0% found this document useful (0 votes)
99 views4 pagesUnderstanding the Information Processing Cycle
The document describes the information processing cycle in a computer, which consists of 5 steps: input, processing, output, storage and distribution. The input converts external signals into binary codes for the processor. Processing coordinates and controls system operations. The output shows the processed information. Storage preserves programs and data. Distribution sends the results to other processes.
Uploaded by
ScribdTranslationsCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
99 views4 pagesUnderstanding the Information Processing Cycle
The document describes the information processing cycle in a computer, which consists of 5 steps: input, processing, output, storage and distribution. The input converts external signals into binary codes for the processor. Processing coordinates and controls system operations. The output shows the processed information. Storage preserves programs and data. Distribution sends the results to other processes.
Uploaded by
ScribdTranslationsCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
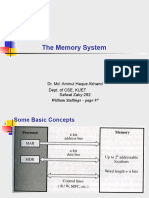
INFORMATION PROCESSING CYCLE
It is a set of steps that the computer follows to receive data, process
it according to the instructions of a program, display the resulting
information to the user, and store the results.
The information processing cycle has 5 parts:
Input: Allows you to enter instructions and data into the computer. It
converts external signals into binary codes that are interpreted by
the processor. The most common input units are the keyboard,
mouse, and scanners; and recently, microphones with voice
recognition programs.
Processing: It is the brain of the computer. Its function is to
coordinate and control all the operations carried out by the system; It
reads each instruction, analyzes them and executes them.
Output: They allow the information processed by the computer to be
displayed, visually or in print. The most common output units are the
monitor and the printer.
Storage: These are devices that are used to preserve programs and
data permanently in files and folders. The information found in them
is loaded into main memory so that the processor can execute it.
The main ones are floppy disks, hard drives, compact disks and
Distribution:
The records of the output data are called "Report Documents".
For example: The sheets that are sent to the technical registry.
Information documents can become source documents for future
processing.
OPERATIONS IN DATA PROCESSING
1. REGISTRATION.
It has to do with the transfer of data to some form of standardized
document throughout the processing cycle. Example: a teacher
CHRISTHOPHER FREIRE 2nd SC
writes down the points obtained by the students on his list and at the
end of the semester he calculates the final grades and writes them
down on his list. Receives a report card and places the final grades
there, records them on the grade sheet that is sent to the student
and then delivers the report to the respective office.
2. DUPLICATION.
It consists of reproducing data in many documents or forms.
Example: you can record a report by typing it and at the same time
make carbon copies. In another case, type it into the computer, then
print and photocopy it as a document.
3. VERIFICATION.
It consists of carefully checking the data to avoid any errors.
Example: Typed reports can be re-read for correction.
4. SEPARATION.
The data is separated into several categories. Example: a group of
questionnaires for students, can be separated according to gender
or by courses.
5. CLASSIFICATION.
In the organization of data in a specific order. Example: The names
in the telephone list have been sorted in alphabetical order. In this
case, the data is classified without separating. Sorting can also be
done after separation.
Another example: an employee record file contains name, social
security number, and place of employment. If the file must be sorted
according to the alphabetical order of the names, the "name field" is
called "KEY".
6. INTERCALATION.
Two or more sets of data that have been sorted with the same key
are taken and summarized to form a single set of data: For example,
Two packets of numerically sorted cards, the same ones that are
being collated and filed in the combined packet during the passing of
the cards. If the cards have the same number, a sub-rule determines
CHRISTHOPHER FREIRE 2nd SC
which one should be filed. When one packet is empty the cards from
the other are placed at the end of the combined packet.
7. CALCULATION.
The word calculation refers to the computation, account or
investigation that is made of something through mathematical
operations. The concept is also used as a synonym for conjecture. It
is the execution of numerical calculations on data.
8. RECOVERY.
Data recovery refers to the techniques used to recover files that
have been lost or deleted from storage media.
CONCLUSION
In this topic we learned to see how Data processing is structured
and what are each of its definitions?
CHRISTHOPHER FREIRE 2nd SC
BIBLIOGRAPHY
http://www.buenastareas.com/ensayos/Ciclo-De-Procesamiento-De-
Informaci%C3%B3n/5055403.html
https://aicitel.files.wordpress.com/2011/08/clase5_iic.pdf
https://elblogdemercado.wordpress.com/2010/06/15/ciclo-basico-de-
procesamiento-de-datos/