Name:____________________________________________ Date:_________________________ Pd:_______
Biology
Introduction to Lipids
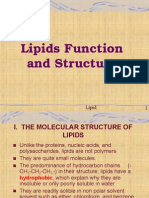
Lipids are a class of organic compounds that include fats, oils, waxes, and steroids. There are several
different kinds of lipids that we will investigate in this activity. It is important to note now that the
monomer of lipids is the fatty acid.
Observe the picture below which shows an example of an unsaturated and a saturated fatty acid. There are
also some pictures of foods that contain saturated and unsaturated fatty acids.
1. Looking at the molecular structure, describe how the unsaturated fatty acid looks different from the
saturated fatty acid.
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
2. What are examples of foods that contain saturated fatty acids, what are some examples of foods that
contain unsaturated fatty acids. Can you make any conclusions about the health of each type of fat on the
human body?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
3. Unsaturated lipids are generally liquid at room temperature (oils) and saturated lipids are generally solid at
room temperature. Looking at the molecular structure, can you make a hypothesis as to why this occurs?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
�Observe the picture below which shows a triglyceride. A triglyceride is the main energy storage molecule
in animals and is made up of 3 fatty acids bonded to a glycerol backbone.
4. Observe the molecular structure. Why do you think this molecule is called a triglyceride?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
5. The fatty acid chains are bound to which molecule? ____________________________________________
6. Think back to previous lessons about monomers/polymers. What chemical reaction do you think joins fatty
acids to this molecule?
___________________________________________________________
7. Think back to previous lessons about monomers/polymers. What chemical reaction do you think breaks
down this molecule?
__________________________________________________________
5. Look at the structure of the top and the bottom fatty acids. They both contain a double bond. What does
that tell you about this fat?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
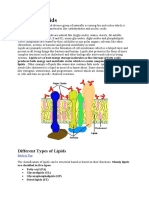
�The picture below shows another type of lipid, called a phospholipid. Phospholipids make up the membrane,
or outer boundary of cells.
Observe the structure of a phospholipid below.
6. How is the molecular structure of the phospholipid similar to a triglyceride? How is it different?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
7. Why do you think it is important that the outer membrane of a cell is made of fat? (Think about how fats
behave in water)
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
Steroids are a type of lipid that act as signaling molecules in living organisms. Steroids all have the same
general molecular structure, made up of 3 hexagonal rings and one pentagonal ring.
8. The steroid “skeleton” picture shows how most steroids look in general. How would you describe the
structure of a steroid?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
9. What makes cholesterol unique from the “steroid skeleton”?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
�Two more examples of steroids are estrogen and testosterone.
Estrogen and testosterone are examples of steroids that act as chemical messengers in the body. Estrogen
signals the development of female characteristics, and testosterone signals the development of male
characteristics.
10. Looking at the molecular structure, how are estrogen and testosterone similar? How are they different?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
Anabolic steroids are produced by scientists in a lab to copy the effects of real testosterone. When people
abuse anabolic steroids they sometimes end up looking like this:
11. Based on what you’ve learned about testosterone how do you think anabolic steroids work?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
12. What do you think are the long-term effects of using anabolic steroids on your body’s own production of
testosterone?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________