Session 9
LASIK SURGERY
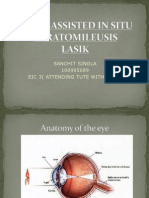
LASIK is a type of eye surgery that uses
lasers to fix vision problems, specifically
those caused by refractive errors. A
refractive error is where your eye fails to
bend light properly, distorting your vision.
It can cause, for example, blurry vision,
nearsightedness, and farsightedness.
“LASIK” is an acronym that stands for
“laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis.”
“In situ” translates into “in position” or
“in place” and “keratomileusis” is the
medical term for the reshaping of the
cornea in your eye.
Why LASIK?
LASIK surgery may be an option for the correction of one of these vision problems:
• Nearsightedness (myopia). When your eyeball is slightly longer than normal or when
the cornea curves too sharply, light rays focus in front of the retina and blur distant
vision. You can see objects that are close clearly, but not those that are far away.
• Farsightedness (hyperopia). When you have a shorter than average eyeball or a cornea
that is too flat, light focuses behind the retina instead of on it. This makes near vision,
and sometimes distant vision, blurry.
• Astigmatism. When the cornea curves or flattens unevenly, the result is astigmatism,
which disrupts focus of near and distant vision.
Your eye doctor will talk with you about whether LASIK surgery or another similar refractive
procedure is an option that will work for you.
� Session 9
Are You a Good Candidate?
Certain health conditions can increase the risks associated with LASIK surgery or make the
outcome less predictable. Doctors may not recommend laser refractive surgery for you if you
have certain conditions, including:
• Autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
• A weakened immune system caused by immunosuppressive medications or HIV.
• Persistent dry eyes.
• Recent changes in vision due to medications, hormonal changes, pregnancy, breast-
feeding or age.
• Inflammation of the cornea, lid disorders, eye injuries or eye diseases, such as uveitis,
herpes simplex affecting the eye area, glaucoma or cataracts.
LASIK surgery is usually not advisable if you:
• Have an eye disease that causes the cornea to thin and bulge, or if you have a family
history of it.
• Have good overall vision.
• Have severe nearsightedness.
• Have very large pupils or thin corneas.
• Have age-related eye changes that cause vision to be less clear.
• Participate in contact sports that may be associated with blows to the face.
If you're considering LASIK surgery, talk to your doctor about your questions and concerns. Your
doctor will discuss whether you're a candidate for the procedure or other similar procedures.
� Session 9
How You Prepare
Steps you can take to prepare for surgery include:
• Know what surgery may cost you. LASIK surgery is usually considered elective surgery,
so most insurance companies won't cover the cost of the surgery. Be prepared to pay
out-of-pocket for your expenses.
• Arrange for a ride home. You'll need to have someone drive you to and from your place
of surgery. Immediately after surgery, you might still feel the effects of medicine given
to you before surgery, and your vision may be blurry.
• Skip the eye makeup. Don't use eye makeup, cream, perfumes or lotions on the day
before and the day of your surgery. Your doctor may also instruct you to clean your
eyelashes daily or more often in the days leading up to surgery, to remove debris and
minimize your risk of infection.