VMware Quick Guide
VMware Quick Guide
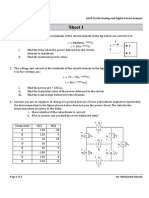
1. vMotion
- vMotion is VMware's live migration technology, allowing a running VM to move from one ESXi host
to another without downtime. Essential for maintenance without disrupting applications.
- Requirements: Shared storage, compatible network configuration, same virtual network, and
similar CPU architecture.
2. High Availability (HA)
- HA is a feature that automatically restarts VMs on another host in the event of a host failure,
minimizing downtime.
- Requirements: Cluster with multiple ESXi hosts, shared storage, redundant networking for
management, and sufficient resources reserved.
3. Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS)
- DRS automates the distribution of VMs across hosts in a cluster based on resource usage to
balance workloads.
- Requirements: Cluster configuration, shared storage, compatible network settings, and compatible
CPU configurations.
4. VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network)
- VLANs segment network traffic to isolate data and improve security within the same physical
network infrastructure.
- Each VLAN has a unique identifier (VLAN ID) and can span multiple hosts if configured properly.
Page 1
� VMware Quick Guide
5. Port Groups
- Port groups define network configurations for VMs on vSwitches. They allow VMs to connect to
specific networks and use specific VLANs.
- Standard vs Distributed Port Groups: Standard port groups are managed individually on each host,
while distributed port groups are managed centrally through vCenter.
6. Shared Storage
- Shared storage is a storage solution accessible by all hosts in a cluster, essential for features like
vMotion, HA, and DRS.
- Common shared storage types include SAN (Storage Area Network), NAS (Network-Attached
Storage), and vSAN.
7. vSwitch (Virtual Switch)
- A vSwitch is a software-based network switch in VMware that enables VMs to communicate within
the same host or with the external network.
- Standard vs Distributed vSwitch: A Standard vSwitch operates on a single host, while a Distributed
vSwitch can be configured across multiple hosts, managed centrally by vCenter.
8. Enhanced vMotion Compatibility (EVC)
- EVC allows hosts with different CPU generations to be compatible for vMotion by masking CPU
differences, enabling migration between them.
9. Datastore
- A datastore is a storage container for VMs, stored on shared storage (SAN, NAS, or vSAN).
Page 2
� VMware Quick Guide
Accessible by multiple hosts, it enables data persistence and mobility for VMs.
10. Admission Control (HA Feature)
- Admission Control reserves resources across the cluster to guarantee enough capacity to restart
VMs on other hosts if one fails.
Page 3