0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views1 pageRun Charts
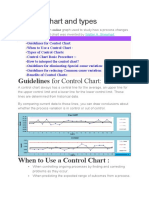
A run chart is a line graph that plots data over time to show trends or patterns in a process without control limits. It has a title, x-axis of time or observation number, y-axis of the measured unit, and center line. Interpretations include shifts, trends, outliers, and alternating data indicating special cause variation. Causes of variation are common from normal variability or special from external influences significantly changing performance.
Uploaded by
baskaran.marieCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views1 pageRun Charts
A run chart is a line graph that plots data over time to show trends or patterns in a process without control limits. It has a title, x-axis of time or observation number, y-axis of the measured unit, and center line. Interpretations include shifts, trends, outliers, and alternating data indicating special cause variation. Causes of variation are common from normal variability or special from external influences significantly changing performance.
Uploaded by
baskaran.marieCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd