0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views1 pageQueuing Theory Formulas and Concepts
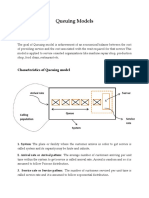
The document outlines key formulas and concepts in queuing theory, including waiting time, service time, and response time. It presents various models such as M/M/1 and M/G/1, along with utilization and Little's law. Additionally, it describes different probability distributions relevant to queuing analysis, including deterministic, uniform, and exponential distributions.
Uploaded by
mika3halleuxCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views1 pageQueuing Theory Formulas and Concepts
The document outlines key formulas and concepts in queuing theory, including waiting time, service time, and response time. It presents various models such as M/M/1 and M/G/1, along with utilization and Little's law. Additionally, it describes different probability distributions relevant to queuing analysis, including deterministic, uniform, and exponential distributions.
Uploaded by
mika3halleuxCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd