0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views3 pagesUnderstanding Myopia, Hypermetropia, and Refraction
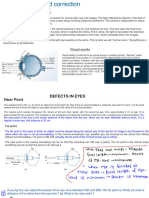
The document discusses three common vision defects: myopia (near-sightedness), hypermetropia (far-sightedness), and presbyopia (age-related vision decline), along with their causes and corrective measures. It also explains atmospheric refraction, which is the bending of light due to varying air densities, leading to phenomena such as the twinkling of stars and mirages. Additionally, it highlights the effects of atmospheric refraction on the visibility of celestial bodies and the colors observed during sunrise and sunset.
Uploaded by
charvikamadduriCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views3 pagesUnderstanding Myopia, Hypermetropia, and Refraction
The document discusses three common vision defects: myopia (near-sightedness), hypermetropia (far-sightedness), and presbyopia (age-related vision decline), along with their causes and corrective measures. It also explains atmospheric refraction, which is the bending of light due to varying air densities, leading to phenomena such as the twinkling of stars and mirages. Additionally, it highlights the effects of atmospheric refraction on the visibility of celestial bodies and the colors observed during sunrise and sunset.
Uploaded by
charvikamadduriCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd