Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worksheet Chemistry Electrolysis Ks4
Worksheet Chemistry Electrolysis Ks4
Uploaded by
helenaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet Chemistry Electrolysis Ks4
Worksheet Chemistry Electrolysis Ks4
Uploaded by
helenaCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrolysis for KS4 Chemistry - Worksheet
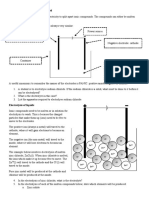
1. Complete the diagram with the following labels: anode, cathode, electrode,
electrolyte, anion and cation
2. Describe an ionic bond.
…………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
3. Why can’t a solid ionic substance conduct electricity?
…………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
4. Why can molten and solutions of ionic substances conduct electricity?
…………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
Electrolysis for KS4
Chemistry
5. Why is electrolysis used to extract metals like Aluminium from their ores
(oxides)
…………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
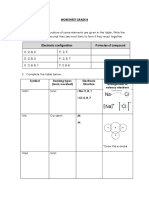
6. Complete the table
Substance electrolysed What is formed at the What is formed at the
cathode anode
molten lead iodide
Sodium chlorine
Copper sulfate solution
calcium bromide
solution
molten aluminium oxide
7. Complete the half equations
a) Na+ + …… → Na
b) Ca2+ + …… → Ca
c) …… + 2e- → Cu
d) Zn2+ + 2e- → …..
8. Complete the half equations
a) 2Cl- → Cl2 + …..
b) 2F- → ….. + 2e-
c) 2O2- → …… + 4e-
d) …… → Br2 + 2e-
Electrolysis for KS4
Chemistry
Electrolysis for KS4 Chemistry - Worksheet (Answers)
1. Complete the diagram with the following labels: anode, cathode, electrodes,
electrolyte, anion and cation
2. Describe an ionic bond.
Electrostatic attraction between positive ions and negative ions
3. Why can’t a solid ionic substance conduct electricity?
Ions are in a fixed position and cannot move
4. Why can molten and solutions of ionic substances conduct electricity?
Ions are free to move and carry the charge
5. Why is electrolysis used to extract metals like Aluminium from their ores
(oxides)
Electrolysis for KS4
Chemistry
They are more reactive than carbon, so can’t be extracted by heating with
carbon.
6. Complete the table
Substance electrolysed What is formed at the What is formed at the
cathode anode
molten lead iodide lead iodine
molten sodium chloride Sodium chlorine
Copper sulfate solution copper oxygen
calcium bromide hydrogen bromine
solution
molten aluminium oxide aluminium oxygen
7. Complete the half equations
a) Na+ + e- → Na
b) Ca2+ + 2e- → Ca
c) Cu2 + 2e- → Cu
d) Zn2+ + 2e- → Zn
8. Complete the half equations
a) 2Cl- → Cl2 + 2e-
b) 2F- → F2 + 2e-
c) 2O2- → O2 + 4e-
d) 2Br- → Br2 + 2e-
Electrolysis for KS4
Chemistry
You might also like
- Chemsheets GCSE 1063 Drawing Molecules 1Document2 pagesChemsheets GCSE 1063 Drawing Molecules 1Talpyn Rakhym0% (2)
- 9647 H2 Chemistry PlanningDocument3 pages9647 H2 Chemistry PlanningNicholas Ow100% (1)
- LAPTOP POWER Sequence Training 1.0.0 PDFDocument52 pagesLAPTOP POWER Sequence Training 1.0.0 PDFrmartins_23947488% (58)
- LAB: Strength in Numbers: BackgroundDocument2 pagesLAB: Strength in Numbers: BackgroundLaisha HernandezNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Physics I C Vector Worksheet IDocument5 pagesSolutions To Physics I C Vector Worksheet IJeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Physics I C Vector Worksheet IDocument5 pagesSolutions To Physics I C Vector Worksheet IJeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- 2021 Kinetics MCQ Quiz - Worked SolnsDocument3 pages2021 Kinetics MCQ Quiz - Worked SolnsPROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Grade 8Document5 pagesWorksheet Grade 8willadahNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equations WorksheetDocument1 pageIonic Equations Worksheetgimarreyes23No ratings yet
- Electroysis WorksheetDocument2 pagesElectroysis WorksheetericaNo ratings yet
- Naming Mixed Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDocument1 pageNaming Mixed Ionic and Covalent Compoundsapi-325791445No ratings yet
- Separation Method QuestionsDocument5 pagesSeparation Method Questionsdanielmahsa100% (1)
- Electrolysis QuestionsDocument53 pagesElectrolysis QuestionsAahaan ShethNo ratings yet
- Revision-2 - On ElectrochemistryDocument12 pagesRevision-2 - On ElectrochemistryKiro RemonNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On IGCSE Chemical EnergeticsDocument2 pagesWorksheet On IGCSE Chemical EnergeticsSamandarbek Numonov100% (1)
- F321 Group 7Document5 pagesF321 Group 7Doc_CrocNo ratings yet
- Redox WKSHTDocument4 pagesRedox WKSHTMarco ConopioNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Worksheet Redox and Reactivity of MetalsDocument2 pagesChemistry Worksheet Redox and Reactivity of MetalshahaNo ratings yet
- Oxford Resources For IB: Structure 3.1 - The Periodic Table: Classification of ElementsDocument19 pagesOxford Resources For IB: Structure 3.1 - The Periodic Table: Classification of ElementsGian Paolo GerzonNo ratings yet
- PeriodicityDocument6 pagesPeriodicityHadi AlnaherNo ratings yet
- Chap5 IGCSE Chemistry NotesDocument13 pagesChap5 IGCSE Chemistry NotesMisbah Kamran0% (1)
- Acids and Bases Unit Test 2011Document8 pagesAcids and Bases Unit Test 2011jkdfal1No ratings yet
- Le Chatelier WorksheetDocument1 pageLe Chatelier WorksheetRawanఌNo ratings yet
- Precipitation ReactionsDocument3 pagesPrecipitation ReactionsborgiamatriceNo ratings yet
- Pioneer Junior College H2 Chemistry (9647) An Introduction To The Chemistry of Transition ElementsDocument31 pagesPioneer Junior College H2 Chemistry (9647) An Introduction To The Chemistry of Transition ElementsTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds and Mixtures WorksheetDocument4 pagesElements, Compounds and Mixtures WorksheetKaren Orlanski100% (1)
- Chemistry-Ch 21 - Experimental Design and Separation TechniquesDocument11 pagesChemistry-Ch 21 - Experimental Design and Separation TechniquesHassan Riaz100% (1)
- Electrolysis PDFDocument14 pagesElectrolysis PDFBaryaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Chemical Energetics ExerciseDocument5 pagesChapter 7 Chemical Energetics ExerciseAri Adiantari100% (1)
- 6 NP UQq TRX 8 B 2 Js ZC 2 NQTDocument7 pages6 NP UQq TRX 8 B 2 Js ZC 2 NQTOm KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Net Ionic Equations-ProblemsDocument3 pagesNet Ionic Equations-ProblemsChikuta ShingaliliNo ratings yet
- WS2 IG I Chemistry (1) SEPERATING MIXTURESDocument4 pagesWS2 IG I Chemistry (1) SEPERATING MIXTURESRaj MalkanNo ratings yet
- 27.2 Alcohols Ial Cie Chemistry QPDocument16 pages27.2 Alcohols Ial Cie Chemistry QPabdelrahmanNo ratings yet
- Catholic Junior College H2 Chemistry 9729 2019 Practical Handbook - Part 6Document13 pagesCatholic Junior College H2 Chemistry 9729 2019 Practical Handbook - Part 6Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Worksheet IDocument53 pagesElectrolysis Worksheet Iaqsa chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Percentage Purity WorksheetDocument2 pagesPercentage Purity Worksheetbrot100% (2)
- Electrolysis WorksheetDocument2 pagesElectrolysis WorksheetPranav ChiploonkarNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Worksheet 2Document11 pagesElectrolysis Worksheet 2Menaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Worksheet Redox WSDocument4 pagesChapter 20 Worksheet Redox WSMostafa Ahmed100% (1)
- IGCSE Chemistry Oxygen Hydrogen and Carbon DioxideDocument15 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Oxygen Hydrogen and Carbon DioxideS M AkashNo ratings yet
- POGIL Oxidation and Reduction-S-1Document6 pagesPOGIL Oxidation and Reduction-S-1demyeets64No ratings yet
- Net Ionic Equations WSDocument2 pagesNet Ionic Equations WSJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Atomic Structure Multiple ChoiceDocument13 pages1.1 Atomic Structure Multiple ChoiceAmmaarah PatelNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Unit 10 ExtractionDocument17 pagesIGCSE Unit 10 ExtractionIsuriy AdasuriyaNo ratings yet
- Chem NotesDocument300 pagesChem NotesTeejay MakazhuNo ratings yet
- Charles Law PDFDocument3 pagesCharles Law PDFIvan BayonaNo ratings yet
- 9 and 19 MCQDocument18 pages9 and 19 MCQrania samirNo ratings yet
- 3 Experiment ChemistryDocument30 pages3 Experiment ChemistryThangavel SarujanNo ratings yet
- Task 1: Group 1 - The Alkali MetalsDocument4 pagesTask 1: Group 1 - The Alkali MetalsNeen NaazNo ratings yet
- Worksheet ElectrochemistryDocument1 pageWorksheet ElectrochemistryShreya GiriNo ratings yet
- Redox Practice Test 1Document21 pagesRedox Practice Test 1Edon BediNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 10.6Document2 pagesWorksheet 10.6SavithaBroonan100% (1)
- Grade 6 Chemistry Annual Term Revision WorksheetsDocument9 pagesGrade 6 Chemistry Annual Term Revision WorksheetsAbhayNo ratings yet
- 12 Electron Energy and Light-SDocument6 pages12 Electron Energy and Light-SSelma CedilloNo ratings yet
- Experimental Techniques (TOPIC 2)Document17 pagesExperimental Techniques (TOPIC 2)ChaudhryAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Transition Metals QuestionsDocument6 pagesChemistry Transition Metals Questionspersonpeople100% (1)
- G8 SC Practice Test #1Document7 pagesG8 SC Practice Test #1pixelhoboNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-01: Science & Technology (Class-10) Chapter 1. Chemical Reaction and EquationsDocument1 pageCbse Test Paper-01: Science & Technology (Class-10) Chapter 1. Chemical Reaction and EquationsGMSUNDARINo ratings yet
- Food Tests - Aiming For Grade 8Document5 pagesFood Tests - Aiming For Grade 8AleNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Chemistry Electrolysis ks4Document2 pagesWorksheet Chemistry Electrolysis ks487nairpriyankkaNo ratings yet
- 6A Electrochemistry - AnswerDocument6 pages6A Electrochemistry - AnswerWong Wai Lun100% (1)
- Gems Genesis: 9caieDocument4 pagesGems Genesis: 9caieBhavya darjiNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis MasteryDocument8 pagesElectrolysis MasteryDonald ZhuoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - Electrolysis Part 1Document13 pagesLesson 8 - Electrolysis Part 1Dishna KarunasekaraNo ratings yet
- Forces, Movement, Shape and Momentum 1 QPDocument14 pagesForces, Movement, Shape and Momentum 1 QPJeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- Chemistry WorkBook For Dummies (PDFDrive) - Pages-31-35Document5 pagesChemistry WorkBook For Dummies (PDFDrive) - Pages-31-35Jeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Science Homework #1 - Lab Safety: View The Picture Below and Answer The Questions On The Next PageDocument2 pagesIGCSE Science Homework #1 - Lab Safety: View The Picture Below and Answer The Questions On The Next PageJeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line HWDocument6 pagesMotion in A Straight Line HWJeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- Identifying Cations FlowchartDocument1 pageIdentifying Cations FlowchartJeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- Lab Safety Skills Worksheet 3Document2 pagesLab Safety Skills Worksheet 3Jeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- Paperless Productivity With SmallpdfDocument22 pagesPaperless Productivity With SmallpdfJeffrey Piggott100% (1)
- Kinematics Vocabulary: Units and Vectors and Scalars!Document17 pagesKinematics Vocabulary: Units and Vectors and Scalars!Jeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- T1 Exp - Density of Microscope SlideDocument1 pageT1 Exp - Density of Microscope SlideJeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- 2 AccelerationDocument12 pages2 AccelerationJeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- M10 ProblemsDocument13 pagesM10 ProblemsJohnNo ratings yet
- Datasheet HM-12001500 Asia EN V202207Document2 pagesDatasheet HM-12001500 Asia EN V202207evellyne.projetosNo ratings yet
- Silicone Rubber BushingsDocument8 pagesSilicone Rubber BushingsEdwin Cob GuriNo ratings yet
- DMX512 Decoder Operating Instructions: 1.featureDocument2 pagesDMX512 Decoder Operating Instructions: 1.featuresenel102No ratings yet
- Zelio Timer Relays - RUZC2MDocument5 pagesZelio Timer Relays - RUZC2MFredy Aparco IngaNo ratings yet
- Ul 1283 BulletinDocument4 pagesUl 1283 BulletinMboriko MwashaNo ratings yet
- Roy Choudhury, D - Networks and Systems-New Academic Science Limited (2014)Document959 pagesRoy Choudhury, D - Networks and Systems-New Academic Science Limited (2014)Prakash VermaNo ratings yet
- Marquette Cardiosmart - Service ManualDocument117 pagesMarquette Cardiosmart - Service Manualahmadba70No ratings yet
- 218.wireless Power Transfer by High Frequency Resonating CoilsDocument1 page218.wireless Power Transfer by High Frequency Resonating CoilsANAND KRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Exercise Q (Chapter 2,3)Document3 pagesExercise Q (Chapter 2,3)Aly Rajaie Anna RusliNo ratings yet
- Magnetism (Grade 12 Physics)Document17 pagesMagnetism (Grade 12 Physics)dezaminpitargue07100% (1)
- Active Compact Line Array System V2208P V1212P V1218P SeriesDocument16 pagesActive Compact Line Array System V2208P V1212P V1218P Seriesmarco escobarNo ratings yet
- Solar PCU Inverter Three Phase PDFDocument2 pagesSolar PCU Inverter Three Phase PDFHarish Kumar GNo ratings yet
- Tractor D6G - SIS PDFDocument2 pagesTractor D6G - SIS PDFEduardo TorresNo ratings yet
- 2010-09-02 023416 VtcsDocument3 pages2010-09-02 023416 VtcsEdi NastaseNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: W-Series WDU 2.5Document5 pagesData Sheet: W-Series WDU 2.5nisha_khanNo ratings yet
- Balancing Li-Ion Li-Polymer Batteries Battery Balancing Circuit - Electronics Projects CircuitsDocument1 pageBalancing Li-Ion Li-Polymer Batteries Battery Balancing Circuit - Electronics Projects CircuitsStefan CorneaNo ratings yet
- DRV 8860Document46 pagesDRV 8860diego alejandro quiroga ramosNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: BGY887BDocument12 pagesData Sheet: BGY887BwayanwijaNo ratings yet
- Quad Gated Non-Inverting Power Driver: Features DescriptionDocument6 pagesQuad Gated Non-Inverting Power Driver: Features DescriptionEfrén GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Liebert Iton CX: Quick-Start Guide - 600VA, 230VDocument2 pagesLiebert Iton CX: Quick-Start Guide - 600VA, 230VAdityaPatniNo ratings yet
- Motortronics Training - 2012Document95 pagesMotortronics Training - 2012daly2daly100% (1)
- Popular Electronics - April 1955Document132 pagesPopular Electronics - April 1955sezaroNo ratings yet
- P65-18-XDHHW2-M: Quadruple Broadband AntennaDocument2 pagesP65-18-XDHHW2-M: Quadruple Broadband Antennazeeshanriaz1077No ratings yet
- 2008 Mazda MPV - Brake - On-Board Diagnostic (ABS)Document84 pages2008 Mazda MPV - Brake - On-Board Diagnostic (ABS)lo mio es mioNo ratings yet
- Cuttler Hammer Wiring-DiagramsDocument9 pagesCuttler Hammer Wiring-DiagramsReggieNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis of Ac Power System-Edith Clarke Volume I, IIDocument4 pagesCircuit Analysis of Ac Power System-Edith Clarke Volume I, IIhosseinhakan100% (1)
- SM Examples and SolutionsDocument16 pagesSM Examples and SolutionsTausique SheikhNo ratings yet