Data Science Mind Map PDF Download
Uploaded by
Maziyar GhData Science Mind Map PDF Download
Uploaded by
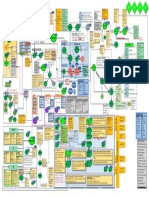
Maziyar Gh- Data Science Mind Map: Provides a comprehensive mind map visualization for data science concepts, tools, and methodologies, organized in a branching manner.
Data Science Mind Map by Pianalytix
[Link].1 K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN)
[Link].2 Logistic Regression
[Link].3 Naive Bayes
[Link] CSV
5.1.1 Structured Data
[Link].4 Decision Tree
[Link] Excel
[Link] Classification
5.1 Data Collection
[Link].5 Support Vector Machines (SVM)
[Link] Text Documents
5.1.2 Unstructured Data
[Link] Image [Link].6 Random Forest
5.2.1 Missing Values [Link].7 Neural Networks (including Deep Learning models)
1.1.1 Supervised Learning
5.2.2 Duplicates [Link].8 Gradient Boosting (e.g., XGBoost, LightGBM)
5.2.3 Outliers [Link].9 Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA)
5.2.4 Inconsistent Formats [Link].1 Linear Regression
5.2 Data Cleaning
[Link] Deduplication [Link].2 Polynomial Regression
[Link] Imputation [Link].3 Lasso and Ridge Regression
5.2.5 Techniques
[Link] Filtering [Link] Regression [Link].4 Support Vector Regression (SVR)
[Link] Normalization [Link].5 Random Forest Regression
5.3.1 Exploring Relationships between variable [Link].6 Gradient Boosting (e.g., XGBoost, LightGBM) for regression
[Link] Histographs [Link].7 Gaussian Processes
[Link] Scatter Plot 5.3.2 Visualization 5.3 Data Exploration [Link].1 Fuzzy C-Means
[Link] BoxPlot [Link].2 k-Means
5.3.3 Statistical Measures [Link].3 DBSCAN (Density-Based Spatial
Clustering of Applications with Noise)
[Link] Scaling
[Link] Clustering
[Link].4 Mean-Shift
[Link] Encoding Categorical variables
[Link].5 Gaussian Mixture Models (GMM)
5.4.1 Techniques 5.4 Feature Engineering
[Link] Creating new features [Link].6 Agglomerative Clustering
[Link].7 Spectral Clustering
[Link] Reducing Dimensionality using PCA
[Link].8 Affinity Propagation
[Link] Hypothesis Testing
[Link].1.1 Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
[Link] Correlation Analysis [Link] Analysis
1.1 Classical Learning
5.5.1 Techniques 5.5 Statistical Analysis [Link].1.2 Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA)
[Link] Regression Analysis
[Link].1.3 t-SNE (t-Distributed Stochastic
[Link] Time Series Analysis Neighbor Embedding)
[Link] Prediction [Link].1.4 Isomap (Isometric Mapping)
[Link].1 Dimensionality Reduction
[Link] Selecting Algorithm [Link].1.5 Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF)
[Link] Classification [Link].1.6 Autoencoders
[Link] Training Models [Link].1.7 Locally Linear Embedding (LLE)
5.6.1 Machine Learning Models 5.6 Model Building
[Link] Clustering [Link].1.8 Laplacian Eigenmaps
[Link].1.9 Random Projection
[Link] Dimensionality Reduction and Visualization
[Link].1 Precision
[Link] Learning
[Link].2.1 Scatter Plots
1.1.2 Unsupervised Learning
[Link].2Recall [Link] Evaluating Performance
[Link].2.2 Heatmaps
[Link].3 Mean Squared Error
[Link].2.3 Parallel Coordinates
Accuracy
[Link].2.4 RadViz
5.7.1 Cross Validation
[Link].2.5 Andrews Curves
[Link].2 Visualization
5.7.2 Performance
[Link].2.6 Star Plots
5.7.3 Holdout Testing
[Link].2.7 Chord Diagrams
[Link] Grid Search 5.7 Model Evaluation and Optimization
5.7.4 Techniques [Link].2.8 Sankey Diagrams
[Link] Bayesian Optimization
[Link].2.9 Treemaps
5.7.5 K Fold Cross-Validation
[Link].2.10 Force-
directed Graphs
5.7.6 Generalizations
[Link].1 Hill Climbing
5.8.1 Effectively Communicated to Stakeholders
[Link] Pattern Search [Link].2 Random Search
[Link] Matplotlib
5.8 Communication and Visualization
[Link].3 Pattern Search Method
[Link] Seaborn 5.8.2 Meaningful Visual's
[Link].1 Apriori Algorithm
[Link] ggplot2
[Link] Association Rule Learning
[Link].2 FP-Growth Algorithm
5.9.1 Findings
5.9 Reporting and Decision-Making
5.9.2 Recommendations
[Link].1 One-class SVM (Support Vector Machine)
[Link] Discrete (Countable)
[Link].2 Isolation Forest
6.1.1 Numeric
[Link] Anomaly Detection
[Link] Continuous (Measurable)
[Link].3 Local Outlier Factor (LOF)
6.1 Data
[Link] Nominal
[Link].4 Autoencoders
6.1.2 Categorical
[Link] Ordinal
[Link].1 Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
6.2.1 Mean [Link] Generative Models
[Link].2 Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)
6.2.2 Median 6.2 Measure of Central Tendancy
1.2.1 Deep Q-Network(DQN)
6.2.3 Mode
1.2.2 Q-Learning
6.3.1 z-Distribution
1.2.3 A3C
1.2 Reinforcement Learning
6.3.2 t-Distribution
6.3 Distributions 1.2.4 Genetic Algorithm
6.3.3 chi-square-Distribution
1.2.5 SARSA
6.3.4 f-Distribution
1.3.1 Stacking
6.4.1 Null Hypothesis
[Link] Random Forest
6.4.2 Alternate Hypothesis 1.3.2 Bagging
6.4.3 Significance Level
[Link] AdaBoost
6.4.4 Critical Region 1.3 Ensemble Learning
6.4 Hypothesis Testing [Link] XGBoost
6.4.5 p-Value
1.3.3 Boosting [Link] GradientBoost
6.4.6 q-Value
[Link] CatBoost
6.4.7 1-Tailed test (Lower/Upper Tail)
[Link] LightGBM
6.4.8 Tow Tailed Test
[Link] List
6.5.1 Recall
[Link] Set
6.5.2 Precision
6 .Mathematics
2.1.1 Python Basic's [Link] Tuples
6.5 Confusion Matrix
6.5.3 Accuracy
[Link] File I/O
6.5.4 F1 Score
[Link] Functions
6.6.1 Right Skewness
6.6 Skewness [Link] Numpy
6.6.2 Left Skewness
[Link] Pandas
6.7 Kurtosis 2.1 Python
[Link] Matplotlib
6.8.1 Bernoulli
[Link] Seaborn
6.8.2Geometric
2.1.2 Libraries [Link] Scikit-Learn
6.8.3 Binomial
6.8 Probability Distribution [Link] TensorFlow
6.8.4 Poission
[Link] Keras
6.8.5 Exponential
[Link] PyTorch
6.8.6 Normal Distribution
[Link] SciPy
6.9.1 Mutually Exclusive Events
[Link] Vectors
6.9.2 Independent Events
[Link] List
6.9.3 Joint Probability
2.2.1 R Basic's [Link] DataFrame
6.9.4 Union Probability
[Link] Matrix
6.9.5 Marginal Probability 6.9 Probability Basics
[Link] Language [Link] Array
6.9.6 Conditional Probability
[Link] dplyr
6.9.7 Bayes Theorem
[Link] ggplot2
6.9.8 Probability Mass Function PMS
2.2 R Programming [Link] tidyr
6.9.9 Probability Density Function PDF
Start Here [Link] readr
6.10 ANOVA
[Link] Stringr
2.2.2 Libraries
6.11.1 Confidence Interval / Level
[Link] Lubridate
6.11.2 Standard Error 6.11 Central Limit Theorem
[Link] Shiny
6.11.3 Margin of Error
[Link] t-Series
7.1 Pycharm
[Link] ggmap
7.2 Jupyter
DATA SCIENCE [Link] Sqldf
7.3 Colaboratory
2.3.1 RDBMS
7 .IDE
7.4 Spyder
2.3.2 Command Query
7.5 R-Studio
2.3.3 Handling Null Values
7.6 VS Code
2.3.4 Indexes
2.3 SQL (Database)
[Link] Django
2.3.5 Joins
[Link] Flask 8.1.1 Web Frameworks
2.3.6 Key Constraints
[Link] Ruby on Rails
2.3.7 Sub Query
8.1 web Application's
[Link] Heroku
2.3.8 Creating Tables
[Link] AWS 8.1.2 Cloud Platforms
3.1.1 Tree maps
[Link] Azure
[Link] Flask
Depends on Nature of your data 3.1.2 Bar Charts
[Link] Express 8.2.1 Framework
3.1 Choosing Right Visualization
8.2 API's
[Link] Ruby on Rail
3.1.3 Heatmaps
[Link] Cloud Platforms 8.2.2 Deploy the API
[Link].1Portable Container 8.3.1.1Docker 8.3.1 Tool's
3.1.4 Line Graphs
8.3.2 Run Consistently across different Environment
[Link] Docker Hub 8.3 Containerization
3.1.5 Box Plots
[Link] Kubernetes 8.3.3 Deploy
[Link] Colud Based containers Services
3.1.6 Scatter Plot
8.4.1 AWS Lambda
[Link] Events
3.1.7 Histogram
[Link] Schedule them 8.4.2 Trigger Functions
8.4 Serverless Computing 3.2.1 Scatter Plot
[Link] Expose them as API's
Identifying Potential Patterns or Outliers
8 .Deploy 3.2 Exploratory Data Visualization 3.2.2 Histograms
8.4.3 Azure Functions
8.4.4 Google Cloud functions 3.2.3 Box Plot
[Link] Tableau
[Link] Distribution
[Link] Power BI 8.5.1 Tool's
3.2.4 Explore [Link] Relationship
[Link] Ploty Dash
8.5 Dashboard and Reporting
[Link] Variation
[Link] Dedicated Servers
8.5.2 Deploy
3.3.1 Highlight Key Findings
[Link] Cloud Platforms
3.3 Story telling and Narrative 3.3.2 Overall Message
8.5.3 Shared as Stand alone Files
3.3.3 Design your Visualization accordingly
8.6.1 Reusable Code
[Link] Sampling
[Link] PyPi (Python) Reduce Complexity
8.6 Packages or Library
3.4.1 Aggregation Techniques [Link] Grouping
[Link] CRAN (R) 8.6.2 Publish Packages
[Link] Binning
8.6.2.3NPM ([Link])
3.4 Data reduction and Summarization
[Link] Mean
8.7.1 Version Control [Link] Visualization Provide Additional Insight
3.4.2 Summary Statistics [Link] Median
8.7.2 Code Sharing
[Link] Percentiles
8.7.3 Collaborating Team
[Link] Additional Information
8.7.4 1 GitHub 8.7 Collaboration Platforms
3.5.1 Enhance Visualization
8.7.4 Platforms
[Link] Highlight Key Element
[Link] GitLab
3.5.2 Easily Understandable
[Link] Open Source Projects
8.7.5 Publish Repositories
3.5.3 Visually Appealing
[Link] Private Repository
Color can enhance Visualization
[Link] Brightness
3.5 Color and Aesthetics 3.5.4 Perceptual Properties
[Link] Hue
[Link] Accessiable
3.5.5 Color Blind
[Link] Distinguishable
9.1.1 Define Project Goals
[Link] Categorical
Clearly define the problem and project goals
3.5.6 Data Type
9.1.2 Identify Business Objectives 9.1 Problem Definition
[Link] Continuous
9.1.3 Formulate Research Questions
3.6.1 Explore data Dynamically
3.6.2 Filter Subsets
9.2.1 Internal Data Sources
3.6.3 Gain deeper Insight
Gather relevant data from various sources
9.2.2 External Data Sources
9.2 Data Acquisition [Link] Linked Visualization
9.2.3 Data Collection Methods
[Link] Zooming
9.2.4 Data Storage and Management
[Link] Panning
[Link] Sliders
3.6 Interactive Visualization
[Link] Handling Missing Values [Link] Dropdown Menus
3.6.4 Interactivity
[Link] Handling Outliers 9.3.1 Data Cleaning
[Link].1 Tableau
[Link] Tools
[Link] Data Imputation
[Link].2 Power BI
[Link] Data Scaling
Clean, preprocess, and transform the data
[Link].1 Matplotlib
[Link] Encoding Categorical Variables 9.3.2 Data Transformation 9.3 Data Preparation
[Link] Libraries [Link].2 GGplot2
[Link] Feature Scaling
[Link].3 Seaborn
[Link] Feature Extraction
3.7.1 Holistic View of Data
[Link] Feature Selection 9.3.3 Feature Engineering
3.7.2 Trends Over Time
[Link] Feature Creation
3.7.3 Summary Statistics
3.7.4 Multiple Visualization
9.4.1 Data Visualization
3.7.5 KPIS
9.4.2 Descriptive Statistics 3.7 Dashboard Creation
Explore and visualize the data for insights
3.7.6 Interactive Elements
9.4.3 Correlation Analysis 9.4 Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
[Link] Metrices
9.4.4 Data Profiling
3.7.7 Monitor [Link] Detect Anomalies
9.4.5 Patterns and Insights
[Link] Make data driven Decisions
[Link] Matplotlib
[Link] Regression Models 3.8.1 Python [Link] Seaborn
3.8 Data Visualization Libraries
[Link] Classification Models [Link] Plotty
9.5.1 Supervised Learning
[Link] Decision Trees 3.8.2 R [Link] ggplot2
[Link] Support Vector Machines (SVM) 4.1 Identify the Target Website 4.1.1 Website(s) [Link] Scrape Data [Link].1 Data Extraction
Choose appropriate models based on the problem and data
[Link] BeautifulSoup
[Link] Clustering Algorithms
9.5 Model Selection
[Link] Scarpy
[Link] Dimensionality Reduction 9.5.2 Unsupervised Learning
4.2.1 Libraries
[Link] Puppeteer
[Link] Anomaly Detection
[Link] Selenium
4.2 Select a web Scraping tool or Library
[Link] Neural Network Architectures
[Link] Comfortable Programming Language
[Link] Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
9.5.3 Deep Learning 9 Data Science Life Cycle [Link] Complexity
4.2.2 Tool's Best Suits
[Link] Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
[Link] Website Structure
[Link] Transfer Learning
[Link] Required Interaction
[Link] HTML Structure
9.6.1 Data Splitting (Train-Validation-Test)
4,3 Understand Website structure 4.3.1 Inspect Page Source [Link] CSS Selectors
9.6.2 Model Initialization
[Link] XPath
Train the selected models using prepared data
9.6.3 Optimization Algorithms
9.6 Model Training [Link] Text
9.6.4 Loss Functions
[Link] Links
9.6.5 Model Fitting
4.4 Extract Data 4.4.1 Data Fields [Link] Images
9.6.6 Model Evaluation
[Link] Tables
[Link] Scraping [Link] Form Inputs
9.7.1 Accuracy Metrics 4.5.1 Multiple pages
Evaluate the performance of trained models using appropriate metrics
9.7.2 Precision and Recall 4.5.2 Next Page link
4.5 Handle Pagination and Navigation
9.7 Model Evaluation
9.7.3 ROC Curve 4.5.3 Requires Navigation
9.7.4 Confusion Matrix 4.5.4 Dynamic Content loading
9.7.5 F1 Score [Link] Java Script
4.6.1 Dynamic Content Loaded
9.8.1 Hyperparameter Optimization [Link] AJAX Request
Fine-tune model parameters for better results 4.6 Handle Dynamic Content
9.8.2 Cross-Validation [Link] Selenium
9.8 Model Tuning
4.6.2 Tools to interact with Website
9.8.3 Ensemble Methods [Link] Puppeteer
9.8.4 Regularization Techniques 4.7.1 Handling missing values
4.7.2 Converting datatypes
9.9.1 Integration with Applications Implement and integrate the model into production systems 4.7 Data Cleaning and Preprocessing
4.7.3 Removing unwanted characters
9.9 Model Deployment
9.9.2 API Development
4.7.4 Normalization
9.9.3 Model Versioning
[Link] CSV
[Link] JSON
9.10.1 Performance Monitoring Continuously monitor model performance and make necessary adjustments
4.8 Store the Extracted Data 4.8.1 Common Formats
[Link] Excel
9.10 Model Monitoring
9.10.2 Drift Detection
[Link] Databases
9.10.3 Feedback Loop 4.9 Respect Website Policies and Etiquette
9.11.1 Revisit Previous Stages Iterate through previous stages to refine and improve the models
9.11.2 Data Updates and Retraining 9.11 Iteration and Improvement
9.11.3 Model Enhancements
9.12.1 Present Findings and Insights
Present findings, insights, and results to stakeholders
9.12.2 Visualizations and Dashboards 9.12 Communication and Reporting
9.12.3 Recommendations and Next Steps
CONTENT
[Link] Learning [Link] Scraping [Link]
[Link] Language [Link] Analysis [Link]
[Link] Visualization [Link] [Link] Science Life Cycle
© 2023 All rights reserved. Pianalytix Edutech Pvt. Ltd. retains the copyright for this material worldwide.
You might also like
- Six Sigma Project Guideline: Relevance of Topic: Suitable For: Own ContributionNo ratings yetSix Sigma Project Guideline: Relevance of Topic: Suitable For: Own Contribution2 pages
- Dokumen - Tips - Cheat Sheet Building A Knime Workflow For Beginners Excel Reader Xls Reads ContentNo ratings yetDokumen - Tips - Cheat Sheet Building A Knime Workflow For Beginners Excel Reader Xls Reads Content1 page
- Competitor Analysis and User Testing InsightsNo ratings yetCompetitor Analysis and User Testing Insights1 page
- Inovacne Am400 Cpu1608tn NPN PLC Cpu Product Note English 20 4 20No ratings yetInovacne Am400 Cpu1608tn NPN PLC Cpu Product Note English 20 4 202 pages
- PODS Lite Conceptual Model Diagram - Final - v1No ratings yetPODS Lite Conceptual Model Diagram - Final - v11 page
- Reference Case Management Current Version Security Access ConfigurationNo ratings yetReference Case Management Current Version Security Access Configuration2 pages
- V-Mask Techniques for RPS Control ChartsNo ratings yetV-Mask Techniques for RPS Control Charts1 page
- Area D Substantive Procedures CompilationNo ratings yetArea D Substantive Procedures Compilation1 page
- Integer Factorization Algorithms ExplainedNo ratings yetInteger Factorization Algorithms Explained92 pages
- Planning Implementing and Evaluating Understanding The Connections100% (1)Planning Implementing and Evaluating Understanding The Connections24 pages
- FAQ - Season of War - Thondia 27-10-2022No ratings yetFAQ - Season of War - Thondia 27-10-20221 page
- Stacks Questions and Answers - Sanfoundry PDFNo ratings yetStacks Questions and Answers - Sanfoundry PDF4 pages
- Read CID Register and Display On A PC ScreenNo ratings yetRead CID Register and Display On A PC Screen6 pages
- Linak Techline Modbus Installation Guide Ver C EngNo ratings yetLinak Techline Modbus Installation Guide Ver C Eng41 pages
- Product Guide 2024 Valent BioSciences BiostimulantsNo ratings yetProduct Guide 2024 Valent BioSciences Biostimulants25 pages
- Police Administration 3rd Edition by Larry K Gaines Test BankNo ratings yetPolice Administration 3rd Edition by Larry K Gaines Test Bank315 pages
- Math3 q3 Module 1 Identifying Odd and Even NumbNo ratings yetMath3 q3 Module 1 Identifying Odd and Even Numb17 pages