Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TRICHOMONIASIS
Uploaded by
kenrvOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TRICHOMONIASIS
Uploaded by
kenrvCopyright:
Available Formats
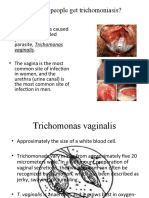
TRICHOMONIASIS A protozoal infection, trichomoniasis affects about 15% of sexually active females and 10% of sexually active males.
Common sites of infections in females include the vagina, urethra and, possibly, the endocervix, bladder, Bartholins glands, or Skenes glands; in males, the lower urethra and, possibly, the prostate gland, seminal vesicles, or epididymis. It may be transmitted by an asymptomatic carrier who harbors the organism in the urogenital tract. It may increase the risk of contracting HIV from an infected partner.
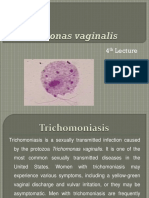
Causes: Trichomonas vaginalis, a tetraflagellated, motile protozoan Clinical Manifestations: Vaginal discharge that is thin (sometimes frothy) yellow to yellow-green, malodorous, and very irritating. Severe itching, redness, swelling, dyspareunia, dysuria; occasionally, postcoital spotting, menorrhagia, dysmenorrheal. An accompanying vulvitis may result, with vulvovaginal burning and itching. STRAWBERRY SPOTS multiple small petechiae.
Complications: - Trichomoniasis is associated with increased risk of transmission of HIV. - may cause a woman to deliver a low-birth-weight or premature infant. - also associated with increased chances of cervical cancer - evidence implies that infection in males potentially raises the risks of prostate cancer development and
spread due to inflammation.
Diagnostic tests: - Microscopic examination of vaginal or seminal discharge or urine specimen is positive for T. vaginalis. - Inspection with a speculum often reveals vaginal and cervical erythema (redness) with multiple small petechiae (strawberry spots). - pH testing of a trichomonal discharge will demonstrate a pH greater than 4.5. Treatment: - Metronidazole (both partners receive a one-time loading dose and a smaller dose three times a day for 1 weeek. The one time dose is more convenient; consequently, compliance tends to be greater. The week long treatment has occasionally been noted to be more effective. Nursing Management: - Some patients complain of an unpleasant but transient metallic taste when taking metronidazole. Nausea and vomiting, as well as a hot, flushed feeling, occur when this medication is taken with an alcoholic beverage (disulfiram-like reaction). In view of this side-effect, the patient is strongly advised to abstain from alcohol while taking this medication.
Metronidazole therapy is contraindicated in patients with some blood dyscrasias or central nervous system diseases, in the first trimester of pregnancy, and in women who are breastfeeding.
You might also like
- A Simple Guide to Sexually Transmitted DiseasesFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Sexually Transmitted DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- TRICHOMONIASISDocument39 pagesTRICHOMONIASISAlunaficha Melody KiraniaNo ratings yet
- The Complete Guide to Trichomoniasis: Symptoms, Risks, Diagnosis & TreatmentsFrom EverandThe Complete Guide to Trichomoniasis: Symptoms, Risks, Diagnosis & TreatmentsNo ratings yet
- Tricho MoniasisDocument38 pagesTricho MoniasisAkhmad Ikhwan BaidlowiNo ratings yet
- Trichomonas VaginalisDocument17 pagesTrichomonas VaginalisAndi MuhammadNo ratings yet
- How Do People Get Trichomoniasis?: VaginalisDocument7 pagesHow Do People Get Trichomoniasis?: VaginalisPearl Raiza HadaniNo ratings yet
- Trichomonas VaginalisDocument2 pagesTrichomonas Vaginalistutan_santosNo ratings yet
- Urethral DischargeDocument26 pagesUrethral DischargeZahra ArainNo ratings yet
- TrichDocument30 pagesTrichwadige4668No ratings yet
- Trichomonas Vaginalis: Geographical Distribution: World WideDocument8 pagesTrichomonas Vaginalis: Geographical Distribution: World WidesuqylNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading 2003Document14 pagesJournal Reading 2003Zhul Thaa PurpleholicNo ratings yet
- Trichomonas VaginalsDocument15 pagesTrichomonas VaginalsDaniel AtiehNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Infections and PregnancyDocument19 pagesSexually Transmitted Infections and PregnancyBeyins TiuNo ratings yet
- VaginitisDocument54 pagesVaginitisgloria100% (1)
- Flagellates-2 by DR Gallardo: - MetronidazoleDocument7 pagesFlagellates-2 by DR Gallardo: - MetronidazoleJayricDepalobosNo ratings yet
- Trichomoniasis: T. Vaginalis Is A Parasitic Protozoan, and The Taxonomic Position Is Based On The ClassificationDocument15 pagesTrichomoniasis: T. Vaginalis Is A Parasitic Protozoan, and The Taxonomic Position Is Based On The Classificationrave robNo ratings yet
- Gynaecology: Gum, Fertility, Contraception, and UrogynaecologyDocument46 pagesGynaecology: Gum, Fertility, Contraception, and UrogynaecologyOccamsRazorNo ratings yet
- Gynecology StudyguideDocument39 pagesGynecology StudyguideGameron777No ratings yet
- Syndromic Management of Sexually Transmitted InfectionsDocument76 pagesSyndromic Management of Sexually Transmitted Infectionsnamita100% (2)
- Trichomonas Vaginalis (FINAL)Document31 pagesTrichomonas Vaginalis (FINAL)Veigner Whyng Cabugayan100% (1)
- 1362256258.5314trichomonas VaginalisDocument17 pages1362256258.5314trichomonas Vaginalisricky hutagalungNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Presentation..Docx 19 To 25Document12 pagesParasitology Presentation..Docx 19 To 25freelancerhamzaabbasiNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy: PharmacologyDocument57 pagesChemotherapy: PharmacologyIshika ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Tract Infections, Sexual Transmitted Diseases, and HIV in ObstetricDocument58 pagesReproductive Tract Infections, Sexual Transmitted Diseases, and HIV in ObstetricAbdulrahman NajiNo ratings yet
- STDS: Trichomoniasis: Trichomonas Vaginalis, Which Can Be Found in The Female Vagina or Urethra and in TheDocument2 pagesSTDS: Trichomoniasis: Trichomonas Vaginalis, Which Can Be Found in The Female Vagina or Urethra and in TheSupermarsopaMarsopitaMarsoperaNo ratings yet
- Trichomonas Vaginalis InfectionDocument2 pagesTrichomonas Vaginalis InfectionMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- GONORRHOEADocument16 pagesGONORRHOEAWishie ParlourNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care in Clients With General Disturbance inDocument48 pagesNursing Care in Clients With General Disturbance inJADE MAIKHA A. MIERGASNo ratings yet
- Synonyms Causative Agents Incubatiob Period Mode of Transmission Signs and Symptoms Period of Communicability Diagnostic Test Medical Management Nursing Management ComplicationsDocument13 pagesSynonyms Causative Agents Incubatiob Period Mode of Transmission Signs and Symptoms Period of Communicability Diagnostic Test Medical Management Nursing Management ComplicationsYnah DominiqueNo ratings yet
- 10 TrichomonasDocument22 pages10 TrichomonasBoateng DerrickNo ratings yet
- Chapter 53: Nursing Management: Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument4 pagesChapter 53: Nursing Management: Sexually Transmitted Diseasesjefroc100% (1)
- Urethritis, STD, Mycoplasma or Chlamydia InfectionDocument11 pagesUrethritis, STD, Mycoplasma or Chlamydia InfectionbetebetNo ratings yet
- Report On Sexually Transmitted Diseases & PregnancyDocument4 pagesReport On Sexually Transmitted Diseases & PregnancyAdnan Akram, MD (Latvia)No ratings yet
- Kahong, Imdalmani ReportDocument14 pagesKahong, Imdalmani Reportaisa baladjiNo ratings yet
- Sti Management and PitfallsDocument39 pagesSti Management and PitfallsDr.Lakshmiprasad LNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted InfectionsDocument48 pagesSexually Transmitted InfectionsYsabella LlanetaNo ratings yet
- Common STI's in General PracticeDocument52 pagesCommon STI's in General Practice201802027 Mayada ArmaatusNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary SystemDocument7 pagesGenitourinary SystemMary Angel VelascoNo ratings yet
- Tricho Moni As IsDocument23 pagesTricho Moni As IsClaudia Narinda R. PNo ratings yet
- TrichomoniasisDocument7 pagesTrichomoniasisAugustus CaesarNo ratings yet
- Oral and Intestinal FlagellatesDocument3 pagesOral and Intestinal FlagellatesChristine BuenNo ratings yet
- Vulvovaginitis: by James Holencik, DODocument70 pagesVulvovaginitis: by James Holencik, DOSyarifa YuliaNo ratings yet
- 5 T vagenalis تشخيص 5Document5 pages5 T vagenalis تشخيص 5بلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Gonorrhea and SyphilisDocument55 pagesGonorrhea and Syphilisjoshy221196No ratings yet
- Medical Microbiology: Sti (STD)Document90 pagesMedical Microbiology: Sti (STD)Brother GeorgeNo ratings yet
- LGV by OyeyemiDocument23 pagesLGV by OyeyemiOyeyemi AdeyanjuNo ratings yet
- Trichomoniasis OutlineDocument2 pagesTrichomoniasis OutlineShing Shang ShongNo ratings yet
- 54.vaginal DischargeDocument40 pages54.vaginal DischargebenNo ratings yet
- Approach To Vaginal Discharge: DR Faisal Al Hadad Consultant of Family Medicine & Occupational Health PSMMCDocument16 pagesApproach To Vaginal Discharge: DR Faisal Al Hadad Consultant of Family Medicine & Occupational Health PSMMCSupekshya ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Vulvitis: Inflammation of The External Female Genitalia, Called The VulvaDocument11 pagesVulvitis: Inflammation of The External Female Genitalia, Called The VulvaNazurah AzmiraNo ratings yet
- Chlamydia and Nonspecific UrethritisDocument4 pagesChlamydia and Nonspecific UrethritisErfina BasriNo ratings yet
- Trichomonas: Presented by Suman Chaudhary MSC Ii Sem Public HealthDocument40 pagesTrichomonas: Presented by Suman Chaudhary MSC Ii Sem Public HealthShravani ShagapuramNo ratings yet
- 5b. Handout TrichomonasDocument19 pages5b. Handout TrichomonasDerick SemNo ratings yet
- Ngu Guide 2016Document26 pagesNgu Guide 2016DeaMindySasmitaNo ratings yet
- 51 Vaginal Discharge & PIDDocument45 pages51 Vaginal Discharge & PIDcollinsmagNo ratings yet
- What's in A Name ?Document43 pagesWhat's in A Name ?ismat altayeb aliNo ratings yet
- Gynecology Case Formulation Group-2 Section-BDocument25 pagesGynecology Case Formulation Group-2 Section-Bastak ghisingNo ratings yet
- URETHRITIS - Yulia W 026Document20 pagesURETHRITIS - Yulia W 026Yulia WidiastutiNo ratings yet
- Male GonorrhoeaDocument27 pagesMale Gonorrhoeajalan_zNo ratings yet
- Carcinoma of The Cervix LDocument29 pagesCarcinoma of The Cervix Lapi-19916399No ratings yet
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (32)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (82)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceFrom EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (51)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- The Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeFrom EverandThe Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesFrom EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1412)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Critical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsFrom EverandCritical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (39)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (254)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (170)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (46)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (60)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet