Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Overview, Scenario, Crossword Puzzle
Overview, Scenario, Crossword Puzzle
Uploaded by
AnanthvasanthaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Overview, Scenario, Crossword Puzzle
Overview, Scenario, Crossword Puzzle
Uploaded by
AnanthvasanthaCopyright:
Available Formats
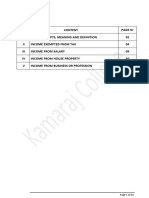
OVERVIEW OF SECTION I
Section I of the syllabus comprises of the initial two chapters –
Chapter 1 Basic Concepts
Chapter 2 Residential Status and Scope of Total Income.
In Chapter 1, we would introduce you to the fundamental concepts of income-tax
law in India. Since income-tax is levied on the total income of a person, it is
important for you to know who all and which entities are covered under the
definition of “person” and how to go about computing the total income of such
person. At Intermediate level, we will discuss in detail the procedure for
computation of total income and tax liability of an individual. The concepts of
“previous year” and “assessment year” are very significant in income-tax law.
“Previous year” is the financial year immediately preceding the assessment year.
Income earned during the previous year is chargeable to tax during the assessment
year immediately following the previous year. You have to understand the meaning
and scope of “income” under the Income-tax law. Also, it is important to know the
rates of income-tax, surcharge and cess for different persons to compute their tax
liability. All these are dealt with in Chapter 1.
Chapter 2 deals with determination of residential status of a person and the scope
of total income. It is the residential status of a person that determines the scope
of income chargeable to tax in his/her/its hands. For example, in case an individual
is a resident and ordinarily resident, his global income would be chargeable to tax
in India. However, if he is a non-resident, the income accrued and received outside
India will not be chargeable to tax in India, unless it is specifically deemed to accrue
or arise in India. The concept of “deemed to accrue or arise in India” is important
and is dealt with in detail in this chapter. An individual’s residential status is
determined on the basis of the number of days of his stay in India in the current
previous year or in the current previous year and in the earlier previous years.
However, there is also a concept of deeming an individual, who is a citizen of India
to be a resident based on fulfilment of certain criteria. The number of days of his
stay in India is, however, not relevant for attracting this deeming provision. These
aspects are dealt with in detail in Chapter 2.
© The Institute of Chartered Accountants ofPage
India 1
Before we commence learning the subject of income-tax law, we would like to
introduce you to this interesting subject through a Scenario, in which Anisha, an 18
year old girl, is trying to understand the ABCs of income-tax law. Anisha has just
joined B. Com in a popular college in Mumbai. She is elated as she has qualified
the CA Foundation examination held in June, 2023 with flying colours. She has
registered for CA Intermediate course and is eligible to appear for the examination
in May, 2024. She has downloaded the BoS Mobile App and is able to access all
learning material of Board of Studies (BoS) of ICAI and recorded lectures for
different subjects at one place. She had viewed the BoS live classes for the
Foundation course online and found them very useful for understanding the
concepts, problem solving and preparation for the examination. She is looking
forward to viewing the BOS Live Learning Classes which is to commence shortly for
CA Intermediate course. She is especially keen on learning income-tax law, since
income-tax aspects relating to different income earned by her family members crop
up during dinner table conversations. Therefore, she wants to begin understanding
the different concepts of income-tax by relating the same to the income earned by
her immediate family and relatives.
Read the Scenario below and the “Points to Ponder” raised by Anisha. Most of you
will be in the same age group as Anisha. Being in the same peer group as her, you
can help her find answers by reading Chapters 1 and 2 and understanding the basic
concepts of income-tax law and the provisions for determining residential status
and scope of total income. Also, do solve the Crossword Puzzle given at the end.
SCENARIO
Anil, aged 50 years, is carrying on business of retail trade in Mumbai. Anil’s parents
aged 78 years and 82 years stay with him. Anil’s wife, Asha, aged 47 years, is a
popular baker in her locality in Mumbai. She receives orders from customers in the
nearby localities in Santa Cruz, Mumbai and bakes cakes, pastries and cookies at
home and delivers them. She also grows seedlings and saplings in pots in her
garden for sale. She sold some of her jewellery this year. Both Anil and Asha have
© The Institute of Chartered Accountants ofPage
India 2
fixed deposits with banks from which they earn interest. Anil has invested in shares
of various Indian companies in his name and earned dividend therefrom. Anil and
Asha have one son, Abhinav, aged 24 and one daughter, Anisha, aged 18 years, to
whom you have already been introduced. All of them are citizens of India.
Abhinav has completed MBA in Marketing from a reputed University in India in
May, 2023 and is working as a Marketing Executive in Beta Ltd. in Mumbai from 1st
June, 2023 for a salary of ` 3 lakh per month. This being his first job, he gifted a
smart phone to Anisha from his first salary which he received in June, 2023. He
won ` 20,000 in Maharashtra State Lottery in August, 2023. Abhinav got a job offer
in New York and resigned his job in Beta Ltd. on 20th September, 2023. He left
for New York on 27th September, 2023 and joined his new job in Gamma Inc in
New York from 1st October, 2023. He opened a bank account in New York and his
salary from Gamma Inc is credited to that account.
Anil’s brother Kishore, aged 48 years, moved to the USA in the year 2005. He is
now a citizen of USA and is employed with a consultancy firm in the USA. He has
house properties in India from which he derives rental income. He also derives
income of ` 16 lakhs from a business controlled in Mumbai. He visits India during
the month of December every year with his wife Reema, aged 45 years, and son
Madhav, aged 19 years, and stays in India for the whole month. Anil and Kishore
purchased adjacent houses in New York, USA in April, 2023 from which they earn
rental income, which is credited to their bank account in the USA. Anil visited his
brother in the USA from 15th June, 2023 to 3rd July, 2023 along with Asha. They have
not made any other foreign trips during the year. Their foreign trips are of the
duration of less than one month every year.
Anil’s younger sister Nidhi, a citizen of India, got married and settled in UAE in
the year 2010. She also derives income of ` 18 lakhs from a business
controlled in Mumbai. She has fixed deposits in a bank in UAE from which
she gets interest. Nidhi is not liable to pay tax in UAE. Like her brother,
Kishore, she also visits India in the month of December every year and stays
for the whole month.
The following “Points to Ponder” are raised by Anisha. You have to help her find
answers to them. Anil tells her that his total income computed as per the
Income-tax Act, 1961 is likely to be around ` 75 lakhs and Asha’s total income is
likely to be around ` 20 lakhs for A.Y.2024-25.
© The Institute of Chartered Accountants ofPage
India 3
Points to Ponder Write your response after reading
Chapter 1
(1) Anisha is interested in knowing whether she and Abhinav
would be assessees as per the Income-tax Act, 1961.
Would Anisha and Abhinav be assessees under the Income-
tax Act, 1961?
(2) She wants to know whether the previous year for her father
and her brother for the assessment year 2024-25 would be the
same. Would the previous year remain the same for both of
them? If not, why?
© The Institute of Chartered Accountants ofPage
India 4
(3) She is curious to know whether the following would be income
under the Income-tax Act, 1961 –
(i) Profits from business of retail trade carried on by her father
(ii) Profits earned by her mother from business of sale of
cakes, biscuits and cookies
(iii) Salary earned by Abhinav from Beta Ltd.
(iv) Lottery winnings of Abhinav
(v) Dividend received by her father from Indian companies.
Points to Ponder Write your response after reading
Chapter 1
(4) She is keen to know whether surcharge would be levied on the
total income of her mother and father. Would surcharge be
leviable? If so, at what rate? Assume that their actual income
is the same as the estimated income.
(5) Anil’s father’s HUF consists of ancestral properties, the income
from which is assessed as income of the HUF. Anisha finds the
concept of HUF fascinating. She is curious to know whether
the wife, daughter-in-law and grandchildren would be
members of a HUF, and if so, would they be co-parceners also.
She is also keen in knowing whether a married daughter would
© The Institute of Chartered Accountants ofPage
India 5
be a co-parcener of her father’s HUF.
(i) Who amongst the following are members of Anil’s father’s
HUF?
1. Anil’s mother
2. Asha and Reema
3. Abhinav, Anisha and Madhav
(ii) Who amongst the following are co-parceners of Anil’s
father’s HUF?
1. Anil’s mother
2. Asha and Reema
3. Nidhi
4. Abhinav, Anisha and Madhav
Anisha is also keen in knowing the residential status of her family members and relatives for A.Y.2024-25, i.e., whether they
would be –
1. Resident and Ordinarily Resident (ROR)
2. Resident but not ordinarily resident (RNOR)
3. Non-resident
4. Deemed resident?
Family member/Relative Calculate the number of days Determine the Residential Status after reading
of stay in India Chapter 2
[ROR/RNOR/Non-resident/deemed resident]
A. Anil, her father
© The Institute of Chartered Accountants ofPage
India 6
B. Asha, her mother
C. Abhinav, her
brother
D. Kishore, her uncle
E. Nidhi, her aunt
Based on the residential status arrived at above, help her find out which of the incomes listed in column (2) below would be
included in the hands of these persons while computing their total income.
(1) (2) (3)
Family member/ Particulars of profits/gains/receipts Whether the profits/gains/receipts
Relative would be included in computing his/her
total income?
Write Yes/No against each item after
reading Chapters 1 and 2
A. Anil, her father 1. Rental income from house in New York, USA
2. Profits from business of retail trade
© The Institute of Chartered Accountants ofPage
India 7
3. Interest on bank fixed deposits
4. Dividend from Indian companies
B. Asha, her mother 1. Profits from sale of cakes, pastries and
cookies
2. Profits from sale of saplings and seedlings
3. Interest on bank fixed deposits
4. Gains from sale of jewellery
(1) (2) (3)
Family member/ Particulars of profits/gains/receipts Whether the profits/gains/receipts
Relative would be included in computing his/her
total income?
Write Yes/No against each item after
reading Chapters 1 and 2
C. Abhinav, her brother 1. Salary from Beta Ltd. in Mumbai
2. Salary from Gamma Inc in New York
3. Maharashtra State Lottery winnings
© The Institute of Chartered Accountants ofPage
India 8
D. Kishore, her uncle 1. Rental income from house in New York, USA
2. Salary from consultancy firm in USA
3. Income from a business controlled in
Mumbai
4. Rent from properties in India
E. Nidhi, her aunt 1. Income from business controlled in Mumbai
2. Interest on bank fixed deposits in UAE
Point to Ponder - In case Kishore decides to resettle in India and returns permanently to India on 1st
October, 2023, what would be his residential status for the A.Y.2024-25, if he decides to retain his US
citizenship? Which items of income would be included in Kishore’s total income in India from the items
listed in column (2) above corresponding to Kishore? Write your response after reading Chapter 2.
© The Institute of Chartered Accountants ofPage
India 9
CROSSWORD PUZZLE
© The Institute of Chartered Accountants ofPage
India 10
ACROSS
2. The ………….. to a section spells out the exceptions/conditions to the
provision contained therein.
4. In order to constitute an ……….... (acronym), persons must join for a
common purpose or action and their object must be to produce income.
6. Income-tax is levied on the total income of the previous year of every
………....
8. Section 4 is the ……….…..section of the Income-tax Act, 1961.
11. Previous year means the financial year immediately preceding the …………...
year.
13. Income taxable under the Income-tax Act is classified under ……………. heads.
14. ………………... payable for service rendered in India would be treated as earned
in India and would be deemed to accrue or arise in India.
15. The first step in computation of total income is determination of ………….
status.
18. A ………….…… is issued by the CBDT to give effect to a provision contained in
the Income-tax Act, 1961.
19. Income-tax is a ……. Tax
DOWN
1. Residential status of a company which is not an Indian company would be
determined on the basis of its …. (acronym)
3. An individual who stays in India for 182 days or more in the P.Y.2023-24 is
a …………. in India in that year.
4. A person by whom any tax or any other sum of money is payable under
the Income-tax Act, 1961.
5. An individual earning income of ` 50,10,000 would be entitled to ………….
relief.
7. A ……….….. is issued by the CBDT to clarify doubts relating to the provisions
of the Income-tax Act, 1961.
9. Some members of the ……………. (acronym) are called co-parceners.
© The Institute of Chartered Accountants ofPage
India 11
10. An individual who is deemed resident under section 6(1A) would by default
be a ………………... (acronym).
12. The …………... to a section gives a clarification to the provision contained
therein.
16. The definition of income under the Income-tax Act, 1961 is an ……………
definition.
17. ………..… paid by an Indian company outside India would be deemed to
accrue or arise in India.
Scan the following QR code to find out the answers to the Scenario and
Crossword puzzle.
Scan the code
© The Institute of Chartered Accountants ofPage
India 12
You might also like
- Accounting Services AgreementDocument2 pagesAccounting Services AgreementEiuol Nhoj Arraeugse50% (2)
- UWN011 - NRI With GST DeclarationDocument5 pagesUWN011 - NRI With GST DeclarationSrigandh's WealthNo ratings yet
- Residential Status AssignmentDocument4 pagesResidential Status AssignmentSimran Kaur Khurana100% (1)
- Tax AljamiaDocument22 pagesTax AljamiaFlash Light100% (2)
- LTTSL - L&T Technology Services Income Tax Computation SheetDocument3 pagesLTTSL - L&T Technology Services Income Tax Computation SheetdhruvNo ratings yet
- Invoice No.: Remit To Date Correspondence To Remit ToDocument2 pagesInvoice No.: Remit To Date Correspondence To Remit ToJuan Josè Castro AvilaNo ratings yet
- Cloud AP 1099 and Withholding Tax SetupDocument14 pagesCloud AP 1099 and Withholding Tax SetupSrinivasa Rao AsuruNo ratings yet
- Section 1Document12 pagesSection 1Shermadurai VNo ratings yet
- CS 3Document12 pagesCS 3Mallika VermaNo ratings yet
- Final DT MCQ BookletDocument95 pagesFinal DT MCQ BookletSavya Sachi100% (1)
- Residential StatusDocument19 pagesResidential StatusZatch Series UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- FPSB India / Public 1: FPSBI/M-VI/04-01/09/SP-12Document13 pagesFPSB India / Public 1: FPSBI/M-VI/04-01/09/SP-12bhaw_shNo ratings yet
- AFP Case Study AnamikaDocument7 pagesAFP Case Study Anamikavenkat sbiNo ratings yet
- Income Tax RetrnDocument21 pagesIncome Tax RetrnHema joshiNo ratings yet
- Moot ProblemDocument3 pagesMoot ProblemjerinNo ratings yet
- Interesting Aspects in Non-Resident TaxationDocument39 pagesInteresting Aspects in Non-Resident TaxationKANNAPPAN NAGARAJANNo ratings yet
- Income Tax FinalDocument20 pagesIncome Tax FinalSiddarood KumbarNo ratings yet
- QP 1Document7 pagesQP 1Shankar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Taxation Final ProjectDocument12 pagesTaxation Final ProjectShreya KalyaniNo ratings yet
- 04 - Taxation Law QDocument4 pages04 - Taxation Law QKiko BautistaNo ratings yet
- 6 Additional Self Test Problems 4Document3 pages6 Additional Self Test Problems 4Chaitanya TallapaneniNo ratings yet
- Principle of TaxationDocument7 pagesPrinciple of TaxationAnas YawarNo ratings yet
- MOOT PROPOSITION - 1st LINMCC 2021Document4 pagesMOOT PROPOSITION - 1st LINMCC 2021surya shuklaNo ratings yet
- Residential Status FibDocument1 pageResidential Status FibSarvar PathanNo ratings yet
- Law of Taxation 1Document15 pagesLaw of Taxation 1Shubham PathakNo ratings yet
- Residential Status Pratical QuestionsDocument9 pagesResidential Status Pratical QuestionsGaurav MalikNo ratings yet
- MTP 1Document7 pagesMTP 1Aman VithlaniNo ratings yet
- 4) TaxationDocument21 pages4) TaxationKrushna MateNo ratings yet
- A Close Analysis of Section 6 Income Tax Act 1961: Hidayatullah National Law UniversityDocument15 pagesA Close Analysis of Section 6 Income Tax Act 1961: Hidayatullah National Law UniversityPrashant Paul KerkettaNo ratings yet
- Faq NbfaDocument2 pagesFaq NbfaHritik KamalNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 8Document8 pagesPage 1 of 8Mayank MehtaNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument16 pagesQuestion BankTris EatonNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Basics - A Comprehensive Guide PDFDocument42 pagesIncome Tax Basics - A Comprehensive Guide PDFsrinivasa varmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document18 pagesUnit 3Rupesh PatilNo ratings yet
- CTPM ProblemsDocument31 pagesCTPM ProblemsViraja GuruNo ratings yet
- MCQs of Residential Status - Incidence of Tax by CA Kishan KR SirDocument13 pagesMCQs of Residential Status - Incidence of Tax by CA Kishan KR SirHetvi VoraNo ratings yet
- Income Tax: Basic Terms and Provisions Relating To Residential StatusDocument7 pagesIncome Tax: Basic Terms and Provisions Relating To Residential StatusAshika Khanna 1911165No ratings yet
- Basics of Income Tax: Lecture Dated 28th July, 2020Document27 pagesBasics of Income Tax: Lecture Dated 28th July, 2020Ifzal Ahmed ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Income TaxDocument84 pagesIncome TaxA Jalaludeen100% (1)
- 017 Sep 09 AvinashDocument11 pages017 Sep 09 Avinashdeepak goyalNo ratings yet
- Paper 7: Direct Tax Laws & International Taxation: Questions and AnswersDocument19 pagesPaper 7: Direct Tax Laws & International Taxation: Questions and Answersneeraj sharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document18 pagesUnit 3Ujjwal MishraNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Law & PracticeDocument32 pagesIncome Tax Law & PracticeGautam TamtaNo ratings yet
- Tax ExamDocument29 pagesTax ExamAnn Olivia VallavanadanNo ratings yet
- Semester III 52414304 Income Tax Law and Practice-CORE Set Ii Duration: 3 Hours Attempt Any Four Questions. All Questions Carry Equal MarksDocument3 pagesSemester III 52414304 Income Tax Law and Practice-CORE Set Ii Duration: 3 Hours Attempt Any Four Questions. All Questions Carry Equal MarksAnshu kumarNo ratings yet
- SeemaDocument61 pagesSeemaAkash ShewadeNo ratings yet
- The Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA)Document17 pagesThe Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA)Shivani PanwarNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Income TaxDocument10 pages1 Introduction To Income TaxShreyas BhadaneNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 TVM ApplicationDocument4 pagesTutorial 4 TVM ApplicationTrần ThảoNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Basic ConceptsDocument31 pagesIncome Tax Basic ConceptsAbhijit HoroNo ratings yet
- The Institute of Chartered Accountants of Nepal: Suggested Answers of Income Tax and VATDocument8 pagesThe Institute of Chartered Accountants of Nepal: Suggested Answers of Income Tax and VATDipen AdhikariNo ratings yet
- TVM Mini Case StudentsDocument1 pageTVM Mini Case Studentssd231No ratings yet
- Basic ConceptsDocument27 pagesBasic ConceptsNovel Bipin Kr SawNo ratings yet
- Notes On LLB 6th Semester Subject Law of TaxationDocument140 pagesNotes On LLB 6th Semester Subject Law of TaxationSrinivasa RaoNo ratings yet
- Case Study 4Document3 pagesCase Study 4XilcaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Tax Planning Unit - I: I Test Your Skills: (A) State Whether The Following Statements Are True or FalseDocument69 pagesQuestion Bank Tax Planning Unit - I: I Test Your Skills: (A) State Whether The Following Statements Are True or Falselakshit_gupta100% (1)
- Basic Concepts in Income Tax LawDocument39 pagesBasic Concepts in Income Tax LawSiddharth KaranNo ratings yet
- Income Tax - I Previous Years Question Papers: Short Answer Questions (2marks Each)Document17 pagesIncome Tax - I Previous Years Question Papers: Short Answer Questions (2marks Each)Prabhakar BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- 301 Income Tax AjayDocument10 pages301 Income Tax AjayAnkita DashNo ratings yet
- Innocent Spouse Relief: How You May Not Have To Pay Your Taxes!From EverandInnocent Spouse Relief: How You May Not Have To Pay Your Taxes!No ratings yet
- IRCTC Next Generation Eticketing System PDFDocument4 pagesIRCTC Next Generation Eticketing System PDFChirag AmarnaniNo ratings yet
- Vbak-Sales Order Document Header Vbap-Item For Sales Order DataDocument3 pagesVbak-Sales Order Document Header Vbap-Item For Sales Order Datamohamed FareedhNo ratings yet
- Ril PVC Price DT.01.02.2019Document13 pagesRil PVC Price DT.01.02.2019Akshat Engineers Private LimitedNo ratings yet
- PNP Multipurpose Cooperative vs. CIRDocument11 pagesPNP Multipurpose Cooperative vs. CIRPhoebe SpaurekNo ratings yet
- Cashless PDFDocument48 pagesCashless PDFManish Solanki0% (1)
- Real Estate Mathematics Sample Problems (Ref: 0505) : I. Perimeter Fencing ProblemDocument4 pagesReal Estate Mathematics Sample Problems (Ref: 0505) : I. Perimeter Fencing ProblemGeorge Poligratis RicoNo ratings yet
- GSTR1 37aaffo8985r1zz 102023Document4 pagesGSTR1 37aaffo8985r1zz 102023ORANGE FIBERNETNo ratings yet
- GST/HST Credit Application For Individuals Who Become Residents of CanadaDocument4 pagesGST/HST Credit Application For Individuals Who Become Residents of CanadaPritish TandonNo ratings yet
- 10) Collector V Manila Lodge No. 761 - 29 June 1957Document4 pages10) Collector V Manila Lodge No. 761 - 29 June 1957Perlas OcampoNo ratings yet
- Marcelo Steel Corporation vs. Collector of Internal RevenueDocument2 pagesMarcelo Steel Corporation vs. Collector of Internal RevenuesakuraNo ratings yet
- BM2308I002689002Document2 pagesBM2308I002689002Dharmendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Petition For Issuance of Letter of AdministrationDocument4 pagesPetition For Issuance of Letter of AdministrationMa. Danice Angela Balde-BarcomaNo ratings yet
- Assingnment of International Trade Law ON Payment of International SalesDocument15 pagesAssingnment of International Trade Law ON Payment of International SalesManik Singh KapoorNo ratings yet
- FX - Numerical: TT Buying RateDocument8 pagesFX - Numerical: TT Buying Ratesundeepkumar007No ratings yet
- Proposal Project AyamDocument14 pagesProposal Project AyamIrvan PamungkasNo ratings yet
- Paypulse - Step by Step Guide 2LFVDAawsqDocument20 pagesPaypulse - Step by Step Guide 2LFVDAawsqGivengift LilungweNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rates - List of Foreign Currency Rates TodayDocument2 pagesExchange Rates - List of Foreign Currency Rates TodayHasan Bin AliNo ratings yet
- NJC COMMUNIQUE 0621 NAECI 2022 2023 Settlement Rates and Allowances 24.9.21Document11 pagesNJC COMMUNIQUE 0621 NAECI 2022 2023 Settlement Rates and Allowances 24.9.21Sameer MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Final Income TaxationDocument26 pagesChapter 5 Final Income TaxationJason MablesNo ratings yet
- VAT AuditDocument3 pagesVAT AuditZahra NAHIDNo ratings yet
- (Circular E), Employer's Tax Guide: Future DevelopmentsDocument48 pages(Circular E), Employer's Tax Guide: Future DevelopmentsradhakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Tax Law Cases Sem-1Document43 pagesTax Law Cases Sem-1rashmi narayanNo ratings yet
- Roxas v. CTADocument2 pagesRoxas v. CTAJf ManejaNo ratings yet
- Agl Better Bills Sample Bill NecfDocument2 pagesAgl Better Bills Sample Bill Necfnurulamin00023No ratings yet
- Taxationlaw BarlisDocument11 pagesTaxationlaw Barlisjade123_129No ratings yet
- May Card StatementDocument4 pagesMay Card Statementlmcknight93.lmNo ratings yet