Maria Cristina H.
Caniban Grade 12- Copper Physics
Questions:
1.) What is a multi-tester?
- also known as a multimeter, is an electronic measuring instrument that combines several measurement functions in one unit. It
typically can measure voltage, current, and resistance. Some advanced models may also measure other parameters such as
capacitance, frequency, temperature, continuity, and diode testing.
- Multimeters are widely used by electricians, electronics technicians, and hobbyists for troubleshooting, testing, and repairing
electrical and electronic circuits. They are portable, easy to use, and can provide accurate measurements of various electrical
quantities, making them an essential tool in many fields related to electrical engineering and electronics.
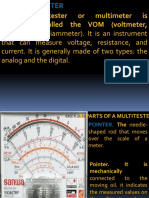
(2-3). What are the parts of a multi-tester? And What are the functions of each part?
- A multi-tester, also known as a multimeter, is a versatile electronic tool used to measure various electrical properties such as voltage,
current, and resistance. The basic parts of a typical multimeter include:
1.) Display Screen: This is where the measurement readings are displayed. It can be an LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) or LED (Light
Emitting Diode) screen.
2.) Selection Knob or Dial: Used to select the desired measurement function such as voltage (AC or DC), current (AC or DC), resistance,
continuity, capacitance, etc. It also often has settings for diode testing and sometimes temperature measurement.
3.) Input Jacks or Ports: These are the sockets where the test leads are plugged in. There are usually multiple jacks labeled for different
types of measurements (e.g., COM for common, VΩmA for voltage, resistance, and current).
4.) Test Leads: These are the cables that connect the multimeter to the circuit or component being measured. Test leads typically have
two probes: one red (positive) and one black (negative). The probes usually have sharp tips for piercing insulation and ensuring good
electrical contact.
5.) Function Buttons: Some multimeters have additional buttons for specific functions such as holding the display reading (HOLD),
selecting the range of measurements (RANGE), or turning on a backlight for the display.
6.) Battery Compartment: Multimeters are powered by batteries, usually 9V batteries, which are housed in a compartment usually
located at the back of the device.
� 7.) Fuse: Many multimeters have an internal fuse that protects the meter from damage due to excessive current. The fuse is usually
located inside the multimeter near the input jacks.
These are the basic parts found in most multimeters. However, depending on the model and features, there might be additional components or
functionalities included.
4.) Picture of a multi-tester with parts.