Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The French Revolution - Mind Map
The French Revolution - Mind Map
Uploaded by
Alishba ZaidiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The French Revolution - Mind Map
The French Revolution - Mind Map
Uploaded by
Alishba ZaidiCopyright:
Available Formats
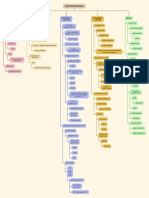
FRENCH REVOLUTION
1. The French Society during the Late 18th Century
The French Society comprised
August 4, 1789
Ends the rights of the aristocracy, the surrender of feudal rights.
1st Estate Clergy including priests, who ran both the Catholic church and some aspects of the country
5. The Abolition of Slavery
June 20, 1789
Nobility including members of the royal family, except for the King; did not have to pay any taxes. Tennis Court Oath members of the French Third Estate Triangular slave trade among Europe, Africa, and America
2nd Estate
gathered in a tennis court at the Palace of Versailles. 1794 convention made it free to all slaves 10 years later
slavery was reintroduced by Napoleon In 1848 slavery was
abolished in the French colonies
3rd Estate Big businessmen, merchants, court officials, peasants, artisans, landless laborers, servants, etc.
August 26, 1789 Declartion of Rights of Man
1790
Civil Constitution of the Clergy nationalizes the Church
2. The Growing Middle Class- New Wave
6. The Revolution and Everyday Life
1791
Educated inspired by ideas of Locke and Rousseau believed that A constitution is framed to limit the powers of the king and to • After 1789 many changes in the lives of men, women,
no group in society should be privileged by birth guarantee basic rights to all human beings and children in France One important law passed the
abolition of censorship.
1792 • Most important legacy of the French Revolution The ideas
Locke “Two Treaties of Government” refuted divine & absolute France becomes a republic, the king is beheaded. Overthrow of
of liberty and democratic rights
the Jacobin republic, a Directory rules France
rights of monarch
1792 7. Napoleon
Austria and Prussia attack revolutionary France, Robespierre,
Rousseau “Social Contract” between people and representatives elected the first Deputy for Paris to the National convention In 1804, Napoleon crowned himself emperor of France.
1793
Montesquieu “The Spirit of Laws” division of powers between Louis XVI and Marie Antoinette were executed
He set out to conquer neighboring European countries
organs of Government. and created kingdoms where he placed members
1792-1794
in 1793, the reign of terror occured due to extreme policies of of his family.
Robespierre. Austria, Britain, the Netherlands, Prussia, and Spain
are at war with France.
3. The Outbreak of the Revolution : Important timelines
1794 He saw his role as a modernizer of Europe.
Robespierre is executed. France is governed by a Directory, a
1770s-1780s committee of five men. The Reign of Terror ends.
Economic Crisis: French Government in deep debt.
1795
1774 National convention dissolved
Louis XVI ascended to the throne He was finally defeated at Waterloo in 1815
1788-1789
Bad harvest, high prices, food riots.
4. Women’s participation in the revolution
May 5, 1789
Estates-General convened, demanded reforms. Women were active participants in the events To discuss and voice their interests women 1946 women in France won the right to vote.
Most of the women of the third estate had to started their own political clubs and newspapers
work for a living Wages were lower than men main demand women must enjoy the
July 14, 1789 So demanded equal pay for equal work. same political rights as men
National Assembly formed. Bastille stormed on July 14. (The Society of Revolutionary and Republican Women
French Revolution started. were one of the most prominent executive clubs during the
French Revolution established May 10, 1793, which lasts in less
than five months.)
You might also like
- H 1976Document61 pagesH 1976Hal ShurtleffNo ratings yet
- Absolute MonarchsDocument30 pagesAbsolute MonarchsBobNo ratings yet
- The French Revolution: Facts That MatterDocument21 pagesThe French Revolution: Facts That Mattersunilkhairnar38No ratings yet
- French RevolutionDocument19 pagesFrench Revolutionliza chawlaNo ratings yet
- The Hitler-Bormann Documents, February-April 1945Document44 pagesThe Hitler-Bormann Documents, February-April 1945api-3831252100% (2)
- Precis by Jean Nicolas Louis DurandDocument363 pagesPrecis by Jean Nicolas Louis DurandGünsu Merin Abbas0% (1)
- Unit 5.2 FRENCH REVOLUTIONDocument38 pagesUnit 5.2 FRENCH REVOLUTIONVega Suffo JiménezNo ratings yet
- Ppt-FRENCH REVOLUTIONDocument51 pagesPpt-FRENCH REVOLUTIONshruti tyagi100% (1)
- Frenchrevolution Cause and EffectsDocument33 pagesFrenchrevolution Cause and Effectsmysterious xNo ratings yet
- La Framboise GenealogyDocument75 pagesLa Framboise GenealogyGuigno Schmuerz100% (1)
- Edexcel IGCSE P1 - 3 The French Revolution, C. 1780-99 PresentationDocument23 pagesEdexcel IGCSE P1 - 3 The French Revolution, C. 1780-99 Presentation(3E13) Leung Nga Ting Natalie 20191D023spss.hkNo ratings yet
- Otto de GrandsonDocument3 pagesOtto de GrandsonGrigor FedanNo ratings yet
- Ix History The French RevolutionDocument7 pagesIx History The French RevolutionRonak SoniNo ratings yet
- French Revolution TimelineDocument2 pagesFrench Revolution TimelineDiane LeeNo ratings yet
- Rafe Blaufarb - The Great DemarcationDocument305 pagesRafe Blaufarb - The Great DemarcationJena Morelli100% (1)
- Generation AXA 1985-2010 - 25 Years in The History of AXA (2010) - AXA SADocument177 pagesGeneration AXA 1985-2010 - 25 Years in The History of AXA (2010) - AXA SAJonathan OngNo ratings yet
- OT LAWANI - HW French Revolution Cause and Effect (Assignment) - 3054958Document2 pagesOT LAWANI - HW French Revolution Cause and Effect (Assignment) - 3054958Osaretin LawaniNo ratings yet
- French Revolution WorksheetDocument4 pagesFrench Revolution WorksheetplarranvicNo ratings yet
- French Revolution Fact File English The French Revolution Fact File - Ver - 7Document3 pagesFrench Revolution Fact File English The French Revolution Fact File - Ver - 7tamilore.ishola.101No ratings yet
- 2nd Unit II French RevolutionDocument1 page2nd Unit II French Revolutiondanile62No ratings yet
- The French Revolution: Presented By: 1789 - 1815Document41 pagesThe French Revolution: Presented By: 1789 - 1815tanyagargNo ratings yet
- History CH 1Document6 pagesHistory CH 1Ravinder KumarNo ratings yet
- History - The French Revolution - Class NotesDocument91 pagesHistory - The French Revolution - Class Notesmusicfactory2008No ratings yet
- CompressedDocument33 pagesCompressedanastasia nandaNo ratings yet
- CK French Revolution SlidesDocument191 pagesCK French Revolution Slidesnr9j2j259mNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Cbse RevolutionDocument27 pagesClass 9 Cbse RevolutionKaleelur RahmanNo ratings yet
- History - Year 3 IP Mid-Year Examination 2011 Revision NotesDocument4 pagesHistory - Year 3 IP Mid-Year Examination 2011 Revision NotesLee Kay HoweNo ratings yet
- Resource Pack - Year 5 - The French Revolution PDFDocument17 pagesResource Pack - Year 5 - The French Revolution PDFAnonymous Y0phZaxNo ratings yet
- French Revolution - Simple English Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFDocument8 pagesFrench Revolution - Simple English Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFAgha Adnan KhanNo ratings yet
- French RevolutionDocument7 pagesFrench Revolutionraman baviskarNo ratings yet
- The Age of The Liberal Revolutions (1789 - 1871) Unit 2 - 2Document49 pagesThe Age of The Liberal Revolutions (1789 - 1871) Unit 2 - 2naiuwu69No ratings yet
- Kerala STD X Social Science I UNIT 01 Revolutions That Influenced The World Study Notes (Eng Med) - Cropped-Pages-1,2-3Document3 pagesKerala STD X Social Science I UNIT 01 Revolutions That Influenced The World Study Notes (Eng Med) - Cropped-Pages-1,2-3Saja Zameer100% (1)
- BrochureDocument2 pagesBrochurewilynjoy marcelinoNo ratings yet
- French Revolution RM 23-24Document8 pagesFrench Revolution RM 23-24Harit ManvarNo ratings yet
- French ReDocument7 pagesFrench ReMukeshChhawariNo ratings yet
- History Notes of Chapter - 1Document19 pagesHistory Notes of Chapter - 1ayushsukla78No ratings yet
- French Revolution, 9, Ch-1Document2 pagesFrench Revolution, 9, Ch-1Khan ArshiNo ratings yet
- French RevolutionIASbabaDocument20 pagesFrench RevolutionIASbabaDhawan GuptaNo ratings yet
- The French RevolutionDocument11 pagesThe French RevolutionKaryssa AquinoNo ratings yet
- Infografía de Línea de Tiempo Timeline Con Años Fechas Multicolor ModernoDocument1 pageInfografía de Línea de Tiempo Timeline Con Años Fechas Multicolor ModernoLiriaNo ratings yet
- Class 9 His CH 1 Study MaterialDocument4 pagesClass 9 His CH 1 Study Materialsadhna yadavNo ratings yet
- French RevolutionDocument10 pagesFrench Revolutionyashwardhanthakur50No ratings yet
- 1333340893Document1 page1333340893Debdeep BhuniaNo ratings yet
- 09 Social Science Key Notes History Ch1 The French RevolutionDocument3 pages09 Social Science Key Notes History Ch1 The French RevolutionManisha SinghNo ratings yet
- 23.2 Guided ReadingDocument1 page23.2 Guided ReadingCharles ShultzNo ratings yet
- Madame Thérèse: Edward ManleyDocument186 pagesMadame Thérèse: Edward ManleyGutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- The French Society During The Late 18th CenturyDocument4 pagesThe French Society During The Late 18th Centuryrashmi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Background of The French Revolution (Final)Document15 pagesBackground of The French Revolution (Final)humza hunainNo ratings yet
- The French RevolutionDocument8 pagesThe French RevolutionArun SainiNo ratings yet
- French Revolution Differentiated Reading Comprehension ActivityDocument11 pagesFrench Revolution Differentiated Reading Comprehension Activityjoaquin villadiegoNo ratings yet
- French Revolution NotesDocument12 pagesFrench Revolution Noteseeren41789No ratings yet
- The French RevolutionDocument5 pagesThe French RevolutionAditya Ratn SinglaNo ratings yet
- MB Download 16700Document4 pagesMB Download 16700Diva ShahNo ratings yet
- History Chapter 1-The French Revolution NotesDocument3 pagesHistory Chapter 1-The French Revolution NotesKhushi TanejaNo ratings yet
- 09 Social Science Key Notes History Ch1 The French RevolutionDocument3 pages09 Social Science Key Notes History Ch1 The French RevolutionkeshavNo ratings yet
- The French Revolution 1789Document36 pagesThe French Revolution 1789goaxeNo ratings yet
- The French RevolutionDocument60 pagesThe French RevolutionArjie GabrielNo ratings yet
- HE Rench Evolution: Liberty, Equality, FraternityDocument52 pagesHE Rench Evolution: Liberty, Equality, FraternityAnonymous HumanNo ratings yet
- The French Revolution: Ancien Regime & The Reign of Terror: LibertéDocument27 pagesThe French Revolution: Ancien Regime & The Reign of Terror: Liberté(1A) Arran KellyNo ratings yet
- French RevolutionDocument13 pagesFrench RevolutionClarisseNo ratings yet
- The French Revolution Class-9 (History)Document2 pagesThe French Revolution Class-9 (History)Harshavardhan RajaramNo ratings yet
- By: Susan M. Pojer Horace Greeley H. S. Chappaqua, NYDocument59 pagesBy: Susan M. Pojer Horace Greeley H. S. Chappaqua, NYAlan RubioNo ratings yet
- The French Revolution CBSE Grade 9Document24 pagesThe French Revolution CBSE Grade 9Anagha Krishna PrasadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 The French RevolutionDocument15 pagesChapter 18 The French RevolutionDolores SantillanNo ratings yet
- Bill of RightDocument26 pagesBill of RightsenoritaNo ratings yet
- French RevolutionDocument22 pagesFrench Revolutionapi-294843376No ratings yet
- Thefrenchrevolution Causes For The French Revolution: 1. Political Causes (Or) Louis Xvi and His ProblemsDocument8 pagesThefrenchrevolution Causes For The French Revolution: 1. Political Causes (Or) Louis Xvi and His ProblemsOm H TiwariNo ratings yet
- FrenchDocument4 pagesFrenchrotscribdNo ratings yet
- Factors of French RevolutionDocument8 pagesFactors of French RevolutionAkshatNo ratings yet
- International Trade Report Executive Summary Ultimo PeriodoDocument18 pagesInternational Trade Report Executive Summary Ultimo PeriodotijaNo ratings yet
- 8.2 Revolutions of 1830 and 1848Document20 pages8.2 Revolutions of 1830 and 1848bnfpgfyh4kNo ratings yet
- Perry Anderson, Folker Fröbel, Jürgen Heinrichs, y Otto Kreye - On Some Postulates of An Antisystemic PolicyDocument14 pagesPerry Anderson, Folker Fröbel, Jürgen Heinrichs, y Otto Kreye - On Some Postulates of An Antisystemic PolicyLuis GarridoNo ratings yet
- Modern Times (History) : CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesModern Times (History) : CharacteristicsMihaela TomaNo ratings yet
- IHRM CaseDocument7 pagesIHRM CaseAli OvaisNo ratings yet
- (English) France Culture - Fun Facts About France (DownSub - Com)Document4 pages(English) France Culture - Fun Facts About France (DownSub - Com)Xuân Anh ChuNo ratings yet
- JTNews - January 23, 2015Document32 pagesJTNews - January 23, 2015Joel Magalnick100% (1)
- Open SpacesDocument29 pagesOpen SpacesEmime Lee100% (1)
- Culture of FranceDocument4 pagesCulture of FranceRohit SikriNo ratings yet
- The Empress's New Clothes Fashion and Politics in Second Empire FranceDocument8 pagesThe Empress's New Clothes Fashion and Politics in Second Empire FranceIleana PascalauNo ratings yet
- Class 9 French WorksheetDocument5 pagesClass 9 French WorksheetgamingwithbhriguNo ratings yet
- French RevolutionDocument5 pagesFrench RevolutionHeart BrokenNo ratings yet
- Western Gastronomy: Commons, Heritages and Markets: Christian Barrère, Laboratory Regards, University of Reims, FranceDocument16 pagesWestern Gastronomy: Commons, Heritages and Markets: Christian Barrère, Laboratory Regards, University of Reims, FranceBARRERENo ratings yet
- Go 6Document1 pageGo 6api-283130992No ratings yet
- Freewheel Afloat BrochureDocument32 pagesFreewheel Afloat BrochurejmrubyNo ratings yet
- LeadershipDocument16 pagesLeadershipapi-243227891No ratings yet
- FrenchrevolutionDocument57 pagesFrenchrevolutionroopkumar agdariNo ratings yet
- Volume1 PDFDocument840 pagesVolume1 PDFFabrizio MansuetoNo ratings yet
- Napoleon Forges An Empire 1Document5 pagesNapoleon Forges An Empire 1Gladys CancinoNo ratings yet