0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views20 pagesUnderstanding BGP Routing Protocol Basics
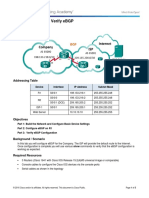
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is essential for routing information between different autonomous systems (AS) on the Internet, allowing data exchange between networks. It operates using a path-vector algorithm and supports features like route aggregation, redundancy, and load balancing. BGP can be configured as External BGP (EBGP) for inter-AS communication and Internal BGP (IBGP) for intra-AS communication, with specific configurations and verification commands provided for practical implementation.
Uploaded by
Abebe GizawCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views20 pagesUnderstanding BGP Routing Protocol Basics
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is essential for routing information between different autonomous systems (AS) on the Internet, allowing data exchange between networks. It operates using a path-vector algorithm and supports features like route aggregation, redundancy, and load balancing. BGP can be configured as External BGP (EBGP) for inter-AS communication and Internal BGP (IBGP) for intra-AS communication, with specific configurations and verification commands provided for practical implementation.
Uploaded by
Abebe GizawCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd