0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views1 pageUnderstanding Indices in Mathematics
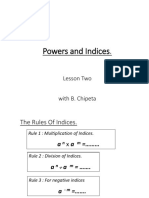
Indices, or exponents, indicate how many times a number is multiplied by itself, with specific rules for multiplication, division, and powers. Key concepts include adding indices when multiplying, subtracting when dividing, and raising an exponent to another power by multiplying indices. Additionally, any number raised to the power of 0 equals 1, negative indices represent reciprocals, and fractional indices denote roots of the base.
Uploaded by
emredersinizCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views1 pageUnderstanding Indices in Mathematics
Indices, or exponents, indicate how many times a number is multiplied by itself, with specific rules for multiplication, division, and powers. Key concepts include adding indices when multiplying, subtracting when dividing, and raising an exponent to another power by multiplying indices. Additionally, any number raised to the power of 0 equals 1, negative indices represent reciprocals, and fractional indices denote roots of the base.
Uploaded by
emredersinizCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd