10/11/2023
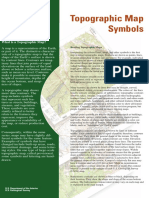
Topographic Maps
Vulcans Throne Quadrangle
Contour Interval = 40 feet
Contour Lines on Topographic Maps
• Topographic maps depict the Earth’s surface using
contour lines.
• Contour lines show elevation above and below sea
level (sea level = 0 feet)
• Every 5th contour is an index contour and is darker in
color
Topographic Maps
Understanding contour lines / map interpretation
N
E
W
1
� 10/11/2023
Each map has its own specific contour interval
Contour Interval (CI) = the difference in elevation between two
adjacent contour lines
To calculate the CI, divide the difference in elevation of two adjacent
index contours by the number of divisions (usually 5) between the two
index contours
The contour interval is generally shown
on the map below the scale bars
Rules of Contours
1. Contour lines connect points of
equal elevation
2. Contour lines never intersect or
cross unless they are merged in
a vertical or overhanging cliff
3. Contour lines never split
2
� 10/11/2023
Rules of Contours
4. Closed contours represent hills.
Rules of Contours
5. Closed contours with hachures (short lines that are perpendicular to
the contour) represent depressions
Rules of Contours
6. Every contour line closes on itself. Either within or beyond the
limits of the map. If beyond the limits of the map, the contour
line will run to the edge of the map.
3
� 10/11/2023
Rules of Contours
7. Contours “V” uphill when they cross a stream or valley.
“V’s” point in the upstream direction, streams flow downhill
Rules of Contours
8. Contours “V” in the uphill direction when they cross a stream or valley
Contours “V” in the downhill direction when they cross a ridge
The crest of a ridge or bottom of a valley runs through the middle of the “V”
Rules of Contours
9. Steeper slopes are
represented by closely
spaced contours.
Gentle slopes are
represented by more widely
spaced contours.
4
� 10/11/2023
Contour map of Yosemite Valley
Map Scale
Feet
El Capitan, Yosemite Valley
Rules of Contours
10. Where the slope direction reverses, the contour is repeated
e.g., The highest contour on a ridge or the lowest contour in a
valley are always in pairs
5
� 10/11/2023
When constructing a topo map from
elevation data:
• Use a pencil, this is an iterative process
• Locate the highest and lowest points
• Determine the contour interval
• Determine the flow of stream(s)
• Begin drawing contours as though you were
grouping data points into intervals
79
79
76
70
67
76
51
75
63
57
46
52
30
48
23
21
Use a 25’ contour interval (25’, 50’, 75’, etc)
When constructing a topo map you
should remember:
• The rule of “V’s”
• Constantly cross-check between every two adjacent
points
• Use a pencil with a good eraser and have patience
• If you get stuck in a particular area it is best to work in a
different area and then work your way back to the
problem area
• If you have drawn two contours, for 90- and 100-foot
contours, the elevation data between these contours
must be:
Greater than 90’ and less than 100’ (91-99’)
6
� 10/11/2023
Topographic Profiles
A topographic profile is a diagram that shows the configuration or
change in elevation of the land surface along a given line.
700
680
660
640
620
600
580
560
A B
Elevation Feet Above Sea Level
Steps for Constructing Topographic Profiles
(Steps 1, 2, and 3 pertain to creating a profile grid, which we usually furnish for you)
1) Determine the location of the profile on the map
2) Determine the highest and lowest elevation along
line
3) Construct the profile grid
4) Align grid with the profile line on the map
5) Transfer contour values from map to profile grid
6) Connect dots along the profile
4) Align the grid along the profile line on the
map
7
� 10/11/2023
5) Transfer contour values from the map to
the grid and connect the dots
Final Profile
Stream
½ Contour Interval
Your final profile should look something like this
Remember:
• Extend the profile from point A to A’
• Label the Stream
• Note: the bottom of the depression & the river bed are ½ contour interval
below adjacent contours