Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study Psychia
Drug Study Psychia
Uploaded by
Cherry Mae AlitoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study Psychia
Drug Study Psychia
Uploaded by
Cherry Mae AlitoCopyright:
Available Formats
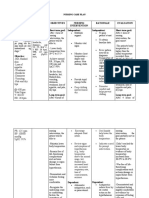
DRUG STUDY Patient; __________________________________________________________Age: __________Hospital No._____________ Room No.
____________ Impression Diagnosis: ______________________________________________ Attending Physician: _________________________________________ Allergy to: _______________________________________________________ Indication/ Mechanism of Drug Action Generic/ Name & Classification Generic : Valproate sodium Timing: Brand: Depacon Duration: * As adjunct to treat simple or complex absence seizures, complex partial seizures, myoclonic seizures and generalized tonic-clonic seizures * To treat acute manic phase of bipolar disorder Classification: Other Form: Chemical Class: Carboxylic acid derivative Therapeutic Class: Anticonvulsant * To prevent migraine headache Dose, Strenght & Formulation Ordered: Indications: * To treat simple or complex seizures,, complex partial seizures, myoclonic seizures and generalized tonic-clonic seizures as monotherapy. CNS: Agitation, ataxia, confusion, depression, dizziness, drowsiness, euphoria, hallucinations, headache, hyperesthesia, hupothermia, lethargy, loss of zeizure control, sedation, suicidal ideation, tremor, vertigo, weakness EENT: diplopia, nytgamus, pharyngitis, spots before eyes ENDO: galactorrhea, hyperglycemia Gi: abdominal pain, anorexia, constipation, diarrhea, elevated liver function test results, hepatotoxicty, increased appetite, indigestion, nausea, vomiting Adverse/ Side Effects Drug Interaction Nursing Responsibilities 1. Urge patient to avoid alcohol during therapy 2. Urge woman to notify prescriber at once about suspected or known pregnancy 3. Urge family or caregiver to watch for closely for suicidal tendencies, especially when therapy starts or dosage changes. 4. Rationale Client Teaching
1. Give valproate sodium with food. 2. Watch patient closely for suicidal tendencies, particularly when therapy starts and dosage changes. 3. Monitor patient drug level as ordered, especially early in therapy and if patient takes other drugs 4. Advise patient to avoid hazardous activities during therapy 5. Instruct patient to swallow capsules whole
- to minimize GI irritation - depression may worsen temporarily during these times, possibly leading to suicidal ideation - interactions can alter the blood level
- drug may affect mental and motor performance - to prevent irritation to mouth and throat
Indication/ Mechanism of Drug Action Generic/ Name & Classification Dose, Strenght & Formulation Mechanism of Action: May decrease seizure activity by blocking reuptake of gammaaminobutyric acid (GABA), the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. GABA suppresses the rapid firing of neurons by inhibiting voltage-sensitive sodium channels.
Adverse/ Side Effects Drug Interaction Nursing Responsibilities
Rationale
Client Teaching
GU: menstrual irregularities HEME: eosinophilia, hematoma, leukopenia, prolonged bleeding time, thrombocytopenia, dysarthria SKIN: alopeica, diaphoresis, erythema, jaundice, petechiae, photosensitivity, pruritus, SJS
Indication/ Mechanism of Drug Action Generic/ Name & Classification Dose, Strenght & Formulation
Adverse/ Side Effects Drug Interaction Nursing Responsibilities
Rationale
Client Teaching
Indication/ Mechanism of Drug Action Generic/ Name & Classification Generic : lithium carbonate Brand: Carbolith Mechanism of Action: May increase presynaptic degredation of the cathecolamine neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine and norepinephrine; inhibit their release at neural synapses; and decrease postsynaptic receptor sensitivity. These actions may correct overactive cathecolamine systems in patients with mania Dose, Strenght & Formulation Indications: To treat recurrent bipolar affective disorder, to prevent bipolar disorder depression
Adverse/ Side Effects Drug Interaction Nursing Responsibilities CNS: ataxia, coma, confusion, depression, dizziness, drowsiness, headache, lethargy, seizures,, syncope CV: arrythmias, ECG changes, edema EENT: dental caries, dry mouth, exopthalmus ENDO: diabetes insipidus, euthyroid goiter, hypothyroidism, myxedema GI: adbominal distention and pain, anorexia, diarrhea, nausea, thirst GU: stress incontennce, urinaryfrequency HEME: leukocytosis MS: muscle twitching and weakness RESP: dyspnea SKIN: ance, alopecia, thin hair 1. Administer lithium after meals 2. Be aware that lithium affects intracellular and extracellular potassium ion shift, which can cause ECG changes such as flattened or inverted T waves 3. Weigh patient daily
Rationale
Client Teaching
- to slow absorption from GI tract and reduce adverse reaction - it can increase the risk of cardiac arrest
1. Advise patient to take lithium with or after meals to minimize adverse reactions 2. Inform patient that frequent urination, nausea, and thirst may occur during the first few days of treatment 3. Caution patient not to stop taking lithium or adjust dosage without first consulting prescriber 4. Instruct patient to report signs of toxicity such as diarrhea, drowsiness, muscle weakness and tremor
- to detect sudden weight changes - lithium alters blood glucose tolerance - to detect enlargement because drug may cause goiter
Classification: Chemical Class: Alkaline metal Therapeutic Class: Antidepressant, antimanic
4. Monitor blood glucose level often in diabetic patient 5. Palpate thyroid gland
Indication/ Mechanism of Drug Action Generic/ Name & Classification Dose, Strenght & Formulation
Adverse/ Side Effects Drug Interaction Nursing Responsibilities
Rationale
Client Teaching
5. Urge patient to avoid hazardous activities until drug CNS effects are known 6. Advise patient to maintain normal fluid and sodium intake 7. Emphasize the importance of complying with scheduled check ups and laboratory test
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (843)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Swan CatheterDocument3 pagesSwan CatheterJoshNo ratings yet
- 2 JKKDocument10 pages2 JKKImam PutraNo ratings yet
- Ansi A117 1 1992Document90 pagesAnsi A117 1 1992Faouzi SouissiNo ratings yet
- May 3, 2014Document10 pagesMay 3, 2014Nancy SpencerNo ratings yet
- Case Report Amenore SekunderDocument16 pagesCase Report Amenore SekunderNinta Karina Astila SembiringNo ratings yet
- Registration Form: Bangladesh Maritime Training Institute (Bmti)Document1 pageRegistration Form: Bangladesh Maritime Training Institute (Bmti)California KnightNo ratings yet
- Bovine Disease Diagnostic ManualDocument38 pagesBovine Disease Diagnostic ManualRachel AutranNo ratings yet
- Session 2-Milk and Milk ProductDocument39 pagesSession 2-Milk and Milk ProductZul Fiqriyani SafitriNo ratings yet
- Synthesis Paper On The Use of Hip-Hop and Rap Music in Music TherapyDocument9 pagesSynthesis Paper On The Use of Hip-Hop and Rap Music in Music TherapyJosh kuhlNo ratings yet
- 2.2 - A Career in MedicineDocument23 pages2.2 - A Career in MedicineXiomaraNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) : Overview: Dr. Sanjay MathurDocument57 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment (EIA) : Overview: Dr. Sanjay MathurDebattri DasNo ratings yet
- The Definitive Guide To Health CoachingDocument196 pagesThe Definitive Guide To Health CoachingBlas Espinel Freire100% (3)
- A Case On Periampullary Carcinoma.: Presented by DR Sumaiya Tasnim TanimaDocument34 pagesA Case On Periampullary Carcinoma.: Presented by DR Sumaiya Tasnim TanimaJobaer MahmudNo ratings yet
- English 1201 Annotated BibliographyDocument5 pagesEnglish 1201 Annotated Bibliographyapi-450491009No ratings yet
- Building A Digital Health Innovation Ecosystem Framework Through Design Science ResearchDocument6 pagesBuilding A Digital Health Innovation Ecosystem Framework Through Design Science ResearchFahmi AlaydrusNo ratings yet
- CMC Vellore Summer Admission Bulletin 2020 Revised 16 Nov 2020Document58 pagesCMC Vellore Summer Admission Bulletin 2020 Revised 16 Nov 2020Allen ChrysoNo ratings yet
- Ralph Choate, PCG Public Partnerships, LLC Subject Matter ExpertDocument1 pageRalph Choate, PCG Public Partnerships, LLC Subject Matter ExpertPCG Public Partnerships, LLCNo ratings yet
- IDEA TEST - Identity and Eating DisordersDocument12 pagesIDEA TEST - Identity and Eating DisordersLeire Sanz MuleroNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document64 pagesModule 1angelito alaras83% (6)
- Sample First Aid Kit Suggested ContentsDocument1 pageSample First Aid Kit Suggested ContentsM ANo ratings yet
- Company Profile - AG NutriceuticalDocument5 pagesCompany Profile - AG NutriceuticalNorina GenistonNo ratings yet
- Preventing Slips and Trips in Kitchens and Food Service: HSE Information SheetDocument4 pagesPreventing Slips and Trips in Kitchens and Food Service: HSE Information SheetsampathdtNo ratings yet
- HyperthermiaDocument3 pagesHyperthermiaKatrina Yvet BacomoNo ratings yet
- Schedule - 1 (Related To Rules 2.6) Convocation Ceremony Application FormDocument2 pagesSchedule - 1 (Related To Rules 2.6) Convocation Ceremony Application Formgaurav karmacharyaNo ratings yet
- Donna Edens WorkshopDocument11 pagesDonna Edens WorkshopBenhmed Khadija86% (14)
- WANTED SDS For 100 OilDocument11 pagesWANTED SDS For 100 OilKaran Kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- Albon, Igao, Maldo, QuirongDocument4 pagesAlbon, Igao, Maldo, Quirongcoosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- Lung Capacity Lab: Part A: Vital CapacityDocument3 pagesLung Capacity Lab: Part A: Vital CapacityhansenNo ratings yet
- Accident Form 1 - Claimant's Statement of Accident PDFDocument3 pagesAccident Form 1 - Claimant's Statement of Accident PDFBfp RegionOne Pasuquin IlocosNorteNo ratings yet
- Healthcast The Customisation of Diagnosis Care and Cure-Pwc-2010 PDFDocument58 pagesHealthcast The Customisation of Diagnosis Care and Cure-Pwc-2010 PDFEhli HibreNo ratings yet