0% found this document useful (0 votes)
206 views2 pagesTrigonometry Formulas Guide
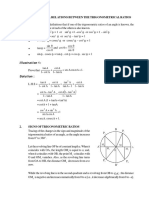
The document provides formulas and identities for trigonometric functions. It includes:
1) Basic trigonometric identities for sin, cos, sec, cosec, and tan.
2) Important trigonometric ratio identities involving multiples of pi/2 and pi.
3) Formulas for trigonometric functions of allied angles such as -θ, 90±θ, 180±θ, 270±θ.
4) Formulas for trigonometric functions of the sum or difference of two angles.
Uploaded by
DIVYANSHUCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
206 views2 pagesTrigonometry Formulas Guide
The document provides formulas and identities for trigonometric functions. It includes:
1) Basic trigonometric identities for sin, cos, sec, cosec, and tan.
2) Important trigonometric ratio identities involving multiples of pi/2 and pi.
3) Formulas for trigonometric functions of allied angles such as -θ, 90±θ, 180±θ, 270±θ.
4) Formulas for trigonometric functions of the sum or difference of two angles.
Uploaded by
DIVYANSHUCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd