices have a mean of $1,732 and a standard deviation of $298. What is the probability that for a sample of 45 invoices, the average invoice is greater than $1,800? a) 0.563 b) 0.063 c) 0.437 d) 0.937
The time it takes to complete the assembly of an electronic component is normally distributed with a standard deviation of 4.38 minutes. If we select 20 components at random, what is the probability that the standard deviation for the time of assembly of these units is less than 3.0 minutes? a) 0.05 b) 0.005 c) 0.025 d) 0.01 You have recently joined a Weight Watchers club. Suppose that the number of times you expect to visit the club in a month is represented by a normally distributed random variable with a mean of 12 and a standard deviation of 2.50. Over the course of the next year, what is the probability that you average more than 13 visits to the club? a) 0.1554 b) 0.4177 c) 0.3446 d) 0.0823 The number of students using the ATM on campus daily is normally distributed with a mean of 237.6 and a standard deviation of 26.3. For a random sample of 55 days, what is the probability that ATM usage averaged more than 230 students per day? a) 0.9756 b) 0.9483 c) 0.9838 d) 0.9524 The amount of time that you have to wait before seeing the doctor in the doctors office is exponentially distributed with a mean of 15.2 minutes and a standard deviation of 15.2 minutes. If you take a random sample of 35 patients, what is the probability that the average wait time is greater than 20 minutes? a) 0.28 b) 0.26 c) 0.24 d) 0.03
If a random sample of size n is drawn from a normal population, then the sampling distribution of sample means will be: a) normal for all values of n b) normal only for n > 30 c) approximately normal for all values of n d) approximately normal only for n > 30 If the standard error of the sampling distribution of the sample proportion is 0.02049 for samples of size 500, then the population proportion must be either a) 0.2 or 0.8. b) 0.5 or 0.5. c) 0.3 or 0.7. d) 0.6 or 0.4. Random samples of size 36 each are taken from a large population whose mean is 120 and standard deviation is 39. The mean and standard error of the sampling distribution of sample mean, respectively, are: a) 120 and 39. b) 120 and 6.5. c) 39 and 120. d) 6.5 and 120. In a survey of 472 personnel directors, 63% thought that they would be hiring new personnel over the next three months. Which of the following represents a 98% confidence interval for the proportion of all personnel directors planning to hire personnel over the next three months? a) 0.63 0.057 b) 0.63 0.047 c) 0.63 0.042 d) 0.63 0.052 In developing an interval estimate for a population mean, a sample of 40 observations was used. The interval estimate was 28.76 1.48. Had the sample size been 160 instead of 40, the interval estimate would have been a) 28.76 0.37 b) 28.76 0.74
c) 7.19 1.48 d) 7.19 1.82 The 95% confidence interval for the population proportion given a sample size n = 2200 and sample proportion p = 0.214 is computed as a) 0.214 1.96 (0.00875) b) 0.214 1.645 (0.00875) c) 0.214 1.96 (0.000075) d) 0.214 1.645 (0.000075) The upper limit of 90% confidence interval for the population proportion given a sample size n = 300 and sample proportion p = 0.1833 is equal to a) 0.1466 b) 0.1395 c) 0.2271 d) 0.2200 Which of the following statements is false? a) If a sample has 16 observations and a 90% confidence estimate for is needed, the appropriate t-score is 2.602 b) If a sample has 16 observations and a 99% confidence estimate for is needed, the appropriate t-score is 2.947 c) If a sample has 20 observations and a 95% confidence estimate for is needed, the appropriate t-score is 2.093 d) The t distribution, like the z distribution, is symmetric about the mean =0 In order to estimate the average daily down time, a manufacturer randomly samples 40 days of production records and found a mean of 51.576 minutes and standard deviation of 75.9 minutes. An 80% confidence interval is given by: a) 51.675 1.28(12.0) b) 51.675 1.28(75.9) c) 51.675 1.304(12.0) d) 51.675 1.304(8.7) A random sample of size 15 taken from a normally distributed population
revealed a sample mean of 75 and a sample variance of 25. The upper limit of a 95% confidence interval for the population mean would equal: a) 77.769 b) 72.231 c) 72.727 d) 77.273 The supervisor of a production line believes that the average time to assemble an electronic component is 14 minutes. Assume that assembly time is normally distributed with a standard deviation of 3.4 minutes. The supervisor times the assembly of 14 components, and finds that the average time for completion was 11.6 minutes. What are the appropriate null and alternative hypotheses? a) H0: 14 and H1: <14 b) H0: 14 and H1: >14 c) H0: =14 and H1: 14 d) H0: 14 and H1: =14 Which of the following statements is most accurate? a) Unable to reject the null hypothesis at 0.10. b) Reject the null hypothesis at = 0.025, but not at = 0.05. c) Reject the null hypothesis at = 0.05, but not at = 0.01. d) Reject the null hypothesis at = 0.008. The manufacturer of a new product claims that his product will increase output per machine by at least 29 units per hour. A line manager adopts the product on 15 of his machines, and finds that the average increase was only 26 with a standard deviation of 6.2. What are the appropriate null and alternative hypotheses? a) H0: =29 and H1: 29 b) H0: 29 and H1: < 29 c) H0: 29 and H1: = 29 d) H0: > 29 and H1: 29 Using a 5% significance level, which of the following statements is true?
a) Reject H0 if t statistic < 1.761. b) Reject H0 if t statistic > 2.16. c) Reject H0 if t statistic < -1.761. d) Reject H0 if t statistic < -2.16. The value of the test statistics is a) 1.240. b) 1.874. c) -1.240. d) -1.874. Which of the following statements is most accurate? a) Reject the null hypothesis at = 0.10. b) Unable to reject the null hypothesis at 0.10. c) Reject the null hypothesis at = 0.05, but not 0.10. d) Reject the null hypothesis at = 0.01, but not 0.05. As shift manager at a local fast food place, you are responsible for ensuring quality control. You do not want to weigh all the frozen hamburger patties that get delivered by your supplier to make sure they weigh four ounces on average, so you have one of your minimum wage earners do it. Assume that the standard deviation of the weight of hamburger patties is known to be 0.1 ounces. You tell your employee that as a shipment comes in, select 20 patties at random. Find the average weight for the 20 patties. If the average weight is less than 3.95 ounces, reject the shipment. What is the significance level associated with your decision rule? a) 0.015 b) 0.008 c) 0.023 d) 0.013 Suppose that you want to test H0: = 0.54 against H1: < 0.54 based on a sample of n = 25 and s= 13.2. Let m be the sample mean. What would the test statistic be? a) (m - 0.54) / 34.848 b) (m - 0.54) / 2.64 c) (m -0.54) / 0.528
d) (m -0.54) / 0.2789 An assembly line will be shut down for maintenance if the defect rate exceeds 2.3%. Suppose you adopt a 5% significance level and take a random sample 200 items off the assembly line and compute the proportion that are defective. For what values of the sample proportion will the assembly line be shut down? a) 0.034 b) 0.038 c) 0.036 d) 0.040 A professor claims that the average score on a recent exam was 83. Assume that the test scores are normally distributed. You ask some people in class how they did, and you record the following scores: 82, 77, 85, 76, 81, 91, 70, and 82. Suppose you want to test whether the professors statement was correct. What are the null and alternative hypotheses? a) H0: = 83 and H1: > 83 b) H0: = 83 and H1: < 83 c) H0: = 83 and H1: 83 d) H0: > 83 and H1: 83 What is the appropriate decision rule? a) Reject H0 if t statistic > t,n-1. b) Reject H0 if t statistic < - t/2,n-1 or > t/2,n-1. c) Reject H0 if t statistic = t,n-1. d) Reject H0 if t statistic < - t,n-1. Which of the following is the most accurate statement about the p-value? a) p-value > 0.10 b) p-value < 0.05 c) p-value < 0.10 d) p-value < 0.01 A local transportation planning group is concerned about the lack of car-
pooling on the part of commuters. They are afraid that the proportion of local drivers car-pooling is below the national average of 20%. What are the appropriate null and alternative hypotheses? a) H0: > 0.20 and H1: 0.20 b) H0: = 0.20 and H1: 0.20 c) H0: = 0.20 and H1: > 0.20 d) H0: = 0.20 and H1: < 0.20 As shift manager at a local fast food place, you are responsible for ensuring quality control. You do not want to weigh all the frozen hamburger patties that get delivered by your supplier to make sure they weigh four ounces on average, so you have one of your minimum wage earners do it. Assume that the standard deviation of the weight of hamburger patties is known to be 0.1 ounces. You tell your employee to choose 25 patties at random and find the average weight. For what values would you tell the employee to reject the shipment, if you wanted the probability of a Type I error to be 0.10 or less? a) Reject the shipment if weight < 3.955 b) Reject the shipment if weight < 3.975 c) Reject the shipment if weight < 3.965 d) Reject the shipment if weight < 3.985 Which of the following statements is not true? a) A test statistic is a function of the sample data on which the decision to reject or not reject the null hypothesis is to be based. b) A rejection region consists of the set of all test statistic values for which the null hypothesis will be rejected. c) A rejection region consists of the set of all test statistic values for which the alternative hypothesis will be rejected. d) A good hypothesis-testing procedure is one for which the probability of making either type I or type II error is small. A student has been offered part-time work in a laboratory. The professor says that the work will vary from week to week. The number of hours will be between 10 and 20 with a uniform probability density function. What is the probability of getting less than 15 hours in a week? a) 0.
b) 0.8. c) 0.5. d) 0.6. Given that the student gets at least 15 hours in a week, what is the probability that more than 17 hours will be available? a) 0.25. b) 0.4. c) 0.5. d) 0.6. (10 points) Mr W, a stock analyst, claims that he can pick stocks that will outperform the market. You, as the boss of an investment company, decided to give him a chance. During his three-month probation in your company, in 40 out of 66 trading days, the stock he picked has a higher return than the market average (say, better than the Hang Seng Index). Should you keep him or ask him to leave when the probation period expires? Show steps for your conclusion. We will keep the analyst if we found that he can actually outperform the market. On any day, there are approximately half of the stocks doing better than the market average and half worse than the market average. (Remember: average is a measure of central tendency.) So, if a chimpanzee picks a stock on a particularly day (i.e., randomly), it is likely to perform like the market average. Thus, the reference is a chimpanzee whose probability of picking a stock outperforming the market average is 0.5, i.e., =0.5. H0: 0.5 (the stock analyst is doing no better than a chimpanzee) or H0: =0.5 (the stock analyst is doing no better than a chimpanzee) H1: >0.5 (the stock analyst is better than a chimpanzee) The sample proportion is p=44/66 = 0.606. Variance of p under null is (1-)/(n-1) = 0.003846 (an unbiased formula) or (1-)/n = 0.003788 (slightly biased but convenience formula) The sample proportion is distributed as binomial with a mean 0.5 and the variance above. Since n*>=66*0.5 = 33> 9, we can use the normal approximation. Most people would consider probability of 0.05 as small. From normal
table, we find that Pr(Z>1.65) = 0.05. Thus, we reject H0 if z = (p-)/std(p) > 1.65. In our sample, we have (p-)/std(p) = 1.710 (or 1.723 depending on what formula of std(p) we use). Thus, H0 is rejected at 5% significance level. The analyst is better than a chimpanzee. We can also compute the probability of observing the sample proportion at least as extreme as 0.606 under H0 (i.e., the z statistic at least as extreme as 1.71). That is, p-value = Pr(Z>1.71) = 0.0436 (or Pr(Z>1.723) = 0.0424). This computation of p-value confirms our result of testing the hypothesis at 5% level.
You might also like
- Solutions Manual to accompany Introduction to Linear Regression AnalysisFrom EverandSolutions Manual to accompany Introduction to Linear Regression AnalysisRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- UWA Practice Substitution TestDocument38 pagesUWA Practice Substitution Testm3gp13 yoNo ratings yet
- ECON 321 Midterm Practice QuestionsDocument6 pagesECON 321 Midterm Practice QuestionsJR100% (1)
- Final Review QuestionsDocument5 pagesFinal Review QuestionsJeremy PearsonNo ratings yet
- Final Exam 1 - Part A: Confidence Intervals, Hypothesis Tests & ProbabilityDocument13 pagesFinal Exam 1 - Part A: Confidence Intervals, Hypothesis Tests & Probabilityupload55No ratings yet
- Final Examination: SampleDocument7 pagesFinal Examination: SampleJin NguyenNo ratings yet
- UPDATED Practice Final Exams SolutionsDocument39 pagesUPDATED Practice Final Exams SolutionsReza MohagiNo ratings yet
- Final SolDocument5 pagesFinal SolcesardakoNo ratings yet
- Sampletest2 Fall2003Document8 pagesSampletest2 Fall2003Leo SchizoNo ratings yet
- Statisticshomeworkhelpstatisticstutoringstatisticstutor Byonlinetutorsite 101015122333 Phpapp02Document25 pagesStatisticshomeworkhelpstatisticstutoringstatisticstutor Byonlinetutorsite 101015122333 Phpapp02Farah NoreenNo ratings yet
- Quiz8 Ch07 PDFDocument9 pagesQuiz8 Ch07 PDFEarthy Dream TheNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam IIIDocument8 pagesPractice Exam IIIAdam Hylton100% (2)
- NLTK Final Test CLCTC k55Document3 pagesNLTK Final Test CLCTC k55Quỳnh Anh ShineNo ratings yet
- Exam Practise QuestionsDocument42 pagesExam Practise Questionsngcamusiphesihle12No ratings yet
- Quiz 3 SV EDocument10 pagesQuiz 3 SV ENtxawm MuasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document6 pagesAssignment 5sandeep BhanotNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Practice 1 de Thi Thuc Mon XSTKDocument9 pagesFinal Exam Practice 1 de Thi Thuc Mon XSTKbinhvn16.sicNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency and Dispersion MCQsDocument13 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency and Dispersion MCQsCHARAN GOPI KRISHNA Kondapalli100% (1)
- Assignment 5 - Engineering Statistics - Spring 2018Document6 pagesAssignment 5 - Engineering Statistics - Spring 2018UBAID ULLAHNo ratings yet
- AssgDocument3 pagesAssgmkkNo ratings yet
- Stats 3 ReviewDocument7 pagesStats 3 ReviewAnonymous Zv32C1ptNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter ExamDocument6 pages4th Quarter ExamJude TanNo ratings yet
- AP Statistics Practice ExamDocument13 pagesAP Statistics Practice ExamGuy Cecelski50% (2)
- R7210501 Probability & StatisticsDocument2 pagesR7210501 Probability & StatisticssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Prob & Stats Practice Exam 2Document8 pagesProb & Stats Practice Exam 2Cameron HulseNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution AssignmentDocument3 pagesNormal Distribution AssignmentsansamDude0% (1)
- Study Guide - Normal Probability DistributionsDocument13 pagesStudy Guide - Normal Probability DistributionsLamessa GaromaNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers Chapter - 7 Set 1Document6 pagesQuestions & Answers Chapter - 7 Set 1FaridOrahaNo ratings yet
- 2018-IPS Endterm SolsDocument14 pages2018-IPS Endterm SolsAnurag BhartiNo ratings yet
- 10.2 Review AnswersDocument5 pages10.2 Review Answerstam tranchiNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument15 pagesPDFNataliAmiranashviliNo ratings yet
- ECON310 Q1 - KeyDocument5 pagesECON310 Q1 - KeyRefiye ÇakmakNo ratings yet
- Group 5:: Statistical Analysis With Software ApplicationDocument8 pagesGroup 5:: Statistical Analysis With Software ApplicationMitch Tokong MinglanaNo ratings yet
- Econometrics Assignment 2Document3 pagesEconometrics Assignment 2Peter ChenzaNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability ReviewerDocument6 pagesStatistics and Probability ReviewerKlynox MalanumNo ratings yet
- Final Exam 2022Document6 pagesFinal Exam 2022Chandra Bagas AlfianNo ratings yet
- STPM Paper 3 2013t (U)Document2 pagesSTPM Paper 3 2013t (U)KwongKHNo ratings yet
- Statistics Assignment Confidence IntervalsDocument3 pagesStatistics Assignment Confidence IntervalsMai ShaabanNo ratings yet
- Statistics Assignment Confidence IntervalsDocument3 pagesStatistics Assignment Confidence IntervalsMai ShaabanNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument18 pagesStatisticsSushant PatilNo ratings yet
- Samplemid2 SolDocument5 pagesSamplemid2 SolFatimaIjazNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 Estimation Answer KeyDocument4 pagesProblem Set 1 Estimation Answer KeyKezza NoguerraNo ratings yet
- Practice FinalDocument18 pagesPractice Final3456123No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - Hypothesis TestingDocument12 pagesTutorial 3 - Hypothesis TestingNoorNabila0% (1)
- Unit 3 Z-Scores, Measuring Performance: Learning OutcomeDocument10 pagesUnit 3 Z-Scores, Measuring Performance: Learning OutcomeCheska AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam FinalDocument11 pagesPractice Exam FinalMagalyIpiñaNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics For Engineers FinalExam - 2007-1Document8 pagesProbability and Statistics For Engineers FinalExam - 2007-1a.bNo ratings yet
- R04 Introduction To Linear RegressionDocument12 pagesR04 Introduction To Linear RegressionIndonesian ProNo ratings yet
- Introductory Statistics A Problem Solving Approach 2Nd Edition Kokoska Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesIntroductory Statistics A Problem Solving Approach 2Nd Edition Kokoska Test Bank Full Chapter PDFKimberlyWilliamsonepda100% (9)
- Introductory Statistics A Problem Solving Approach 2nd Edition Kokoska Test BankDocument15 pagesIntroductory Statistics A Problem Solving Approach 2nd Edition Kokoska Test Bankjesselact0vvk100% (35)
- Sampling Distributions 10.1. Single Mean:: SolutionDocument15 pagesSampling Distributions 10.1. Single Mean:: SolutionTalha AzanNo ratings yet
- Midterm 2 With SolutionDocument4 pagesMidterm 2 With SolutionFatimaIjazNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Each One of You Are Assigned Roll No Wise 1 Question Individually That You Are SubmittingDocument10 pagesAssignment 1 Each One of You Are Assigned Roll No Wise 1 Question Individually That You Are SubmittingsiddheshNo ratings yet
- 01-Stat2 Exercise Set 1 SolutionDocument6 pages01-Stat2 Exercise Set 1 SolutionVivek PoddarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial_Week10Document3 pagesTutorial_Week10Rasika MalodeNo ratings yet
- MBA Business Statistics and Decision Making Solutions Robert A StineDocument10 pagesMBA Business Statistics and Decision Making Solutions Robert A StineNaresh SehdevNo ratings yet
- Giong Chuong 7Document6 pagesGiong Chuong 7lananh2011No ratings yet
- CMTH380 F18 Test 2 ReviewDocument6 pagesCMTH380 F18 Test 2 ReviewAmit VirkNo ratings yet
- Eco220y Au18Document25 pagesEco220y Au18Stephanie SongNo ratings yet
- Social Economics CoverDocument1 pageSocial Economics CoverJacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- List of Figures and Tables AcknowledgementsDocument1 pageList of Figures and Tables AcknowledgementsJacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Law 5Document1 pageLaw 5Jacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Wealth of Nations (1776) - in England David Ricardo And, To ADocument1 pageWealth of Nations (1776) - in England David Ricardo And, To AJacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Vygotsky Pedagogy Theory BookDocument1 pageVygotsky Pedagogy Theory BookJacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Economics About1Document1 pageEconomics About1Jacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Vygotsky and Pedagogy CoverDocument1 pageVygotsky and Pedagogy CoverJacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Vygotsky and Pedagogy 5Document1 pageVygotsky and Pedagogy 5Jacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Vygotsky's Pedagogy Theory ExplainedDocument1 pageVygotsky's Pedagogy Theory ExplainedJacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Law 4Document1 pageLaw 4Jacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Economics About6Document1 pageEconomics About6Jacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Law and The State: A Political Economy ApproachDocument1 pageLaw and The State: A Political Economy ApproachJacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- The History of Economic Thought from Humanism to MercantilismDocument1 pageThe History of Economic Thought from Humanism to MercantilismJacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Economics About3Document1 pageEconomics About3Jacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Law 1Document1 pageLaw 1Jacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- New Horizons in Law and Economics: Series Editors: Gerrit de GeestDocument1 pageNew Horizons in Law and Economics: Series Editors: Gerrit de GeestJacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Lect6 OperantiDocument1 pageLect6 OperantiJacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Economics AboutDocument1 pageEconomics AboutJacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual: Fundamentals of Corporate Finance 8Document1 pageSolutions Manual: Fundamentals of Corporate Finance 8Jacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Flase Memory Binder1Document2 pagesFlase Memory Binder1Jacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- GEM/IKJ CB495-13 Train BibliographyDocument1 pageGEM/IKJ CB495-13 Train BibliographyJacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Ed Research Methods PlanningDocument1 pageQuantitative Ed Research Methods PlanningJacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- P1: Gem P2: Gem QC: Gem T1: Gem CB495-FMA CB495/Train September 18, 2002 10:54 Char Count 0Document1 pageP1: Gem P2: Gem QC: Gem T1: Gem CB495-FMA CB495/Train September 18, 2002 10:54 Char Count 0Jacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Doing A Literature ReviewDocument120 pagesDoing A Literature ReviewJacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Bib 2Document1 pageBib 2Jacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- P1: Gem P2: Gem QC: Gem T1: Gem CB495-FMA CB495/Train September 18, 2002 10:54 Char Count 0Document1 pageP1: Gem P2: Gem QC: Gem T1: Gem CB495-FMA CB495/Train September 18, 2002 10:54 Char Count 0Jacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Bib 4Document1 pageBib 4Jacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Bib 1Document1 pageBib 1Jacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Index: /ikj /ikj /abeDocument1 pageIndex: /ikj /ikj /abeJacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- P1: Gem P2: Gem QC: Gem T1: Gem CB495-FMA CB495/Train September 18, 2002 10:54 Char Count 0Document1 pageP1: Gem P2: Gem QC: Gem T1: Gem CB495-FMA CB495/Train September 18, 2002 10:54 Char Count 0Jacky C.Y. HoNo ratings yet
- Kingsley Nwagu Viva Voce PresentationDocument48 pagesKingsley Nwagu Viva Voce PresentationKingsley NwaguNo ratings yet
- Vibration Data Analysis Software (Vibdas)Document4 pagesVibration Data Analysis Software (Vibdas)chetan_thakur4278No ratings yet
- Intercomparison of Methods To Estimate Black Carbon EmissionsDocument8 pagesIntercomparison of Methods To Estimate Black Carbon EmissionsJoy RoyNo ratings yet
- RSMM Divya ProjectDocument84 pagesRSMM Divya ProjectGaurav NarayanNo ratings yet
- Exploratory Data AnalysisDocument22 pagesExploratory Data AnalysisjdmarinNo ratings yet
- FlourishingDocument110 pagesFlourishingSebastian VaidaNo ratings yet
- Exemplar 1 PDFDocument57 pagesExemplar 1 PDFWereNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics, 4e: by Ken BlackDocument38 pagesBusiness Statistics, 4e: by Ken BlackvijayNo ratings yet
- StockWatson 3e EmpiricalExerciseSolutions PDFDocument65 pagesStockWatson 3e EmpiricalExerciseSolutions PDFChristine Yan0% (1)
- Internship Proposal - Time Series Analysis For A Telecommunication CompanyDocument1 pageInternship Proposal - Time Series Analysis For A Telecommunication CompanyNashimoNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Presepsi Harga Dan Minat Beli Terhdapa Pembelian SmartphoneDocument10 pagesPengaruh Presepsi Harga Dan Minat Beli Terhdapa Pembelian SmartphoneerinaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Linear RegressionDocument21 pagesLesson 2 Linear RegressionNeerom BaldemoroNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Econometria Jeffrey M Wooldridge PDFDocument4 pagesSolucionario Econometria Jeffrey M Wooldridge PDFMartín Cruzat Riquelme0% (1)
- Language, Culture and Society SyllabusDocument10 pagesLanguage, Culture and Society SyllabusMel Macatangay100% (4)
- Selected Answer: Fals e Answers: Tru e False Selected Answer: AnswersDocument4 pagesSelected Answer: Fals e Answers: Tru e False Selected Answer: AnswersAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Vedanta Bhadani NTCC FinalDocument44 pagesVedanta Bhadani NTCC FinalRiya Prabhavi0% (1)
- An Example For A CVDocument12 pagesAn Example For A CVDavidArrusticoNo ratings yet
- Resnyanskiy 2010Document7 pagesResnyanskiy 2010tataNo ratings yet
- Bradley Et Al. 1999. Goal-Setting in Clinical MedicineDocument12 pagesBradley Et Al. 1999. Goal-Setting in Clinical MedicineFelipe Sebastián Ramírez JaraNo ratings yet
- Multiple Regression Coursera - WordDocument9 pagesMultiple Regression Coursera - WordAbhishekRathourNo ratings yet
- (Smtebooks - Com) Big Data Processing With Hadoop 1st EditionDocument255 pages(Smtebooks - Com) Big Data Processing With Hadoop 1st EditionNiamien AttaNo ratings yet
- ForecastingDocument50 pagesForecastingMitika TutejaNo ratings yet
- GC Bus660 Week 7 Benchmark Data Analysis Case Study Assignment Latest 2016 JulyDocument2 pagesGC Bus660 Week 7 Benchmark Data Analysis Case Study Assignment Latest 2016 JulyCharlotteNo ratings yet
- Data WranglingDocument30 pagesData WranglingYashwanth YashuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Formulating The Research ProblemDocument11 pagesChapter 3: Formulating The Research ProblemKei Emile DaisyNo ratings yet
- TS 2017 - FINAL Web2Document48 pagesTS 2017 - FINAL Web2Anonymous q9eCZHMuSNo ratings yet
- 13-How I Won Singapore's GPT-4 Prompt Engineering Competition - by Sheila Teo - Dec, 2023 - Towards Data ScienceDocument47 pages13-How I Won Singapore's GPT-4 Prompt Engineering Competition - by Sheila Teo - Dec, 2023 - Towards Data ScienceSebastian FloresNo ratings yet
- A Study About The Impact of The City's Economic Condition To The Businesses in Navotas CityDocument8 pagesA Study About The Impact of The City's Economic Condition To The Businesses in Navotas CityEdrilyn Nichole AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document8 pagesAssignment 3vidula pandeNo ratings yet
- Firm performance determinants and financial ratios analysisDocument7 pagesFirm performance determinants and financial ratios analysisalkanm750No ratings yet