Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fetal Circulation
Uploaded by
Leslie Cristine AbadOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fetal Circulation
Uploaded by
Leslie Cristine AbadCopyright:
Available Formats
FETAL CIRCULATION
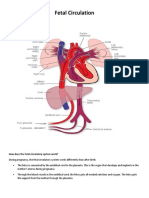
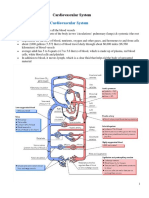
Inside the fetal heart: y y y y Blood enters the right atrium, the chamber on the upper right side of the heart. Most of the blood flows to the left side through a special fetal opening between the left and right atria, called the foramen ovale. Blood then passes into the left ventricle (lower chamber of the heart) and then to the aorta, (the large artery coming from the heart). From the aorta, blood is sent to the heart muscle itself in addition to the brain and arms. After circulating there, the blood returns to the right atrium of the heart through the superior vena cava. About one-third of the blood entering the right atrium does not flow through the foramen ovale, but, instead, stays in the right side of the heart. This blood enters the right ventricle from the right atrium, then exits the right ventricle to end up in, eventually flowing into the pulmonary artery. From there, some of the blood will travel to the lungs. The majority of the blood in the pulmonary artery, however, enters the descending aorta through a special artery called the patent ductus arteriosus (PDA). It then travels through smaller vessels to reach back into the placenta. Because the placenta does the work of exchanging oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) through the mother's circulation, the fetal lungs are not used for breathing. Instead of blood flowing to the lungs to pick up oxygen and then flowing to the rest of the body, the fetal circulation shunts (bypasses) most of the blood away from the lungs. In the fetus, blood is shunted from the pulmonary artery to the aorta through the patent ductus arteriosus. FETAL CIRCULATION 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Oxygenated blood enters the umbilical vein from the placenta Enters ductus venosus Passes through inferior venacava Enters the right atrium Enters the foramen ovale Goes to the left atrium Passes through left ventricle Flows to ascending aorta to supply nourishment to the brain and upper extremeties Enters superior vena cava Goes to right atrium Enters the right ventricle Enters pulmonary artery with some blood going to the lungs to supply oxygen and nourishment Flows to ductus arteriosus Enters descending aorta ( some blood going to the lower extremeties) Enters hypogastric arteries Goes back to the placenta
Special Structures in Fetal Circulation Placenta Where gas exchange takes place during fetal life Umbilical Arteries Carry unoxygenated blood from the fetus to placenta Umbilical Vein Brings oxygenated blood coming from the placenta to the fetus Foramen Ovale Connects the left and right atrium. It pushes blood from the right atrium to the left atrium so that blood can be supplied to brain, heart and kidney Ductus Venosus - Carry oxygenated blood from umbilical vein to inferior venacava, bypassing fetal liver Ductus Arteriosus - Carry oxygenated blood from pulmonary artery to aorta, bypassing fetal lungs.
You might also like
- Fetal Circulation ExplainedDocument4 pagesFetal Circulation ExplainedTina Tin100% (1)
- Fetal Circulation Shunts Blood Away from LungsDocument5 pagesFetal Circulation Shunts Blood Away from Lungsbluemandrake2185No ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument2 pagesFetal CirculationEric Gato100% (3)
- Fetal CirculationDocument6 pagesFetal Circulationkc-orense-1005No ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument27 pagesFetal CirculationSureshChevagoniNo ratings yet
- High Risk Newborn2Document15 pagesHigh Risk Newborn2Catherine Villanueva Sta Monica100% (1)
- Placental AbnormalitiesDocument3 pagesPlacental AbnormalitiesThakoon TtsNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology OverviewDocument39 pagesReproductive Anatomy and Physiology Overviewabera100% (1)
- Meconium Aspiration Syndrome (MAS) GuideDocument12 pagesMeconium Aspiration Syndrome (MAS) GuideAngela AmaoNo ratings yet
- Antepartum PeriodDocument3 pagesAntepartum PeriodjisooNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing Care of The NewbornDocument5 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing Care of The NewbornJeanilynTanNo ratings yet
- Partograph Monitoring Labor ProgressDocument65 pagesPartograph Monitoring Labor ProgressAmyAgustinNo ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument2 pagesFetal CirculationgoldiemareNo ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument12 pagesFetal CirculationRiya Joy83% (6)
- Fetal CirculationDocument2 pagesFetal Circulationanon_414797925No ratings yet
- Amniotic Fluid Embolism (AFE)Document26 pagesAmniotic Fluid Embolism (AFE)sanjivdas100% (1)
- Fetal Skull and Its Significant in LaborDocument40 pagesFetal Skull and Its Significant in Laborazida9075% (4)
- Anaemia in Pregnancy: Dr. Lama MehaisenDocument11 pagesAnaemia in Pregnancy: Dr. Lama MehaisenWendy EvansNo ratings yet
- Components of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument23 pagesComponents of The Cardiovascular SystemMr. DummyNo ratings yet
- Systemic Changes During PregnancyDocument2 pagesSystemic Changes During PregnancyARAugusto67% (3)
- Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument69 pagesRespiratory Distress SyndromeAbraham ChiuNo ratings yet
- Malpresentation and Malposition - PostmaturityDocument29 pagesMalpresentation and Malposition - PostmaturityNishaThakuriNo ratings yet
- Contracted Pelvis Definition, Causes, Diagnosis & ManagementDocument32 pagesContracted Pelvis Definition, Causes, Diagnosis & ManagementNirupama KsNo ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument14 pagesFetal Circulationjoel david knda mj100% (3)
- Prematurity and PostmaturityDocument34 pagesPrematurity and PostmaturityAngelo MolinaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Normal NewbornDocument6 pagesAssessment of The Normal Newborndhalal100% (2)
- Essential Newborn CareDocument14 pagesEssential Newborn CareJhing Rodriguez BorjalNo ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument13 pagesFetal CirculationHarish Kumar Kumawat100% (2)
- Fetal CirculationDocument13 pagesFetal CirculationPraveen YadavNo ratings yet
- Fetal SkullDocument4 pagesFetal SkullSherene Jacob Mathew VaidyanNo ratings yet
- Signs of LaborDocument5 pagesSigns of Labormarianne_07No ratings yet
- Pre EclampsiaDocument8 pagesPre EclampsiaJamie Agbannawag100% (1)
- Malpresentation and Malposition - ShoulderDocument5 pagesMalpresentation and Malposition - ShoulderNishaThakuri100% (1)
- NicuDocument46 pagesNicugoal diggers100% (1)
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument22 pagesTetralogy of FallotHusna Aje100% (1)
- Hydorp Fetalis Complete002Document83 pagesHydorp Fetalis Complete002Sandra Anastasia Gultom100% (1)
- Exclusivebreastfeeding 181003124754Document39 pagesExclusivebreastfeeding 181003124754apalanavedNo ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument22 pagesFetal CirculationJSeasharkNo ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument3 pagesFetal Circulationyusrinastiti100% (1)
- Fetal DevelopmentDocument43 pagesFetal DevelopmentRob N Michelle50% (2)
- Birth Injuries Nursing TeachingDocument24 pagesBirth Injuries Nursing Teachingsaleha sultanaNo ratings yet
- Fetal Skull: Parts, Bones, Sutures & DiametersDocument4 pagesFetal Skull: Parts, Bones, Sutures & Diameterssubashik0% (1)
- Bleeding Disorders of PregnancyDocument66 pagesBleeding Disorders of PregnancyDivine Flores-CamposNo ratings yet
- The Important Measurements of A NewbornDocument3 pagesThe Important Measurements of A NewbornGraciaNo ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument16 pagesFetal CirculationArunashree ajayNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of the Placenta, Including InsufficiencyDocument59 pagesStructure and Function of the Placenta, Including InsufficiencySulis 'Hp' Kartowidjojo100% (1)
- Identifying Clients at RiskDocument57 pagesIdentifying Clients at Riskcoosa liquors100% (1)
- High Risk NewbornDocument20 pagesHigh Risk Newborndmrdy50% (2)
- POLYHYDRAMNIOSDocument2 pagesPOLYHYDRAMNIOSyxly imperialNo ratings yet
- Icterus NeonatarumDocument64 pagesIcterus NeonatarumDeepti KukretiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Reproductive SystemDocument93 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Reproductive SystemMelizza Fajardo BañanoNo ratings yet
- CPDDocument45 pagesCPDVijith.V.kumar100% (1)
- Intrapartum AssessmentDocument22 pagesIntrapartum Assessmentanon_27233321950% (2)
- MenstruationDocument33 pagesMenstruationmskot100% (3)
- Process of LabourDocument6 pagesProcess of LabourAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- The PlacentaDocument3 pagesThe Placentageorgeloto12100% (1)
- Gynaecological Procedure SeminarDocument33 pagesGynaecological Procedure SeminarTausif HaqueNo ratings yet
- AntepartumDocument32 pagesAntepartumphoenix180100% (1)
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Fetal Circulation ComprehensiveDocument2 pagesFetal Circulation ComprehensiveMarisol Jane Jomaya100% (1)