Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PART I-Lesson 1
Uploaded by
Jayrico JumawanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PART I-Lesson 1
Uploaded by
Jayrico JumawanCopyright:
Available Formats
PART I: Lesson 1
DATA PROCESSING
All through the different stages of civilization, man has always tried to look for ways to simplify work and to solve
problems more efficiently. Many problems involved numbers and quantities, so man started looking for easier ways
to count. As society has grown in both size and complexity, so has the data that is generated within it.
Data is defined as any collection of facts. Thus, sales reports, inventory figures, test scores, customers’ name, and
addresses, and weather reports are all examples of data. Even photographs, drawings, and maps are considered data.
Data processing is the manipulation of data into a more useful form. It is the modern name for paperwork and
involves the collecting, processing, and distributing of facts and figures to achieve and desired result. Data
processing includes not only numerical calculations but also operations such as the classification of data and the
transmission of data from one place to another. Data processing system refers to the equipment or devices and
procedures by which the result is achieved.
CATEGORIES OF DATA PROCESSING
I. Manual Data Processing
In some data processing operations, all work is still done using manual procedures. These systems employ
tools and materials such as pencils, pens, multiple-copy forms, carbon forms and filing cabinets.
II. Manual-Mechanical Data Processing
It uses a combination of manual procedures and mechanical equipment. It uses various devices such as
typewriters, sorters, calculators, collators, tabulators, duplicators, and verifiers.
III. Electronic Data Processing
Different types of input, output and storage devices may be interconnected to an electronic computer to
process data.
DATA PROCESSING CYCLE
Regardless of the kind of data processed or the kind of device or equipment used, all data processing systems
involve at least three basic steps: input, processing, and output.
1. Input
In this step the initial data, or input data, are prepared in some convenient form for processing.
2. Processing
In this step the input data are changed, and usually combined with other information to produce data in a
more useful form
3.
Output
Here the results of the preceding processing steps are collected. The particular form of the output data
depends on the use of data.
IPO CYCLE
INPUT PROCESSING OUTPUT
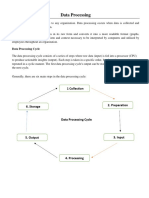
EXPANDED DATA PROCESSING CYCLE
Frequently, three more steps are added to the basic data processing cycle to obtain the expanded data processing
cycle. These three additional steps are origination, distribution, and storage.
1. Origination
It is a step which refers to the process of collecting original data. An original recording of the data is called
a source document.
2. Distribution
This step refers to the distribution of the output data. Recording of the output data are often called report
documents.
3. Storage
Storage is crucial in many data processing procedures. Data processing results are frequently placed in
storage to be used as input data for further processing at a later data.
EXPANDED IPO CYCLE
ORIGINATION
INPUT
PROCESSING STORAGE
OUTPUT
DISTRIBUTION
You might also like
- Data ProcessingDocument18 pagesData ProcessingRizwan Ali100% (1)
- Abed ComputerDocument13 pagesAbed ComputerKaren SalardaNo ratings yet
- Fort I Net Open PortsDocument14 pagesFort I Net Open PortsaboutpanuNo ratings yet
- Data Analytics IT Director in USA Resume Wallace HuDocument2 pagesData Analytics IT Director in USA Resume Wallace HuWallaceHuNo ratings yet
- First Term SS1 Data ProcessingDocument23 pagesFirst Term SS1 Data ProcessingOgar Charles89% (19)
- UptimeDowntimeEventTracking RTtech - SRowlandsDocument56 pagesUptimeDowntimeEventTracking RTtech - SRowlandsalisterjosephNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Information Technology Unit Code: Bit 110: Facilitator: Lilian Munyekenye OkelloDocument54 pagesIntroduction To Information Technology Unit Code: Bit 110: Facilitator: Lilian Munyekenye OkelloDaniel100% (1)
- Salesforce Flows Interview QuestionsDocument4 pagesSalesforce Flows Interview Questionssandeep VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- A-065211-1606734174791-53830-Unit 10 Web Design and Development - KavinDocument115 pagesA-065211-1606734174791-53830-Unit 10 Web Design and Development - KavinRehan RatnaweeraNo ratings yet
- Az-900 Dump - Most Important Questions: DatawolfsDocument186 pagesAz-900 Dump - Most Important Questions: DatawolfsNiranjeni ShineNo ratings yet
- S 4 LogisticsDocument7 pagesS 4 LogisticsLingam RajuNo ratings yet
- A Step-By-step Guide To Extend Standard Data Models in SAP MDG - ZarantechDocument5 pagesA Step-By-step Guide To Extend Standard Data Models in SAP MDG - ZarantechKalpana KadamNo ratings yet
- ZTE ElasticNet UME R18 NM SolutionDocument23 pagesZTE ElasticNet UME R18 NM Solutionهشام رويديNo ratings yet
- DBA Services SOWDocument11 pagesDBA Services SOWDeepak AnuNo ratings yet
- 04 Data ProcessingDocument16 pages04 Data ProcessingVan ImperialNo ratings yet
- The Data Processing CycleDocument22 pagesThe Data Processing CycleAnum KhursheedNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument14 pagesReviewerRhea MendozaNo ratings yet
- Computer Data ProcessingDocument3 pagesComputer Data ProcessingmauriceNo ratings yet
- Data ProcessingDocument26 pagesData Processingangelic kvsbunNo ratings yet
- 1ST Term S1 Data ProcessingDocument20 pages1ST Term S1 Data ProcessingAsabia OmoniyiNo ratings yet
- Data ProcessingDocument4 pagesData ProcessingKwonyoongmaoNo ratings yet
- Data ProcessingDocument29 pagesData Processingkibet kennedyNo ratings yet
- Itc P1Document19 pagesItc P1rayden22No ratings yet
- Data Processing ACC 114: Management Information: SystemDocument38 pagesData Processing ACC 114: Management Information: SystemAkinbami OlorunnifemiNo ratings yet
- 1ST Term SS1 Data Processing Note SumDocument26 pages1ST Term SS1 Data Processing Note SumimoleayooluwaseunNo ratings yet
- The Adelphi College Lingayen, PangasinanDocument6 pagesThe Adelphi College Lingayen, PangasinanEmilie Ann SumalloNo ratings yet
- Comp01 - Lect 1 - Data ProcessingDocument7 pagesComp01 - Lect 1 - Data ProcessingJeiel BaculodNo ratings yet
- Data ProcessingDocument9 pagesData ProcessingJoannah Claire AlforqueNo ratings yet
- 1ST Term S1 Data ProcessingDocument22 pages1ST Term S1 Data ProcessingOlaoye Olumide HabeebNo ratings yet
- Data ProcessingDocument53 pagesData ProcessingMalou Benoza-LansanganNo ratings yet
- 1 ICT LiteracyDocument10 pages1 ICT Literacykurt palivinoNo ratings yet
- Data Processing CycleDocument8 pagesData Processing CycleAmina ButtNo ratings yet
- My Mind Reader'sDocument19 pagesMy Mind Reader'sRANA MUHAMMAD ABDULLAH ZahidNo ratings yet
- About Computers HomeworkDocument12 pagesAbout Computers HomeworkChi SantosNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 3-Data ProcessingDocument21 pagesLECTURE 3-Data Processingjayson virtucio50% (2)
- Basic Operations and Components of A Computer SystemDocument18 pagesBasic Operations and Components of A Computer SystemAbena, Kianne C.No ratings yet
- Data Processing CycleDocument8 pagesData Processing CycleAilen ValdezNo ratings yet
- DA Unit 2Document13 pagesDA Unit 2Eswari KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Data ProcessingDocument11 pagesData ProcessingSolomon AjuloNo ratings yet
- What Is Information ProcessingDocument20 pagesWhat Is Information Processingshanesha blackhoodNo ratings yet
- What Is Data Processing: Cycle, Types, Methods, Steps and ExamplesDocument1 pageWhat Is Data Processing: Cycle, Types, Methods, Steps and Examplesjahremade jahremadeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 DATA Processing and Computer ApplicationDocument31 pagesChapter 3 DATA Processing and Computer ApplicationMelchor CarabayasNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 Data and InformationDocument40 pagesWEEK 1 Data and InformationJan Karl PreciosoNo ratings yet
- Data ProcessingDocument101 pagesData ProcessingKunal Bhodia0% (1)
- Big Picture B: Big Picture in Focus: Uloa. Explain The Computer-BasedDocument18 pagesBig Picture B: Big Picture in Focus: Uloa. Explain The Computer-BasedEagle OrtegaNo ratings yet
- What Is Data Processing?: 1. CollectionDocument7 pagesWhat Is Data Processing?: 1. Collectionarlene bobadillaNo ratings yet
- Acc105 Newest - 230529 - 141356Document43 pagesAcc105 Newest - 230529 - 141356Oyindamola OladeindeNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 27 Computer Based Data ProcessingDocument15 pagesCHAPTER 27 Computer Based Data ProcessingMelady Sison Cequeña100% (1)
- Computer Science LecturesDocument10 pagesComputer Science LecturesPatekJoaquinNo ratings yet
- Lesson-2 - Data ProcessingDocument8 pagesLesson-2 - Data ProcessingGlad RoblesNo ratings yet
- Data Processing and AnalysisDocument26 pagesData Processing and AnalysisMohamed Ali AbdiNo ratings yet
- Data Processing CycleDocument5 pagesData Processing CycleKhan Aagha100% (1)
- Introduction To Data Processing DataDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Data Processing DataAustin AgbasonNo ratings yet
- 8 Data ProcessingDocument17 pages8 Data ProcessingDurga Prasad SmartNo ratings yet
- 2-BCA 10 Lecture 2 - Computer ConceptsDocument36 pages2-BCA 10 Lecture 2 - Computer ConceptsHannah VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Data Processing, Security, AntivirusDocument9 pagesData Processing, Security, AntivirusOgbo IsuNo ratings yet
- Management Control System: Unit 2: Audit Under Computer SystemDocument35 pagesManagement Control System: Unit 2: Audit Under Computer SystemJulie ChristianNo ratings yet
- Data ProcessingDocument9 pagesData ProcessingAlizaNo ratings yet
- Topic Importance of Data ProcessingDocument9 pagesTopic Importance of Data ProcessingPratik KaharNo ratings yet
- Data ProcessingDocument6 pagesData ProcessinganshifhaarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Basic Operations and Components of A ComputerDocument18 pagesLesson 2: Basic Operations and Components of A ComputerNiña Mae C. QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Data, Infn, SystemsDocument68 pagesData, Infn, SystemsKochappen Ipe KumarNo ratings yet
- 4TH QTR Reviewer IotDocument1 page4TH QTR Reviewer Iotmarie parfanNo ratings yet
- Input Processing Output CycleDocument7 pagesInput Processing Output Cycleseven hillsNo ratings yet
- CSC 1 Lesson1Document2 pagesCSC 1 Lesson1Javer BorngoNo ratings yet
- CSC 1 Lesson1Document2 pagesCSC 1 Lesson1Javer BorngoNo ratings yet
- 15 DataprocessingDocument23 pages15 DataprocessingTINOTENDA MUCHEMWANo ratings yet
- Data Processing TaskDocument18 pagesData Processing TaskJericho HernanNo ratings yet
- 01 Data - Processing - CycleDocument6 pages01 Data - Processing - Cyclenikolai bartNo ratings yet
- Business Intelligence Maturity ResearchDocument10 pagesBusiness Intelligence Maturity ResearchAngela Hernández HerreraNo ratings yet
- crm-sales-executive-dashboard-template-excel-sales-executive-dashboard-excel-free-downloadDocument8 pagescrm-sales-executive-dashboard-template-excel-sales-executive-dashboard-excel-free-downloadharshNo ratings yet
- CRM AIRLINES AbstractDocument5 pagesCRM AIRLINES AbstractChandan KumarNo ratings yet
- Art 2018 Empowering Chatbots With Business Intelligence byDocument6 pagesArt 2018 Empowering Chatbots With Business Intelligence byJimmyJhonFernandezZavaletaNo ratings yet
- Apiguide PDFDocument270 pagesApiguide PDFbasis sapNo ratings yet
- Synopsis Sun ClubDocument9 pagesSynopsis Sun Clubrohitgond0741No ratings yet
- Test Midterm-1 2015 05 24 01 23 05 446Document11 pagesTest Midterm-1 2015 05 24 01 23 05 446Kasa Ferenc100% (1)
- (OSCE 11.0) To (Apex One) Upgrade Handy GuideDocument49 pages(OSCE 11.0) To (Apex One) Upgrade Handy GuidesegabysNo ratings yet
- PFE Monitoring System (USER MANUAL)Document4 pagesPFE Monitoring System (USER MANUAL)Anacieto N. MercadoNo ratings yet
- Module.+5+ +Business+Reporting+and+Visual+AnalyticsDocument14 pagesModule.+5+ +Business+Reporting+and+Visual+AnalyticsNicolas Joaquin Sebastian GutierrezNo ratings yet
- MySAP Business SolutionDocument4 pagesMySAP Business SolutionclaudiodonettiNo ratings yet
- SMA Modbus General TI en 10Document24 pagesSMA Modbus General TI en 10Alain RykaertNo ratings yet
- Dell EMC ECS Deployment GuideDocument33 pagesDell EMC ECS Deployment GuidePratip GhoshNo ratings yet
- Extract Transform LoadDocument4 pagesExtract Transform LoadjomanudiNo ratings yet
- Az 400Document43 pagesAz 400harikishorepalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Computer Science: Object Oriented Programming (OOP)Document4 pagesComputer Science: Object Oriented Programming (OOP)aditya keshariNo ratings yet
- (EXT) GenAI Best Practices-Master-SlidesDocument45 pages(EXT) GenAI Best Practices-Master-Slidesশাদসৌম্যNo ratings yet
- Security Design of Aws Nitro SystemDocument39 pagesSecurity Design of Aws Nitro Systemdai fuonNo ratings yet
- Programming in Modern C++Document1 pageProgramming in Modern C++pallaviNo ratings yet
- Mototrbo Application CatalogueDocument36 pagesMototrbo Application CatalogueMuharrem OZTASNo ratings yet