0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views23 pagesVector Calculus Concepts and Applications
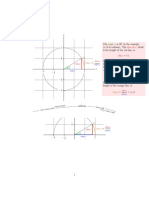
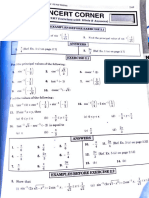
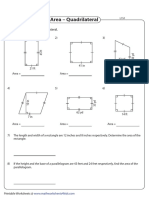
The document discusses vector calculus, focusing on vector differentiation and integration. It covers concepts such as gradient, divergence, curl, and directional derivatives, providing definitions and examples. Additionally, it includes problems and solutions related to these concepts, demonstrating their applications in vector point functions.
Uploaded by
21211a0201Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views23 pagesVector Calculus Concepts and Applications
The document discusses vector calculus, focusing on vector differentiation and integration. It covers concepts such as gradient, divergence, curl, and directional derivatives, providing definitions and examples. Additionally, it includes problems and solutions related to these concepts, demonstrating their applications in vector point functions.
Uploaded by
21211a0201Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd