Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Surface Area Calculator: For Example
Uploaded by
Ram SinghOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Surface Area Calculator: For Example
Uploaded by
Ram SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
Surface Area Calculator
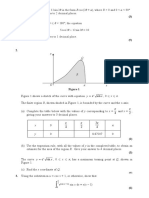
Do you know what is surface area? Surface area is the area of a given object. Surface area is commonly denoted S. Surface area is mostly used to find an area of a 3-dimensional object. A sphere is a three-dimensional shape which looks like round ball. Surface Area of a Sphere is the measure of how much exposed area a sphere has and it's measured in square units. For example :see the calculator mentioned in this page where by putting radius you will get surface area.
Learn More about Math Tutor
Below see the list of all the calculators comes under surface area. Use these to tools to make your calculation easy and fun.
In chemistry
Surface area is important in chemical kinetics. Increasing the surface area of a substance generally increases the rate of a chemical reaction. For example :iron in a fine powder will combust, while in solid blocks it is stable enough to use in structures. For different applications a minimal or maximal surface area may be desired.
In biology
The surface area of an organism is important in several considerations, such as regulation of body temperature and digestion. Animals use their teeth to grind food down into smaller particles, increasing the surface area available for digestion. The epithelial tissue lining the digestive tract contains microvilli, greatly increasing the area available for absorption. Elephants have large ears, allowing them to regulate their own body temperature. In other instances, animals will need to minimize surface area; for example, people will fold their arms over their chest when cold to minimize heat loss. The surface area to volume ratio (SA:V) of a cell imposes upper limits on size, as the volume increases much faster than does the surface area, thus limiting the rate at which substances diffuse from the interior across the cell membrane to interstitial spaces or to other cells. Read More on Live Online Tutoring
Indeed, representing a cell as an idealized sphere of radius r, the volume and surface area are, respectively, V = 4/3 r3; SA = 4 r2. The resulting surface area to volume ratio is therefore 3/r. Thus, if a cell has a radius of 1 m, the SA:V ratio is 3; whereas if the radius of the cell is instead 10 m, then the SA:V ratio becomes 0.3. With a cell radius of 100, SA:V ratio is 0.03. Thus, the surface area falls off steeply with increasing volume. Various approaches to general definition of surface area were developed in the late nineteenth and the early twentieth century by Henri Lebesgue and Hermann Minkowski. While for piecewise smooth surfaces there is a unique natural notion of surface area, if a surface is very irregular, or rough, then it may not be possible to assign any area at all to it. A typical example is given by a surface with spikes spread throughout in a dense fashion. Many surfaces of this type occur in the theory of fractals. Extensions of the notion of area which partially fulfill its function and may be defined even for very badly irregular surfaces are studied in the geometric measure theory. A specific example of such an extension is the Minkowski content of a surface.
Thank You
TutorVista.com
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Latihan Koordinat PDFDocument8 pagesLatihan Koordinat PDFA SNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Introduction To Finite Element Analysis Using SolidWorks by Randy H. ShihDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Finite Element Analysis Using SolidWorks by Randy H. Shihhombre.muerto595957% (7)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Header Ligament Crack Detection and SizingDocument65 pagesHeader Ligament Crack Detection and SizingshabanNo ratings yet
- TD 7 1st PT 22Document4 pagesTD 7 1st PT 22MarivicVichoMonsayacNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Topic 5 - Reversed CurvesDocument3 pagesTopic 5 - Reversed CurvesFeliks Albert RitaNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Sulit 3472/2: 3472/2 Additional Mathematics Paper 2Document11 pagesSulit 3472/2: 3472/2 Additional Mathematics Paper 2Salmizam IzamNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- 2 CylindersDocument20 pages2 CylindersAAKASH JOONNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- CH4 1Document67 pagesCH4 1abhayNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Herons Formula - FinalDocument11 pagesHerons Formula - FinalIX17-41 Suvayu ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Sat Math Practice Test 9 AnswersDocument6 pagesSat Math Practice Test 9 AnswerswwwmacyNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Lecture Notes On Vector Bundles and Characteristic ClassesDocument38 pagesLecture Notes On Vector Bundles and Characteristic Classesvacilando2011No ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Lie Algebra 2Document5 pagesLie Algebra 2симплектик геометрияNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Class X E Book Maths Chapter 13 Height and DistanceDocument9 pagesClass X E Book Maths Chapter 13 Height and DistanceloveboxNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Class 12 Modern, BK Question BankDocument2 pagesClass 12 Modern, BK Question Bankfilm boss ronitchawlaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL C34 - SAM PaperDocument5 pagesEdexcel IAL C34 - SAM PaperSahil KananiNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Spherical Polar Coordinate SystemDocument3 pagesSpherical Polar Coordinate SystemPavithra SridharNo ratings yet
- GruideDocument190 pagesGruideTrần AnNo ratings yet
- Robotics LabDocument7 pagesRobotics LabAbdul Moiz QarniNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Imo Sample Paper Class-9Document2 pagesImo Sample Paper Class-9BhuliNo ratings yet
- Geometry and TrigonometryDocument6 pagesGeometry and TrigonometryAbhay SoniNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- DIN 3971 1980-07 Bevel Gear ParametersDocument24 pagesDIN 3971 1980-07 Bevel Gear Parameterscosta59dac9242100% (2)
- Polyhedra: Engr. Laurenz Junelle OyardoDocument48 pagesPolyhedra: Engr. Laurenz Junelle OyardoSchyrie Alliah GarciaNo ratings yet
- Sundial - How To and MathDocument19 pagesSundial - How To and MathEmma PayneNo ratings yet
- Static of Rigid BodiesDocument9 pagesStatic of Rigid BodiesjustinalmeraNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Department of Education: Cot For Third QuarterDocument6 pagesDepartment of Education: Cot For Third QuarterAlvin Bugayong100% (1)
- Bezier and B-Spline TechnologyDocument58 pagesBezier and B-Spline Technologygln4uNo ratings yet
- Complex NumbersDocument15 pagesComplex NumbersAnonymous jUaHPNGx9lNo ratings yet
- Scott Robertson How To DrawDocument208 pagesScott Robertson How To DrawJorge Braddock50% (2)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Lesson 3 Direct Modeling: ObjectivesDocument40 pagesLesson 3 Direct Modeling: ObjectivesAnonymous rhbWnvNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)