PATOPHYSIOLOGY OF TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
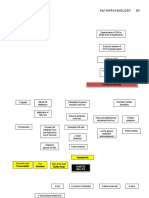
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (DM2)
Cells in the body become
1. Insulin Resistance less responsive to insulin, a
hormone responsible for
Cells do not respond well to insulin.
regulating blood sugar levels.
Results in elevated blood glucose levels As a result, blood glucose
levels remain elevated.
The pancreas, which produces
insulin, may not be able to keep 2. Pancreatic Dysfunction
up with the demand for insulin
due to insulin resistance. This
Pancreas cannot produce enough insulin to overcome
leads to insufficient insulin resistance
production and chronic Leads to chronic hyperglycemia
hyperglycemia (high blood sugar
levels).
Chronic hyperglycemia damages
3. Complications blood vessels and nerves
throughout the body, leading to
Chronic hyperglycemia damages blood vessels and various complications such as
nerves cardiovascular disease, neuropathy
Can cause cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, (nerve damage), nephropathy
(kidney damage), and retinopathy
nephropathy, and retinopathy
(eye damage).
Lifestyle factors such as diet
and exercise play a significant
4. Contributing Factors
role in the development of
DM2. Additionally, genetic
Lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise
predisposition can increase Genetic predisposition
the risk of developing the
condition.