THE URINARY SYSTEM Liver- regeneration
ᴥ FUNCTIONS:
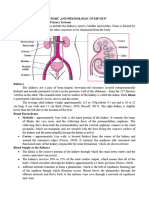
ᴥ Kidney Location and External Anatomy
Elimination of waste products:
- The kidneys lie in a retroperitoneal
- Nitrogenous
position in the superior lumbar region
wastes Stability of the body
- The right kidney is lower than the left
- Toxins
because it is crowded by the liver.
- Drugs
- The lateral surface is convex; the
Regulates aspects of homeostasis
medial surface is concave
- Water balance
- The renal hilus leads to the renal
- Electrolytes
sinus
- Acid-base balance in blood
- Ureters, renal blood vessels,
- Bp
lymphatics, and nerves enter and exit
- RBC production
at the hilus
- Activation of vitamin D
ᴥ Regions:
ᴥ Organs of the Urinary Bladder
Renal cortex
Kidneys
- Outer regions
- Locations:
Renal medulla
Against the dorsal (back) wall
- Inside cortex
T12 TO L3
Illiac crest/ abdomen Renal pelvis
- Right kidney lower than the left - Inner collecting tube
- Attached to the ureters, renal blood - Connected to urethra.
vessels, and nerve at renal hilus ᴥ Internal anatomy
- At top of each kidney is an adrenal Major calyces
gland - Large branches of the renal pelvis
- Commonly sold/donated. - Collect urine draining from papillae
- Coverings: layers of protections - Empty urine into pelvis
Renal capsule - Urine flows through the pelvis &
- Surrounds each kidney ureter to the bladder
- Inside, makes some structure ᴥ KUB ultrasound procedure
Adipose capsule - kidney ureter bladder
- Surrounds kidney - Most common
- Protection ᴥ Nephrons
- Keep kidney in position - Structural & functional units of
- Fat outside kidney kidneys
- Functions: - Responsible for forming urine
- Filter 200L of blood daily - round
- Remove toxins, metabolic waste & - 2 Main structure:
excess ions by urine 1. Glomerulus
- Regulate volume and chemical make - Infront- gate
up of blood - Filter out unhealthy products= urine
- Proper balance of water&salts, - Cluster of blood vessels In the kidney
acids&base where blood filtrations occur
Ureters/paired ureters - Sits w/in a glomerular capsule (1st
- Transport urine from kidney to part of the renal tubule)
bladder - Attached to arterioles on both sides.
Urinary bladder Arterioles regulate blood flow and
- Provides a temporary storage controlling distribution of blood in the
reservoir for urine urinary system organs.
- Pundo ang ihi Afferent arterioles- carries blood into
Urethra the glomerulus
- Transport urine from bladder out of efferent arterioles- carries blood away
the body from glomerulus
� arterioles- mini artery Some materials move from the
peritubular capillaries into the renal
numb fingers- excessive alcohol
tubules
- filter blood out, in unfiltered
- Hydrogen and potassium ions
2. Renal tubule- likod sa nephron
- Creatinine
Glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule
– allows water, ions, and waste to Materials left in the renal tubule move
pass through. toward the ureter
Loop of Henle – helps the kidney
ᴥ Diuretics
conserve fluids while also
Chemicals that enhance the urinary
facilitating excretion of waste
output include:
Proximal and Distal convoluted
tubule – sends filtered nutrients o Any substance not reabsorbed
back into the bloodstream
o Substances that exceed the ability
ᴥ Urine Formation Processes
of the renal tubules to reabsorb
Involuntary / autonomic
1. Filtration o Substances that inhibit Na+
- Nonselective passive process reabsorption
- Occurs in the glomerulus, where
Osmotic diuretics include:
blood plasma is filtered into the renal
o High glucose levels – carries
tubule, allowing water, ions, glucose,
and waste products to pass into the water out with the glucose
tubules while retaining larger o Alcohol – inhibits the release of
molecules like proteins and blood ADH
cells. o Caffeine and most diuretic
- continuous drugs – inhibit sodium ion
2. reabsorption reabsorption
- Process where valuable substances o Lasix and Diuril – inhibit Na+-
that have been filtered is reclaimed, associated symporters
Substances such as: ᴥ Creatinine
o Some water Byproduct/Waste product of chemical
o Glucose compound
o Amino acids Waste product that is filtered out of the
o Ions blood by the kidneys and removed from
- Some reabsorption is passive, most is the body in the urine
active High Creatinine Level means that the
- Most reabsorption occurs in the kidneys are unable to expel the waste
proximal convoluted tubule (kidneys are not working correctly)
- Reject/check/ tanawon kung unsa pa Creatinine tests are conducted BEFORE
pwede ibalik any Contrast Media procedures
ᴥ Materials Not Reabsorbed Patients with high levels of creatinine are
not allowed to be administered with
Nitrogenous waste products (harmful contrast media (kidneys might not be
products that contain excess nitrogen) able to expel the chemical substance)
- Urea – high levels can result in Normal Creatinine levels:
dehydration Men: 0.72 to 1.25 mg/dL
- Uric acid – high levels can result in Women: 0.59 to 1.04 mg/dL
gout Clear Very good
- Creatinine – high levels indicate Light yellow Good
malfunction Yellow Fair
Dark yellow Light dehydrated
Excess water Amber Dehydrated
Brown Very dehydrated
ᴥ Secretion – Reabsorption in Reverse Red Severe dehydrated
ᴥ Physical Characteristics of Urine
� Color and Trasparency Thin-walled tube that carries urine from
- Clear, pale to deep yellow the bladder to the outside of the body by
(urochrome) peristalsis
- Depper yellow color- concentrated Release of urine is controlled by two
- Drugs, vitamins supplements, and sphincters
diet can change the color - Internal urethral sphincter
- Cloudy urine- infection of urinary (involuntary)
tract - External urethral sphincter
Odor (voluntary)
- Fresh urine- slightly aromatic Urethra Gender Differences
- Standing urine- ammonia odor - Length
- Some drugs and vegetables Females – 3–4 cm (1 inch)
(asparagus) alter usual odor Males – 20 cm (8 inches)
pH - Location
- slightly acidic (pH6) with range of Females – along wall of the
4.5 to 8.0 vagina
- diet can alter pH Males – through the prostate and
ᴥ chemical composition of urine penis
95% water & 5% soluted urethra gender differences
Nitrogenous wastes: urea, uric acid, and functions:
creatinine - Females
Normal solutes: carries urine
- Sodium, potassium, phosphate, and The female urethra is tightly
sulfate ions bound to the anterior vaginal wall
- Calcium, magnesium, and Its external opening lies anterior
bicarbonate ions to the vaginal opening and
Abnormally high concentration of posterior to the clitoris
urinary constituents- pathology - Males
ᴥ Ureters passageway of urine and
Slender tubes that convey urine from the sperm cells
kidneys to the bladder Prostatic urethra – runs
within the prostate gland
Ureters enters the base of the bladder
Membranous urethra – runs
through the posterior wall
through the urogenital
- Closes their distal ends as bladder
diaphragm
pressure increases and prevents back
Spongy (penile) urethra –
flow of urine into the ureters
passes through the penis and
Uretral Obstruction
opens via the external urethral
- Sakit ihi
orifice
- Inflammation
ᴥ Micturition (Voiding or Urination)
- Bara
ᴥ Urinary Bladder emptying the bladder
Distension of bladder walls initiates
Smooth, collapsible, muscular sac
spinal reflexes that:
Temporarily stores urine
- Stimulate contraction of the external
Like a collapsible storage of fluids
urethral sphincter
Urinary Bladder Wall
- Inhibit the detrusor muscle and
- Three layers of smooth muscle
internal sphincter (temporarily)
- Mucosa made of transitional
Voiding reflexes:
epithelium
- Stimulates the detrusor muscle to
- Walls are thick and folded in an
contract.
empty bladder
- Inhibit the internal and external
- Bladder can expand significantly
sphincters.
without increasing internal pressure
ᴥ Maintaining Water Balance
ᴥ Urethra
� Normal amount of water in the human Ion therapy Electrolyte h2o/salt
body Soda glucose craving
- Young adult females – 50% Acid balance kidney 1st trimester
- Young adult males – 60%
Baby: not concentrated/ not control Control- 18mknth/ 1 year
- Babies – 75% and half
- Old age – 45%
Probe – ultrasonic wave, non-ionizing, not invasive
Water is necessary for many body
Contrast media- special type of medicine, it visualize soft
functions and levels must be maintained
tissue
ᴥ Maintaining Acid-Base Balance in Blood
Ultrasound-pcos, Fluoroscopy- xray Prodecure-modality
Most acid-base balance is maintained by
the kidneys
Other acid-base controlling systems
- Blood buffers
- Respiration
ᴥ Developmental Aspects of the Urinary
System
Functional kidneys are developed by
the third month
Urinary system of a newborn
- Bladder is small
- Urine cannot be concentrated
Control of the voluntary urethral
sphincter does not start until age 18
months
Urinary infections are the only common
problems before old age
ᴥ Aging and the Urinary System
There is a progressive decline in
urinary function
The bladder shrinks with aging
Urinary retention is common in males
Additional
Palliative treatment- dialysis, no cure only treatment
Creatinine- kidney malfunctions
Secretion- bye
Lasix and diuril- tambal
Kidney- tig labay basura
High creatinine- kidney not able to do its job
Contrast media- very toxic- adverse reaction- mild/ severe
Standing urine- express for a… oxide
Solute- nitrogenous waste
Urethers-esophagus/pharynx pathways
Urinary bladder- temporary stores urine and collapsible
2 ureters 1 urethra
Bladder- 2 gates
Urethra – internal- involuntary feeling kaihion na- open
External-voluntary, muscle, pugong ihi
Pag mag ihi, muscle kay relax Male- sterile rod
Dehydration-excessive urination