Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A1.2 Nucleic Acids Topic Test - Model Answers
A1.2 Nucleic Acids Topic Test - Model Answers
Uploaded by
Ankit MistryOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A1.2 Nucleic Acids Topic Test - Model Answers
A1.2 Nucleic Acids Topic Test - Model Answers
Uploaded by
Ankit MistryCopyright:
Available Formats
First exams in 2025
IB Style Test - Topic A1. 2 Nucleic acids
Theme A - Unity and diversity Level of Organisation: Molecules
Mark scheme
Name ___________________ Time allowed: 30 mins SL / 40 mins HL
Mark: / 22(SL) 29(HL)
Multiple choice questions (3 marks)
1. As they do not have all the characteristics of living things, viruses are not considered to be living
organisms. Therefore which is the best evaluation of the statement, “One universal property of
living things is that they use DNA as the genetic material?”
A. Correct, as all living organisms have DNA as their genetic material.
B. Not correct, some viruses have RNA as their genetic material.
C. Correct as DNA base sequences are the same in all organisms.
D. Not correct because the genetic code is different in all organisms.
2. Which is the most accurate description of a nucleotide?
A. The centre of a chromosome.
B. A combination of DNA and histone protein.
C. A monomer unit of nucleic acids.
D. A nitrogenous base.
3. Which of the following describes the backbone of DNA?
A. Covalent bonding between nitrogenous bases.
B. Hydrogen bonds between deoxyribose and phosphate molecules.
C. Complimentary base pairing.
D. Covalent bonds between deoxyribose and phosphate molecules.
© Richard Scarr & David Faure, InThinking www.thinkib.net/biology
1
First exams in 2025
IB Style Test - Topic A1. 2 Nucleic acids
Theme A - Unity and diversity Level of Organisation: Molecules
Structured answer questions
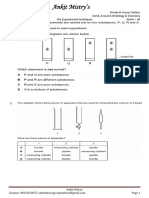
4. Label the following parts of DNA on the diagram of DNA shown below. (5 marks)
a) Hydrogen bond
b) Covalent bond
c) Nitrogenous base
d) Deoxyribose sugar
e) A single nucleotide (by drawing a circle encompassing a single nucleotide)
5. Explain, using the DNA diagram, the meaning of complimentary base pairing. (2 marks).
(Any two of these answers)
The base Adenine (A) always pairs with Thymine (T).
or The base Guanine (G) pairs with Cytosine (C).
Bases from one DNA strand are joined by hydrogen bonds to bases on the other DNA strand.
Base pairs (A-T and C-G ) are equal in length.
Base pairs have the same number of Hydrogen bonds.
© Richard Scarr & David Faure, InThinking www.thinkib.net/biology
2
First exams in 2025
IB Style Test - Topic A1. 2 Nucleic acids
Theme A - Unity and diversity Level of Organisation: Molecules
6. Outline how complimentary base pairing is important in the replication of DNA as the
genetic material. (3 marks)
• DNA Replication is the production of new DNA molecules.
• The new replicated DNA molecule must have the same base sequence (as the parent
DNA).
• When the two strands of a DNA molecule are separated each one is used as a template
to build a new strand.
• Complimentary base pairing ensures that A pairs with T, and C with G, so new strands of
DNA have the same sequence as the original molecule.
...........................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
7. Complete the table to outline the differences between the structure of RNA and DNA
(3 marks).
RNA structure DNA structure
Single stranded molecule Double stranded molecule
Backbone contains ribose (Backbone contains) deoxyribose
Thymine replaced by Uracil Thymine is one of the four bases
...........................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
© Richard Scarr & David Faure, InThinking www.thinkib.net/biology
3
First exams in 2025
IB Style Test - Topic A1. 2 Nucleic acids
Theme A - Unity and diversity Level of Organisation: Molecules
Extended response questions
8. DNA is the genetic material of all living organisms. Outline how it is possible for these
universal DNA molecules to store varied genetic information both within species and
between species.
. (6 marks)
• The DNA base sequence is the store of genetic information / genetic material.
• There are a huge number of different base sequences possibe (in a DNA molecule or a
genome) which provides variety in the genetic information / genomes.
• Different lengths of DNA, or different sequences of the bases causes variation in the
genetic information stored in a genome
• Base sequence is a code/can determine protein structure/amino acid sequence and the
characteristics of an organism.
• Within species there each organism has many genes with a lot of similarity in the DNA
sequence and this gives the species it’s recognisable characteristics.
• There is some variation in the sequence of DNA in some genes even within species giving
elements of variation in characteristics.
• Between species there are more differences in the DNA sequence, which gives more
variation in characteristics.
• Diggerences in the DNA sequence between two species can prevent reproduction
between members of two different species.
...........................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
© Richard Scarr & David Faure, InThinking www.thinkib.net/biology
4
First exams in 2025
IB Style Test - Topic A1. 2 Nucleic acids
Theme A - Unity and diversity Level of Organisation: Molecules
Additional Higher Level only (7 marks)
9. Hershey and Chase used viral bacteriophages to demonstrate that DNA, not protein, is the
genetic material. This investigation used radioactive phosphorus to label DNA.
Outline how radioactive labelling was used in this investigation.
(4 marks)
• Radioactive labelling allows specific molecules to be observed.
• Phosphorus is found in DNA but not protein.
• Bacteriophage DNA was labelled with radioactive phosphorus.
• The radioactive label showed that the DNA part of the virus entered the (bacterial) cell.
• The radioactive labelled DNA was used to make new virus particles showing that DNA
was the genetic material passed from one generation to the next (and not protein).
• 3 marks max if the distinction between protein and DNA as the genetic material is not
clear in the answer.
...........................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
10. A nucleosome is a structural unit of a chromosome. Describe the structure of a nucleosome.
(3 marks)
• DNA molecule wrapped around histone proteins.
• There are 8 histone proteins (in the core of the nucleosome)
• Additional/one histone molecule and linker DNA join nucleosomes together.
...........................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
© Richard Scarr & David Faure, InThinking www.thinkib.net/biology
5
You might also like
- Kami Export - Gene Expression-Translation-S.1617553074Document6 pagesKami Export - Gene Expression-Translation-S.1617553074Camila Corvalan100% (5)
- Lecture 1112 - DNA and ReplicationDocument50 pagesLecture 1112 - DNA and Replicationnizobell100% (1)
- CH8 DNA Structure and Replication 2021Document4 pagesCH8 DNA Structure and Replication 2021EmileMcBrokeNo ratings yet
- The Genetic Material-1Document48 pagesThe Genetic Material-1Windra TrivenNo ratings yet
- IB Biology HL 2.6 WorksheetDocument10 pagesIB Biology HL 2.6 WorksheetKazeNo ratings yet
- A1.2 2025 Topic Test v3Document5 pagesA1.2 2025 Topic Test v3valentinaNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument113 pagesMolecular Biologytummalapalli venkateswara rao80% (10)
- Genetic Organization HandoutDocument8 pagesGenetic Organization HandoutConnorNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Products of DNA TechnologyDocument38 pagesPharmaceutical Products of DNA TechnologyAbdul Al RajaNo ratings yet
- Science10 Q3 Week4Document22 pagesScience10 Q3 Week4Samad Recca T. NatividadNo ratings yet
- When Gender MattersDocument30 pagesWhen Gender MattersJeck Sison100% (2)
- Q1 Sci9 Mod6Document18 pagesQ1 Sci9 Mod6Regine Rafer Escalante100% (2)
- Toxicology and Safety Assessment: (Otc and Dangerous Drugs)Document57 pagesToxicology and Safety Assessment: (Otc and Dangerous Drugs)Sheena GagarinNo ratings yet
- (PDF) Mcqs in Microbiology - Mohammed Bilal - Academia - Edu PDFDocument1 page(PDF) Mcqs in Microbiology - Mohammed Bilal - Academia - Edu PDFM AdnanNo ratings yet
- Lesson-Guide 2module - G9-Biology Module 2 On Template PDFDocument31 pagesLesson-Guide 2module - G9-Biology Module 2 On Template PDFconstancia G, caraan100% (1)
- Biology The Core 2Nd Edition Simon Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesBiology The Core 2Nd Edition Simon Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFjason.collins370100% (13)
- The Dna: Learning Objectives (L.O.)Document13 pagesThe Dna: Learning Objectives (L.O.)masa bedaNo ratings yet
- (Lesson Plan (LP) : Knowledge Skills Attitudes Values References MaterialsDocument3 pages(Lesson Plan (LP) : Knowledge Skills Attitudes Values References MaterialsFloraville Lamoste-MerencilloNo ratings yet
- Biology Today and Tomorrow Without Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions ManualDocument10 pagesBiology Today and Tomorrow Without Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions Manualbiancalongf15100% (33)
- Biology The Core 2nd Edition Simon Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesBiology The Core 2nd Edition Simon Solutions Manualaureliacharmaine7pxw9100% (22)
- Biology The Core 2Nd Edition Simon Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument47 pagesBiology The Core 2Nd Edition Simon Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFCassieYangiosx100% (13)
- Orca Share Media1662355444548 6972424090491517852Document9 pagesOrca Share Media1662355444548 6972424090491517852Mic Houston Mar T. ParroNo ratings yet
- 8 - Genetic MaterialDocument22 pages8 - Genetic MaterialCrisha LimNo ratings yet
- Aab 2209 Cell Bology Suppspecial Exam Marking Scheme (Autorecovered)Document10 pagesAab 2209 Cell Bology Suppspecial Exam Marking Scheme (Autorecovered)Benard apiriNo ratings yet
- 12 Biology Notes Ch06 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument14 pages12 Biology Notes Ch06 Molecular Basis of Inheritancehimanshu kumarNo ratings yet
- Notes On Molecular Basis of Inheritance by ExamsRoadDocument8 pagesNotes On Molecular Basis of Inheritance by ExamsRoadVogolus machatteNo ratings yet
- L2 & 3 The NucleusDocument54 pagesL2 & 3 The NucleusAmarachi MaduabuchiNo ratings yet
- L3+4 - DNA Replication and Genetic Code StudentDocument31 pagesL3+4 - DNA Replication and Genetic Code StudentHaris KhokharNo ratings yet
- 1934 FdocDocument6 pages1934 Fdoctyleryawh2072No ratings yet
- 3.9 DNA Replicaton and The Genetic CodeDocument27 pages3.9 DNA Replicaton and The Genetic CodePratika MNo ratings yet
- SAS For Biochemistry BIO 024 Module 6 1Document33 pagesSAS For Biochemistry BIO 024 Module 6 1vovoka449No ratings yet
- Assignment # 7 Genes & Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pagesAssignment # 7 Genes & Nucleic AcidsCharlou SindacNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 Survival KitDocument35 pagesLife Sciences P2 Survival KitMashamba CoutinhoNo ratings yet
- The Double Helix: Film Activity Student HandoutDocument4 pagesThe Double Helix: Film Activity Student HandoutMatthew Spencer HoNo ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument32 pagesDna StructureHONLETH ROMBLONNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument27 pagesUntitledkabir omotayoNo ratings yet
- Biok - 7.1 - DNA - Structure - and Replication - AHLDocument37 pagesBiok - 7.1 - DNA - Structure - and Replication - AHLZoya PadaniyaNo ratings yet
- BIOL 2050 - Lecture 6Document31 pagesBIOL 2050 - Lecture 6WavyBaconNo ratings yet
- SBI4U Assignmentfor Unit 3 Mini Summative Chapter 6 YuchucaoDocument5 pagesSBI4U Assignmentfor Unit 3 Mini Summative Chapter 6 Yuchucaoyao fengNo ratings yet
- Week 1 DNADocument28 pagesWeek 1 DNAHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- DNA - WikipediaDocument27 pagesDNA - WikipediaAmit KaushikNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Molecular Biology Chapter 10 PDFDocument115 pagesUnit 6 Molecular Biology Chapter 10 PDFc8kewaternotesNo ratings yet
- BioK DP Notes 7.1Document10 pagesBioK DP Notes 7.1Lal ÖzşahinNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Biology - Noted Summaries 2023Document91 pagesGrade 12 Biology - Noted Summaries 2023ganinusaibahNo ratings yet
- 1.2 ReviewDocument3 pages1.2 ReviewAaryan ThavaranNo ratings yet
- Bio 308 Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesBio 308 Lecture NotesPeter Sin-KeoNo ratings yet
- Dna-Structure and Roles of Nucleic AcidDocument8 pagesDna-Structure and Roles of Nucleic AcidParis JarrettNo ratings yet
- IB - MYP5 U6 How Docharacteristics Pass From One Generation To AnotherDocument77 pagesIB - MYP5 U6 How Docharacteristics Pass From One Generation To AnotherCoco LocoNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument61 pagesDNA Structure and Replicationmanuela pardoNo ratings yet
- Properties: GeneticDocument24 pagesProperties: Geneticpalak singhNo ratings yet
- Science 10-Dlp9-Dna-RnaDocument3 pagesScience 10-Dlp9-Dna-RnaSharlene Cecil PagoboNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument10 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritancesahanaNo ratings yet
- Day 2Document8 pagesDay 2Frency BautistaNo ratings yet
- Guess What I'ma Do It My WayDocument59 pagesGuess What I'ma Do It My Wayn.guledNo ratings yet
- Lesson-Guide 2module - G9-Biology Module 2 On TemplateDocument31 pagesLesson-Guide 2module - G9-Biology Module 2 On Templateconstancia G, caraanNo ratings yet
- 10SCI Cells, DNA, Mitosis and Meiosis Booklet 2023Document9 pages10SCI Cells, DNA, Mitosis and Meiosis Booklet 2023Henry SeebeckNo ratings yet
- Basics of Gene Cloning & Cloning Enzymes: Lecture 1 BT-620Document71 pagesBasics of Gene Cloning & Cloning Enzymes: Lecture 1 BT-620laconic777No ratings yet
- Lec3 DNA, RNA, Structure of Nucleic AcidsDocument47 pagesLec3 DNA, RNA, Structure of Nucleic AcidsSITI BAZILAH BINTI BILAK KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- DNA Synthesis and SequenceDocument6 pagesDNA Synthesis and SequenceInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance: By: Dr. Anand ManiDocument130 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance: By: Dr. Anand ManiIndu Yadav100% (3)
- CE6068 Lecture 3Document80 pagesCE6068 Lecture 3林采玟No ratings yet
- Grade-12a - Biology - Worksheet-5 (08.09.23)Document4 pagesGrade-12a - Biology - Worksheet-5 (08.09.23)Dhavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication - BioDocument17 pagesDna Replication - Biorautshreyash22No ratings yet
- A2.3 Viruses HL - Model AnswersDocument3 pagesA2.3 Viruses HL - Model AnswersAnkit MistryNo ratings yet
- A1.1 Water - Topic TestDocument3 pagesA1.1 Water - Topic TestAnkit MistryNo ratings yet
- Private & Group Tuitions IGCSE, A Level & IB Biology & Chemistry Ig Chem Ch2 Experimental Techniques Marks 40 1Document7 pagesPrivate & Group Tuitions IGCSE, A Level & IB Biology & Chemistry Ig Chem Ch2 Experimental Techniques Marks 40 1Ankit MistryNo ratings yet
- Ig Chem CH 2 QP Core v.2Document6 pagesIg Chem CH 2 QP Core v.2Ankit MistryNo ratings yet
- Ig Chem CH 2 QP Core v.1Document6 pagesIg Chem CH 2 QP Core v.1Ankit MistryNo ratings yet
- Ig Chem CH 2 Ms Core v.2Document3 pagesIg Chem CH 2 Ms Core v.2Ankit MistryNo ratings yet
- Ig Chem CH 2 Ms Core v.1Document3 pagesIg Chem CH 2 Ms Core v.1Ankit MistryNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Chemistry 5070/11Document16 pagesCambridge O Level: Chemistry 5070/11Ankit MistryNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: CHEMISTRY 5070/41Document16 pagesCambridge O Level: CHEMISTRY 5070/41Ankit MistryNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Chemistry 5070/32 October/November 2022Document7 pagesCambridge O Level: Chemistry 5070/32 October/November 2022Ankit MistryNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Chemistry 5070/41 October/November 2022Document10 pagesCambridge O Level: Chemistry 5070/41 October/November 2022Ankit MistryNo ratings yet
- Forensic Serology, Blood Stain Pattern Analysis, Forensic Biochemistry and Molecular BiologyDocument56 pagesForensic Serology, Blood Stain Pattern Analysis, Forensic Biochemistry and Molecular Biologyvishnu SNo ratings yet
- Review DNA MitokondriaDocument2 pagesReview DNA MitokondriaMir RimNo ratings yet
- Annual Lesson Plan: Biology FORM 5 2008 Week Date Topic Learning Area RemarkDocument5 pagesAnnual Lesson Plan: Biology FORM 5 2008 Week Date Topic Learning Area RemarkKrull Hzm100% (22)
- Cloning Essay FinalDocument6 pagesCloning Essay Finalapi-319781846No ratings yet
- DNA ExtractionDocument11 pagesDNA ExtractionHoor Ul Ain RounaqNo ratings yet
- Catalytic RnaDocument12 pagesCatalytic RnaDr-Sumanta BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- H+ Magazine - Volume 1Document253 pagesH+ Magazine - Volume 1oliva_e100% (1)
- Cytogenetic TechnologistDocument2 pagesCytogenetic Technologistapi-77399168No ratings yet
- Pason LetterDocument5 pagesPason LetterRoel AbricaNo ratings yet
- 11 Chapter 1Document58 pages11 Chapter 1AmanNo ratings yet
- RPT Biology Form 4Document10 pagesRPT Biology Form 4edain84No ratings yet
- Silver Sol Scientific ResearchDocument3 pagesSilver Sol Scientific ResearchALKESWW100% (1)
- Dr. Kruti Pandya Research PublicationsDocument10 pagesDr. Kruti Pandya Research PublicationsAradhana MehraNo ratings yet
- Title of The Paper (E.g. Why Is The Use of A Mask Effective in Preventing The Transmission of COVID-19 and Which Is The Best Type)Document4 pagesTitle of The Paper (E.g. Why Is The Use of A Mask Effective in Preventing The Transmission of COVID-19 and Which Is The Best Type)dobsNo ratings yet
- DNA Profiling: Aims & ObjectivesDocument3 pagesDNA Profiling: Aims & ObjectivesNikit GoswamiNo ratings yet
- HC70A-W23-Quiz 1Document5 pagesHC70A-W23-Quiz 1remiNo ratings yet
- Biol 103 01 (F16)Document4 pagesBiol 103 01 (F16)bebbuwebbu100% (1)
- GenBio SMILE LP2 Q1 WEEK2Document14 pagesGenBio SMILE LP2 Q1 WEEK2jeknendoNo ratings yet
- Medical BiotechnologyDocument34 pagesMedical Biotechnologyalfi alfathanaNo ratings yet
- Interspecific Hybridization Facilitates Niche Adaptation in Beer YeastDocument18 pagesInterspecific Hybridization Facilitates Niche Adaptation in Beer YeastcdfreaksNo ratings yet
- Nukleus PDFDocument17 pagesNukleus PDFsuci adi malsiNo ratings yet
- Bernard Jude M. Gutierrez, RCH: Chemist License # 11395Document2 pagesBernard Jude M. Gutierrez, RCH: Chemist License # 11395Bernard Jude GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Anti Hiv Using Nano RobotsDocument8 pagesAnti Hiv Using Nano RobotsBharadwaj Santhosh50% (2)
- Aerobic and Anaerobic RespirationDocument6 pagesAerobic and Anaerobic Respiration10A 27 Mahek PanirwalaNo ratings yet
- 355 Homework 1Document16 pages355 Homework 1zeynoleeeNo ratings yet